Fuel cell electrode in-situ preparation method based on microporous layer with double-layer ordered structure
A fuel cell electrode and ordered structure technology, applied to battery electrodes, structural parts, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the material transmission resistance of the membrane electrode, affecting the performance and durability of the battery, and agglomerating or falling off the Pt catalyst. Effects of electrochemical surface area and catalyst stability, increasing electrochemical reaction area, and increasing electrochemical reaction rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
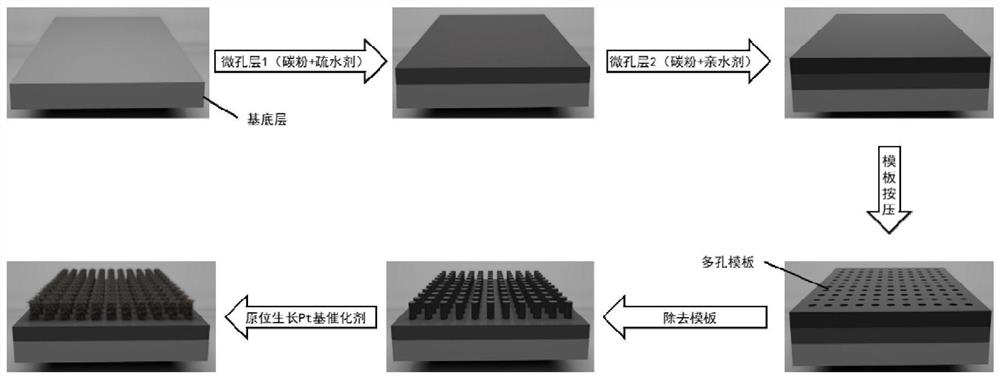
[0040] combined with figure 2 The shown process and process prepare a fuel cell electrode in which platinum-based nanowires are in-situ grown on an ordered microporous layer, and conduct a discharge test. The main steps are as follows:
[0041] (1) Preparation of microporous layer with ordered structure: ① carbon powder (Vulcan XC-72R), PTFE and NH 4 Disperse Cl in the isopropanol dispersion liquid, apply ultrasonically, and evenly spray on the surface of the hydrophobically treated carbon paper, dry it at 70°C for 2h, then put it into a muffle furnace at 370°C for sintering for 30min, take it out and weigh it for calculation, The obtained carbon powder load is 1~1.5mgcm -2 , PTFE: C=15% hydrophobic microporous layer. ②The acid-treated toner (Vulcan XC-72R), Nafion and NH 4 Disperse Cl in the isopropanol dispersion liquid, ultrasonically, and evenly spray on the hydrophobic microporous layer. Before drying, use the AAO template (pore size 0.5 μm, pore spacing 1 μm) to car...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The template parameters for making the microporous layer with ordered structure are 1 μm in pore size and 2 μm in pore spacing. Other relevant parameters in the membrane electrode are the same as in Example 1, and the battery test conditions are the same as in Example 1. Under 0.6V working voltage, the current density can reach 1.0Acm -2 , the maximum power density reaches 0.716Wcm -2 .
Embodiment 3
[0048] according to figure 2 The shown process and process prepare fuel cell electrodes in which platinum nanorods are in-situ grown on an ordered microporous layer, and a discharge test is performed. The reducing agent used for the in-situ growth of the platinum catalyst is ascorbic acid, and the obtained catalyst exhibits the morphology of nanorods. Other relevant parameters in the membrane electrode are the same as in Example 1, and the battery test conditions are the same as in Example 1. Under 0.6V working voltage, the current density can reach 1.0Acm -2 , the maximum power density reaches 0.713Wcm -2 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com