Pathogen-resistant animals having modified aminopeptidase n (ANPEP) genes
A gene and animal technology, applied in a field that further involves the production of anti-pathogen non-human animals or non-human animal lineages, can solve the problems of poor understanding of pathogenesis and no reliable technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0561]The following non-limiting examples are provided to further illustrate the invention.
example 1
[0563]Example 1: Using CRISPR / Cas9 system to produce genetically engineered pigs from oocytes and embryos sourced in vitro
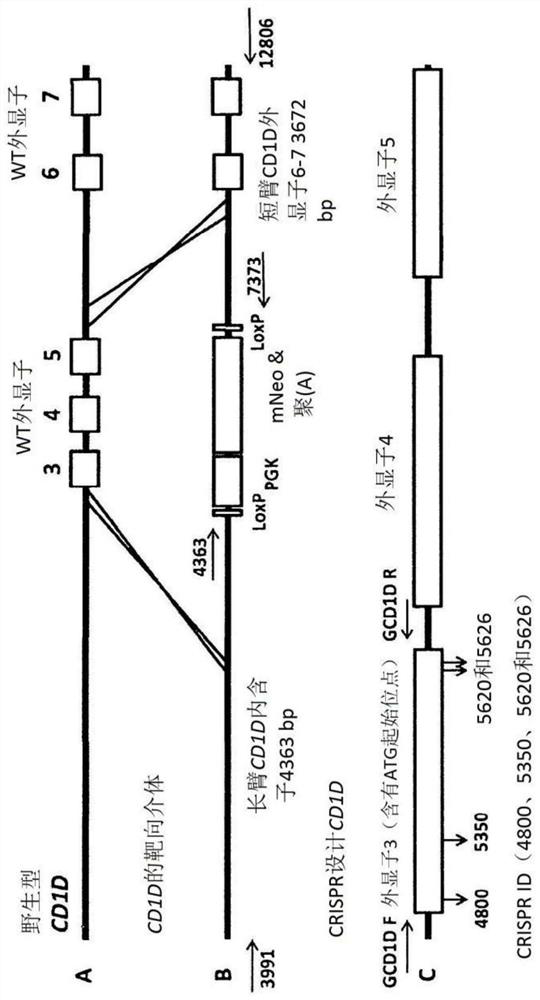
[0564]Recent reports describe homing endonucleases, such as zinc finger nuclease (ZFN), transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) and clustered regularly spaced short palindrome repeats (CRISPR) / CRISPR associations (Cas9) components in the system, the report suggests that genetic engineering (GE) of pigs may now be more efficient. Targeted homing endonuclease can induce double-strand breaks (DSB) at specific locations in the genome, and if donor DNA is provided, it can be achieved by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or stimulation of homologous recombination (HR) Cause random mutations. If the donor DNA is provided along with the targeted nuclease, homing endonuclease can be used to achieve targeted modification of the genome through HR. After introducing specific modifications into somatic cells, these cells are used to produce GE pigs for various ...
example 2
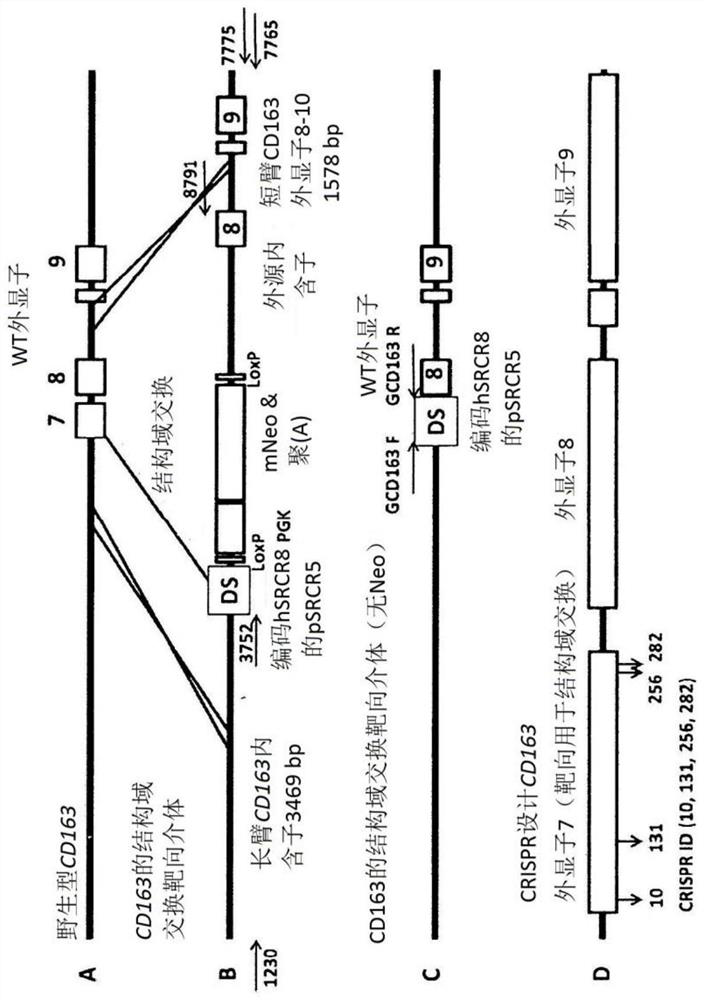
[0663]Example 2: Pigs with modified chromosomal sequence in the gene encoding CD163 protein have increased resistance to PRRSVplus
[0664]Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV) ravaged the pig industry in the past quarter of a century. In this example, it is shown that the CD163-null animals did not show all the clinical signs of infection, lung pathology, viremia, or antibody production that are characteristic of PRRSV infection. It has not only confirmed that PRRSV enters the intermediary; but if animals produced in a similar manner are allowed to enter the food supply, strategies to prevent major economic losses and animal suffering have been described.
[0665]Materials and methods
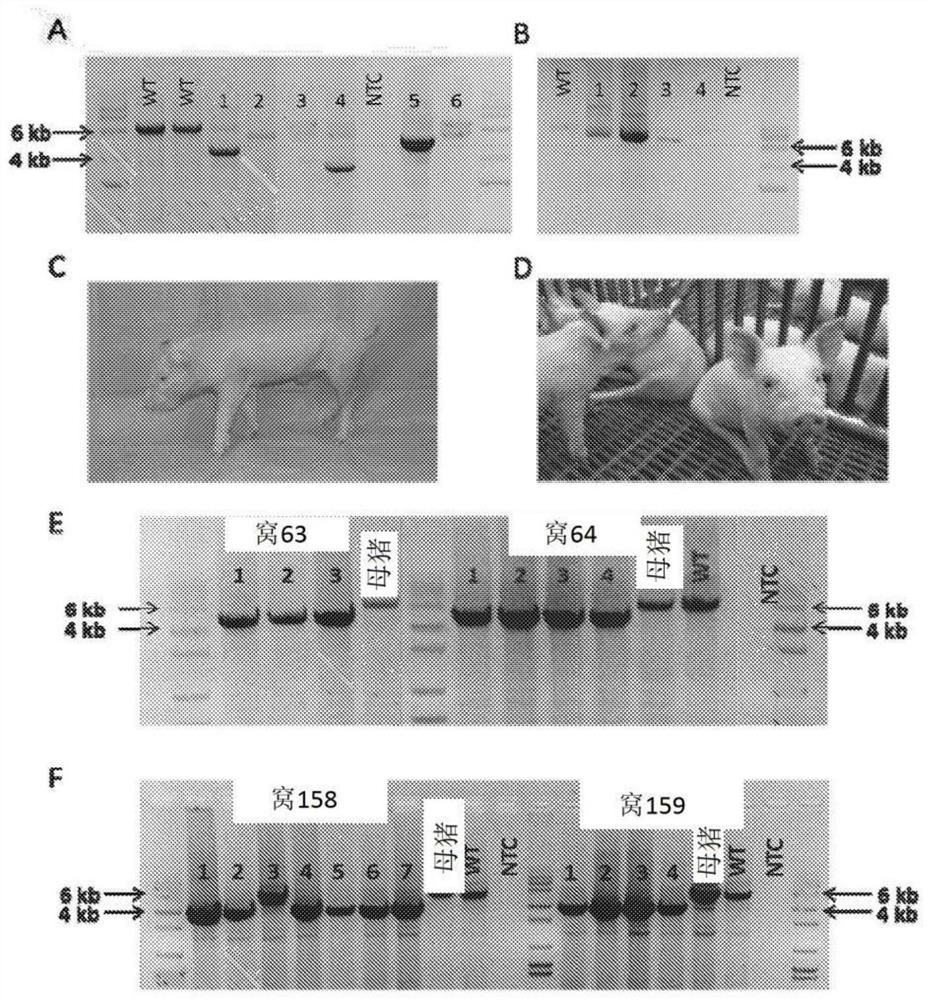
[0666]Genotyping
[0667]Genotyping is based on both DNA sequencing and mRNA sequencing. The genotype of this male animal has an 11 bp deletion in one allele, and 45 amino acids of domain 5 are predicted when translated, resulting in an early stop codon at amino acid 64. In another allele,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com