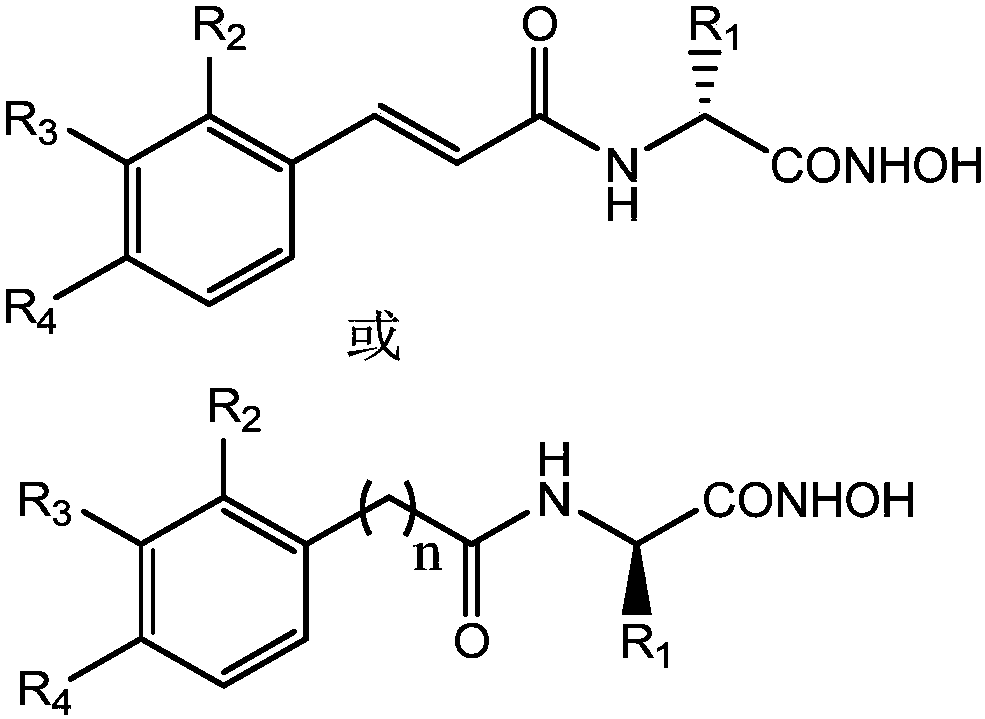
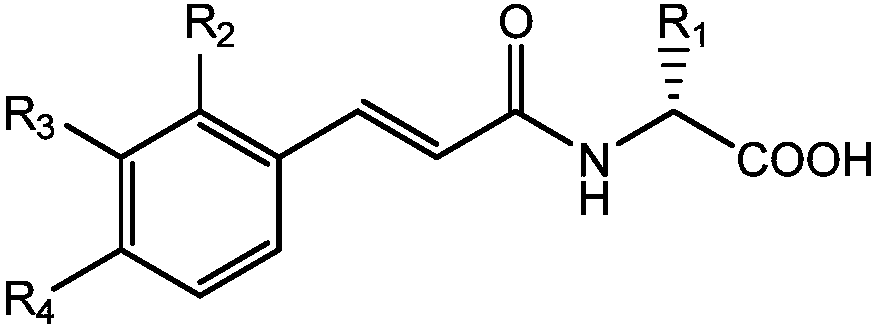
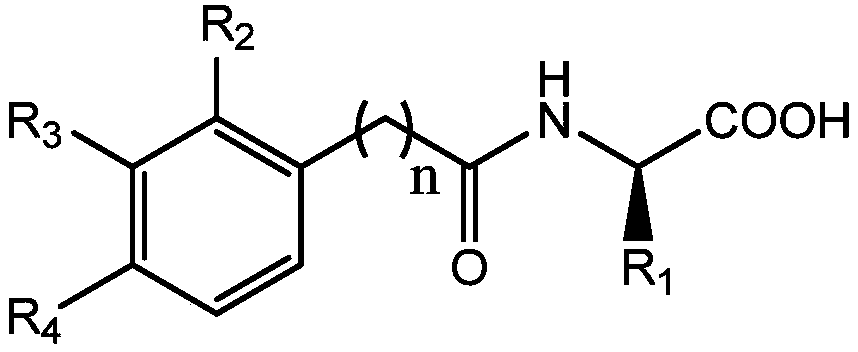
Amino acid-hydroxamic acid aminopeptidase N inhibitor and preparation method thereof
A hydroxime and aminopeptidase technology, which is applied in the field of amino acid hydroxamic acid aminopeptidase N inhibitors and synthesis, can solve the problems of reducing the antigen recognition ability of T cells, reducing the immune function of the body, and accelerating tumor metastasis and deterioration. , to achieve the effect of short synthesis process route, low production cost and rapid reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1: Preparation of the target compound (compound 7a in Table 1).
[0025] (1) Preparation of cinnamoyl-D-alanine ④.
[0026] Dissolve 22.5mmol of cinnamic acid and 24mmol of N-hydroxysuccinimide in 35ml of anhydrous dioxane, and add 24mmol of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide in anhydrous dioxane solution, and react at room temperature for 6 After 1 hour, a white precipitate was formed, and the precipitate was filtered off. The filtrate was slowly added to an aqueous solution containing 24 mmol D-alanine and 24 mmol sodium bicarbonate, and a large amount of white solid precipitated out. The temperature was raised to 50° C., and refluxed for 24 hours. After the reaction is complete, evaporate most of the solvent, add a small amount of water to dissolve the residue and filter out the insoluble matter, adjust the pH of the water phase to 2 with 2mol / L concentrated hydrochloric acid, place it in the refrigerator overnight, and precipitate a white precipitate, filter and dry, ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Preparation of (R)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-(1-methyl-2-hydroxyamino-2-carbonylethyl)-acrylamide (7c).
[0030] The target compound 7c was prepared by the same method, white solid, yield: 80.1%; melting point: 150-152 °C; 1 H-NMR (600MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ10.71(s,1H,OH),8.89(s,1H,NH),8.33(d,J=7.9Hz,NH),7.62(d,J=5.6Hz,2H),7.42(d,J =15.8Hz,1H),7.26(t,J=8.8Hz,2H),6.71(d,J=15.8Hz,1H),4.37-4.32(m,J=7.1Hz,1H),1.24(d,J =7.0Hz, 3H); IR (KBr), ν: 3152, 3028, 2341, 1616, 1400, 1118, 690cm -1 ;ESI-MS: m / z[M-H] - 267.1.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: Preparation of (R)-4-fluoro-N-(1-methyl-2-hydroxyamino-2-carbonylethyl)-benzamide (8a).
[0032] The target compound 8a was prepared by the same method, white solid, yield: 76.6%; melting point: 151-153°C; 1 H-NMR (600MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ8.33(d, J=7.8Hz, NH), 7.28(dd, J=8.6,5.7Hz, 2H), 7.10(d, J=8.9Hz, 2H), 4.41-4.36(m, J=7.1 Hz, 1H), 3.44(s, 1H), 1.18(d, J=7.1Hz, 3H).IR(KBr), ν: 3445, 3174, 2341, 1631, 1542, 1400, 1242, 853cm -1 ;ESI-MS: m / z[M-H] - 225.1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com