O3-type layered positive electrode material for sodium ion battery and method for improving purity of material through element doping
A sodium-ion battery and positive electrode material technology, applied in battery electrodes, positive electrodes, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient material capacity, affecting material cycle performance, impure phase structure, etc., and achieve excellent electrochemical stability performance, optimized capacity and cycle performance, and excellent electrochemical performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
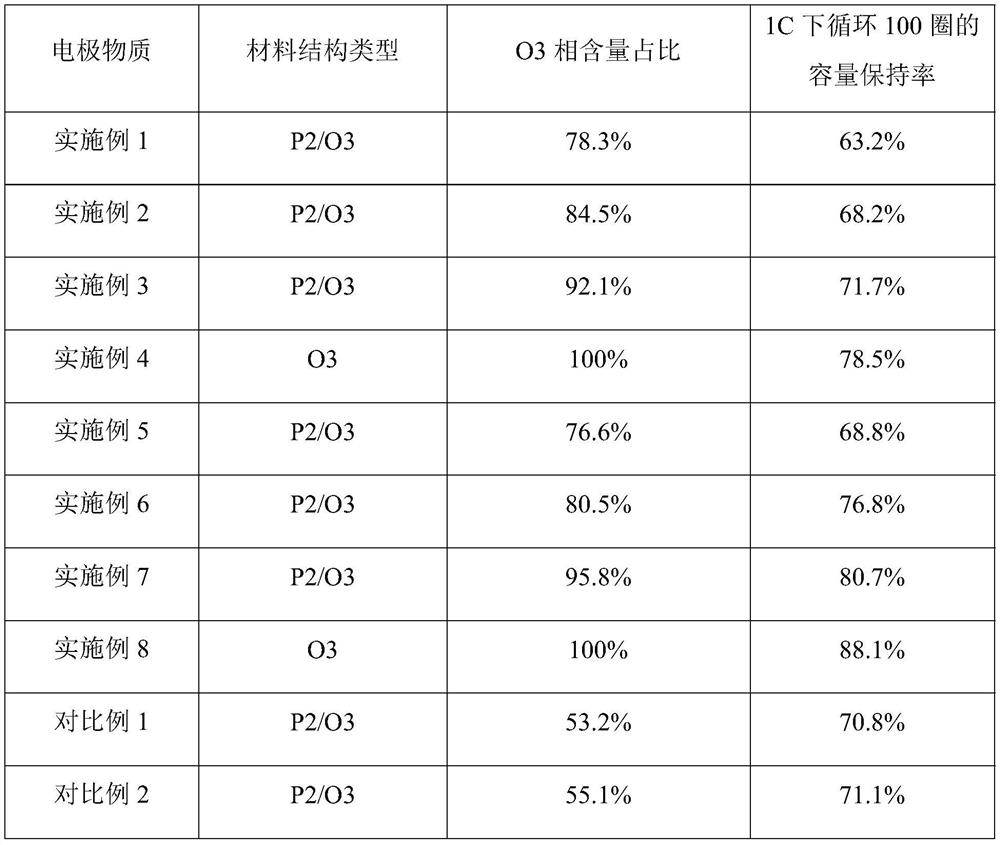
Examples
Embodiment 1
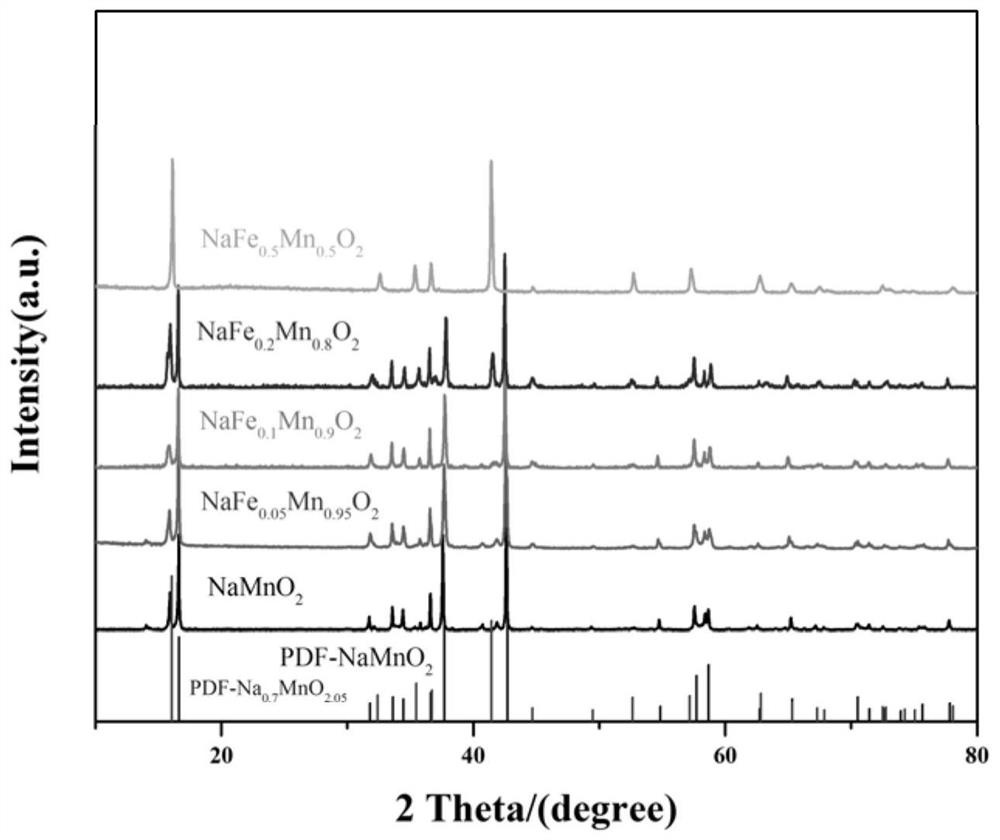
[0021] (1) Preparation of 5% iron-doped NaFe 0.05 mn 0.95 o 2 Cathode material
[0022] Weigh Na according to the corresponding proportion 2 CO 3 , Mn 2 o 3 , Fe 2 o 3 Ball milled for 24 hours, pressed into a disc with a diameter of 10 mm under a pressure of 10 MPa, and calcined at 1000 °C for 12 hours in a muffle furnace to obtain a sample powder.
[0023] (2) For NaFe 0.05 mn 0.95 o 2 Sample powder for XRD test
[0024] Using an X-ray diffractometer, NaFe is obtained using the diffraction effect of X-rays in crystalline substances 0.05 mn 0.95 o 2 The XRD pattern of the sample powder is used to analyze the material effectively with reference to the standard PDF card.
[0025] (3) Preparation of NaFe 0.05 mn 0.95 o 2 Composite cathode
[0026] Mix the prepared positive electrode material with the conductive additive Super-P and the binder polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) in a mass ratio of 7:2:1, and add an appropriate amount of N-methylpyrrolidone. After pul...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Preparation of 10% iron-doped NaFe 0.1 mn 0.9 o 2 Cathode material (with raw material is Na 2 CO 3 , Fe 2 o 3 , Mn 2 o 3 , all the other steps are with embodiment 1).
[0033] (2) For NaFe 0.1 mn 0.9 o 2 Sample powder is carried out XRD test (concrete steps are the same as embodiment 1).
[0034] (3) Preparation of 10% iron-doped NaFe 0.1 mn 0.9 o 2 Composite positive electrode (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1).
[0035] (4) Assemble the sodium ion battery (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1).
[0036] (5) Sodium ion battery test (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1).
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) Preparation of 20% iron-doped NaFe 0.2 mn0.8 o 2 Cathode material (with raw material is Na 2 CO 3 , Fe 2 o 3 , Mn 2 o 3 , all the other steps are with embodiment 1).
[0039] (2) For NaFe 0.2 mn 0.8 o 2 Sample powder is carried out XRD test (concrete steps are the same as embodiment 1).
[0040] (3) Preparation of 20% iron-doped NaFe 0.2 mn 0.8 o 2 Composite positive electrode (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1).
[0041] (4) Assemble the sodium ion battery (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1).
[0042] (5) Sodium ion battery test (the specific steps are the same as in Example 1).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com