Macroporous skeleton hydrophobic mercury removal material, preparation method and application thereof
A hydrophobic material, hydrophobic technology, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, etc., can solve problems such as hindering the reuse of fly ash production raw materials, waste of metal sulfide design capacity, low adsorption capacity and rate, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of reducing resistance, avoiding secondary pollution, and high adsorption rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Set the density to 27 kg / m 3 , 10 blocks with a volume of 1 cm 3 After soaking the polyurethane sponge (PUF) in 50 mL of deionized water, 0.625 mmol of ammonium sulfide solution (mass fraction 20%) was added, that is, the feeding ratio of ammonium sulfide to macroporous skeleton hydrophobic material was 1:16 (mmol / cm 3 ), then add cetyltrimethylammonium bromide whose mass is 1% of the mass of ammonium sulfide, and stir for 1 h to obtain a mixed solution.
[0028] (2) Add 25 mL of 0.025 mol / L copper sulfate solution dropwise into the mixed solution obtained in step (1), stir vigorously for 2 h, and then take out the treated polyurethane sponge.
[0029] (3) Wash the treated polyurethane sponge taken out in step (2) with deionized water and absolute ethanol for 30 min each, then vacuum-dry at 80 °C for 10 h, and the obtained sample is designated as 16CuS@PUF.
[0030] Take 3 cm 3 The 16CuS@PUF was placed in a cylindrical quartz glass fixed-bed reactor with a leng...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Without adding polyurethane sponge, prepare copper sulfide powder, namely:
[0033] (1) Add 0.625 mmol of ammonium sulfide solution (20% by mass fraction) to 50 mL of deionized water, then add cetyltrimethylammonium bromide whose mass is 1% of the mass of ammonium sulfide, and stir for 1 h. A mixed solution was obtained.
[0034] (2) Add 25 mL of 0.025 mol / L copper sulfate solution dropwise into the mixed solution obtained in step (1), and stir vigorously for 2 h.
[0035] (3) The precipitate obtained in step (2) was washed with deionized water and absolute ethanol, and dried in vacuum at 80 °C for 10 h, and the obtained sample was designated as CuS.
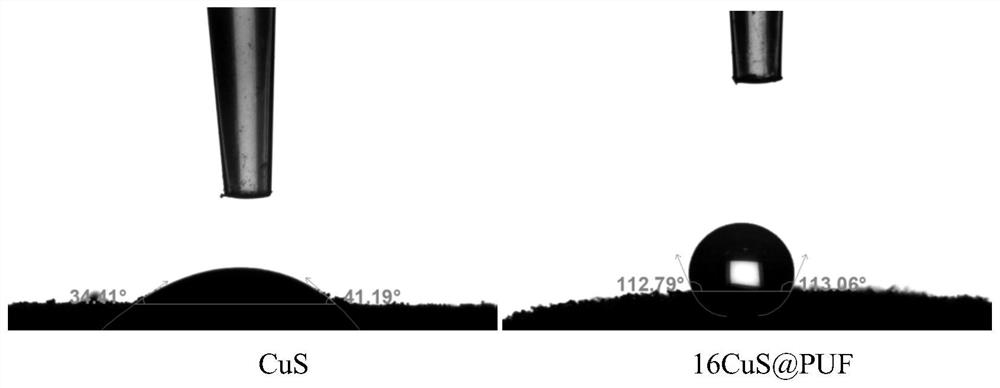
[0036] Test the water contact angle between CuS and 16CuS@PUF, the results are as follows figure 1 As shown, the water contact angle of CuS powder is only about 37°, and the water contact angle of 16CuS@PUF can reach about 113°.
[0037] Take 0.042 g CuS and 7 cm 3 The 16CuS@PUF (theoretically loaded up to 0.042 g CuS) ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) Set the density to 23 kg / m 3 , 10 blocks with a volume of 1 cm 3 After soaking polyethylene foam (PE) in 50 mL deionized water, add 10 mmol ammonium sulfide solution (mass fraction 20%), that is, the feeding ratio of ammonium sulfide to macroporous skeleton hydrophobic material is 1:1 (mmol / cm 3 ), then add dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride whose mass is 5% of the mass of ammonium sulfide, and stir for 2 h to obtain a mixed solution.
[0040] (2) Add 25 mL of 0.4 mol / L zinc sulfate solution dropwise into the mixed solution obtained in step (1), stir vigorously for 1 h, and then take out the treated polyethylene foam.
[0041] (3) The treated polyethylene foam cotton taken out in step (2) was washed with deionized water and absolute ethanol for 20 min each, and then vacuum-dried at 60°C for 12 h, and the obtained sample was designated as ZnS@PE. The zinc sulfide powder sample prepared without adding polyethylene foam cotton is denoted as ZnS.
[0042] take 5 cm ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Water contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Water contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com