A method for accurate temperature detection based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering effect
A technology of surface-enhanced Raman and scattering effects, applied in thermometers, thermometers with physical/chemical changes, measuring heat, etc., can solve problems such as complex structures and manufacturing costs, hindering wide application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
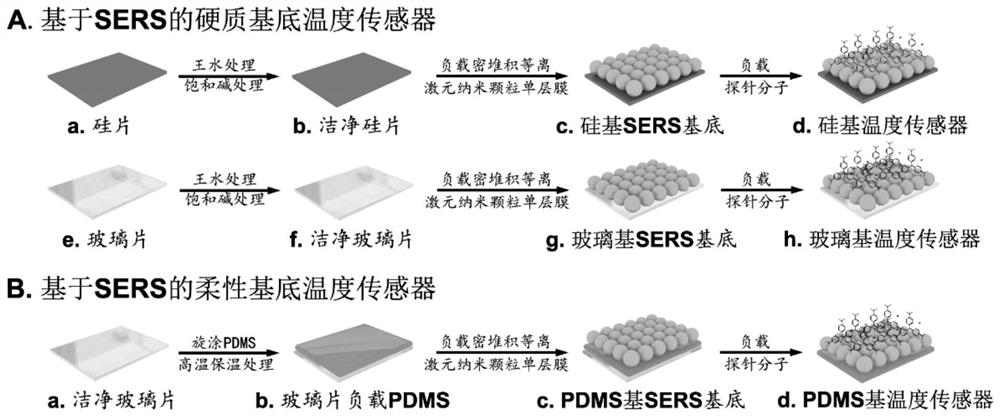
[0038] Firstly, put the used glassware (100 ml two-necked flask and Petri dish) into newly prepared aqua regia and saturated sodium hydroxide solution respectively, soak for 4 hours and 12 hours, wash with ultrapure water, and dry for later use.
[0039] (1) Configure the required raw materials
[0040] ① Use ultrapure water to prepare the required raw materials chloroauric acid and sodium citrate into solutions with a mass percentage concentration of 1%.
[0041] ② Use the organic solvent toluene to prepare oleylamine into an amine-containing organic solution with a molar concentration of 0.001 mol / liter.
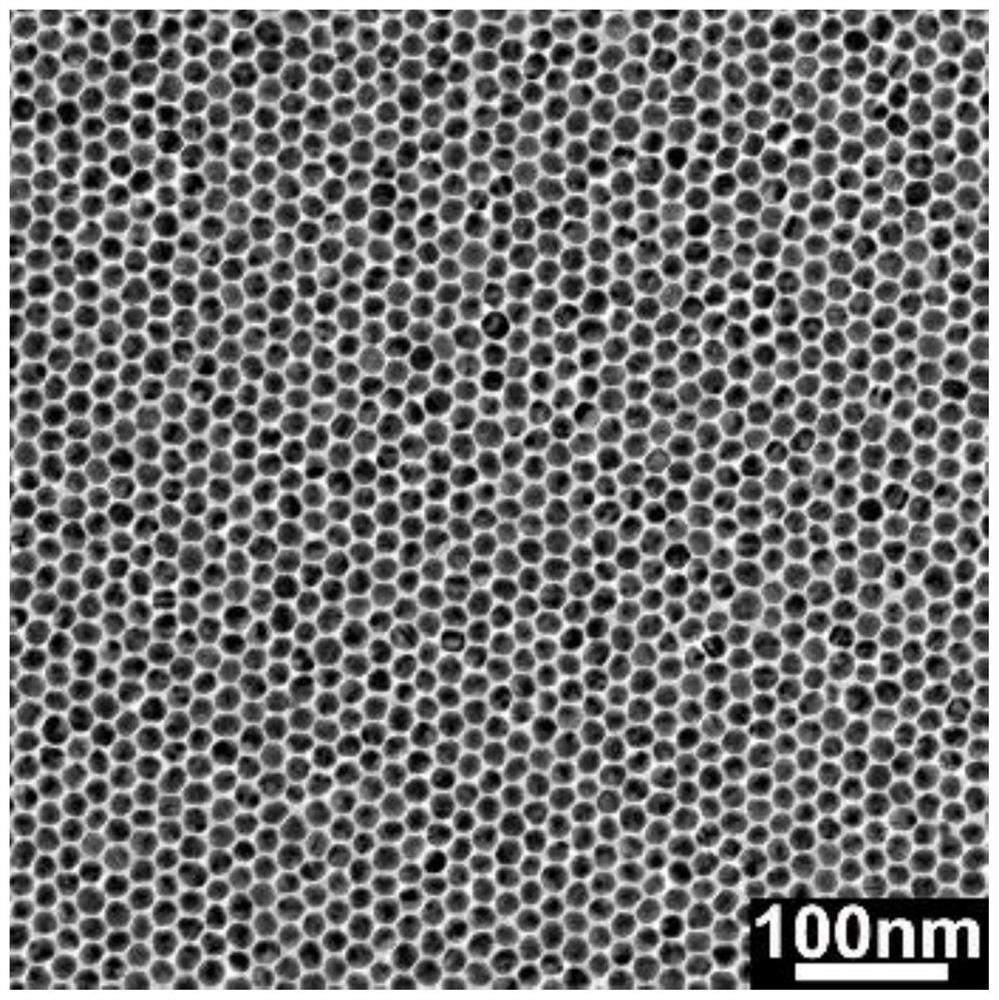
[0042] (2) Add 48 milliliters of ultrapure water into the two-necked flask, and after heating to boiling under stirring, 0.5 milliliters of chloroauric acid solution and 1.5 milliliters of sodium citrate solution are rapidly added into boiling water successively. Keep boiling, heat and reflux for 30 minutes, and cool to room temperature to obtain a water-soluble monodispe...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0063] (1) Configure the required raw materials
[0064] ① Use ultrapure water to prepare the required raw materials silver nitrate and sodium citrate into solutions with a mass percentage concentration of 1%.
[0065] ② Use toluene to prepare dodecylamine into an amine-containing organic solution with a molar concentration of 0.01 mol / liter.
[0066] According to steps (2), (3), (4) and (5), a hard substrate or a flexible substrate loaded with a silver nanoparticle monolayer film is obtained.
[0067] (6) Preparation of temperature sensor
[0068] Fully submerge single-layer film rigid substrates or single-layer film flexible substrates in a 10- -4 moles per liter of methylene blue solution.
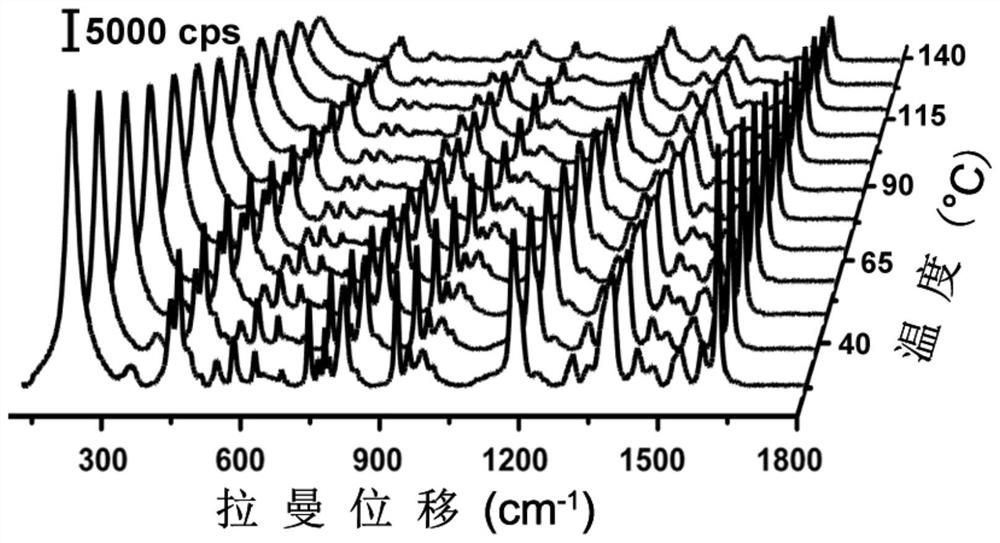
[0069] (7) The excitation wavelength used is 532 nm, and the laser power is 4.25 microwatts.
[0070] (8) The excitation wavelength used is 532 nanometers, and the laser power is 4.25 microwatts.
Embodiment 3
[0072] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0073] (1) Configure the required raw materials
[0074] ① Use ultrapure water to prepare the required raw materials copper nitrate and sodium ascorbate respectively into solutions with a concentration of 1% by mass.
[0075] ② Use toluene to prepare tetradecylamine into an amine-containing organic solution with a molar concentration of 0.0001 mol / liter.
[0076] According to steps (2), (3), (4) and (5), a hard substrate or a flexible substrate loaded with a copper nanoparticle monolayer film is obtained.
[0077] (6) Preparation of temperature sensor
[0078] Fully submerge single-layer film rigid substrates or single-layer film flexible substrates in a 10- -5 moles per liter of rhodamine 6G solution.
[0079] (7) The excitation wavelength used is 785 nm, and the laser power is 500 microwatts.
[0080] (8) The excitation wavelength used is 785 nm, and the laser power is 500 microwatts.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com