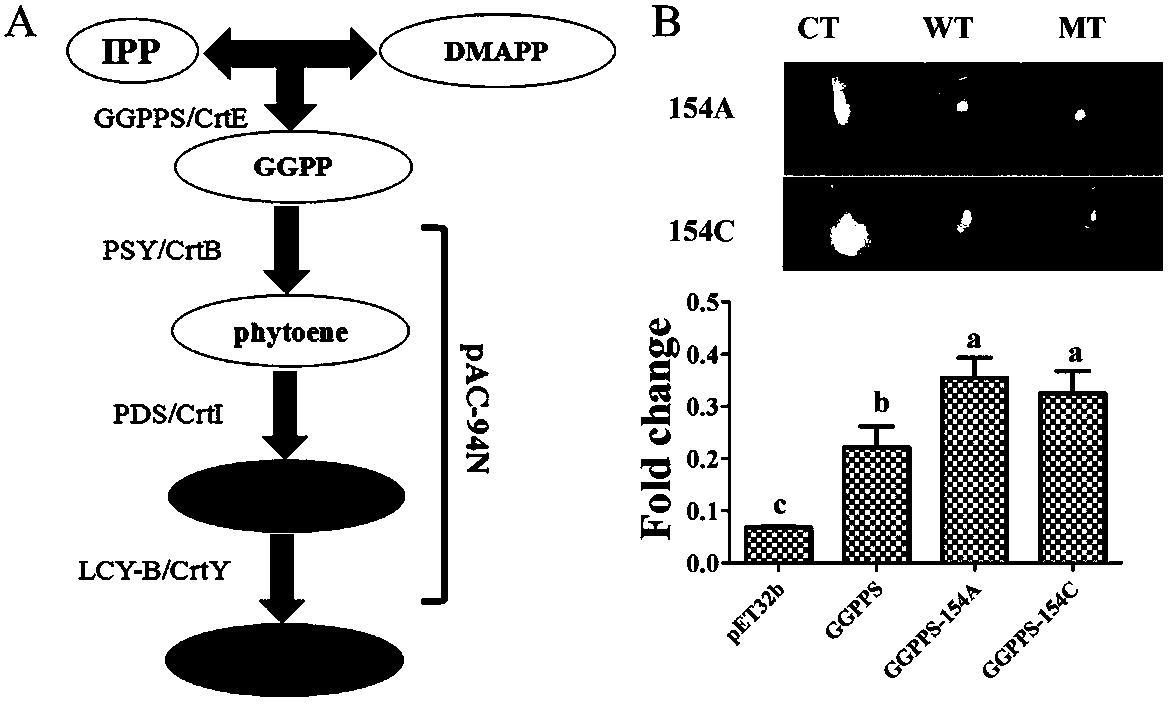
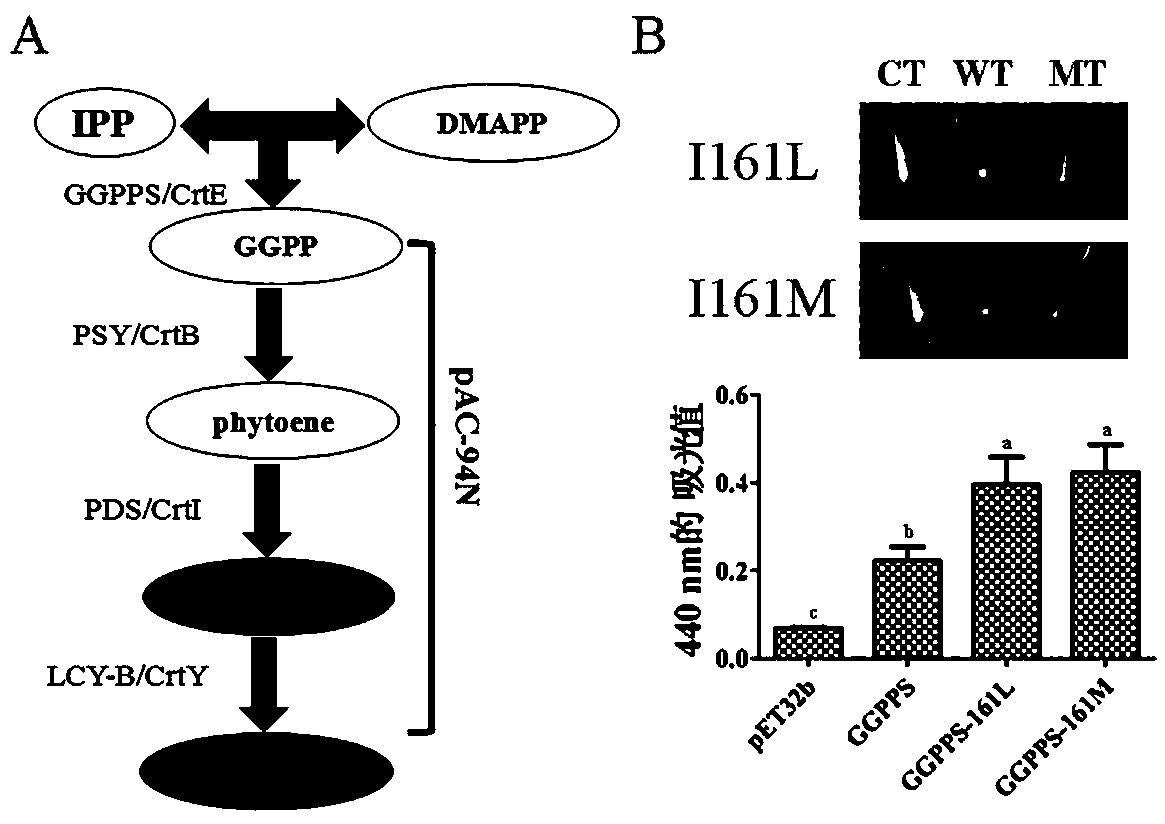
Directed five-site mutant protein GGPPS in enzyme pocket and on enzyme molecule surface
A site mutation and pocket technology, applied in the field of tobacco genetic engineering, can solve the problems of short development time and genetic modification of unused plants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Since the acquisition of the existing geranyl geranyl diphosphate synthase (GGPPS) gene is the basis for related sequence analysis and directed evolution mutation, this example firstly analyzes the existing geranyl geranyl diphosphate synthase (GGPPS) gene. The cloning process of the diphosphate synthase (GGPPS) gene is briefly described as follows.
[0048] First, according to the gene sequence shown in GenBank accession number NM_001325177.1, the primer sequences for PCR amplification were designed as follows:
[0049] Forward primer: 5'-atgagatctatgaatcttgt-3',
[0050] Reverse primer: 5'-attttcacgataagcaatgt-3';
[0051] Tobacco K326 leaf cDNA was used as a template for PCR amplification;
[0052] After the PCR amplification product is detected by electrophoresis, it is recovered, purified, and the recovered and purified PCR product is connected to the pGEMT plasmid;
[0053] Subsequently, the ligation product was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α competent ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] In order to facilitate the detection and analysis of relevant mutation sites, the geranyl geranyl diphosphate synthase (GGPPS) recombinant engineering strain was used for experimental verification in this application. Therefore, the construction process of this engineering strain is discussed in this embodiment. The introduction is as follows.
[0063] First, the recombinant vector pET-32b(+)-GGPPS constructed in Example 1 was co-transformed with the PAC-94N plasmid to express the strain E.coli BL21(DE3), and at the same time, the empty vector pET-32b(+) and PAC- 94N plasmid co-transformation as a negative control strain;
[0064] Subsequently, after culturing overnight, positive clones were selected for identification, and positive clone strains with correct sequencing were preserved or further tested for β-carotene content.
[0065] The detection principle of β-carotene content is: Escherichia coli cannot produce GGPP by itself, while the PAC-94N plasmid contains all...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Since there is no report on the crystal structure of tobacco GGPPS, in order to analyze the protein, based on its amino acid sequence, the inventors performed homology modeling on the enzyme. During the modeling process, the optimal template is 3kro, with a score of 0.993 (TM-score is used to measure the matching degree of two protein structure models, the score ranges from 0 to 1, and 1 means a perfect match), root mean square error The deviation value (RMSD) was 0.36 Å, the sequence identity (IDEN) was 74.9%, and the protein structure coverage (Cov) was 99.7%.
[0068] The substrates C5-DMAPP, C10-GPP, and C15-FPP were docked to the GGPPS catalytic pocket using the Rosetta_docking program, respectively. By looking for the best binding position of receptor small molecule compound and enzyme action, so as to predict its binding mode. The final analysis results show that the 154th, 161st and 218th positions are located in the catalytic pocket of the enzyme, and the bind...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com