Organic light-emitting device and preparation method thereof
A technology of electroluminescent devices and organic light-emitting layers, applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as damage, inapplicability to mass production, and limit the performance of luminescent devices, and achieve simplified preparation The effect of excellent process and device performance and excellent electron transport performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
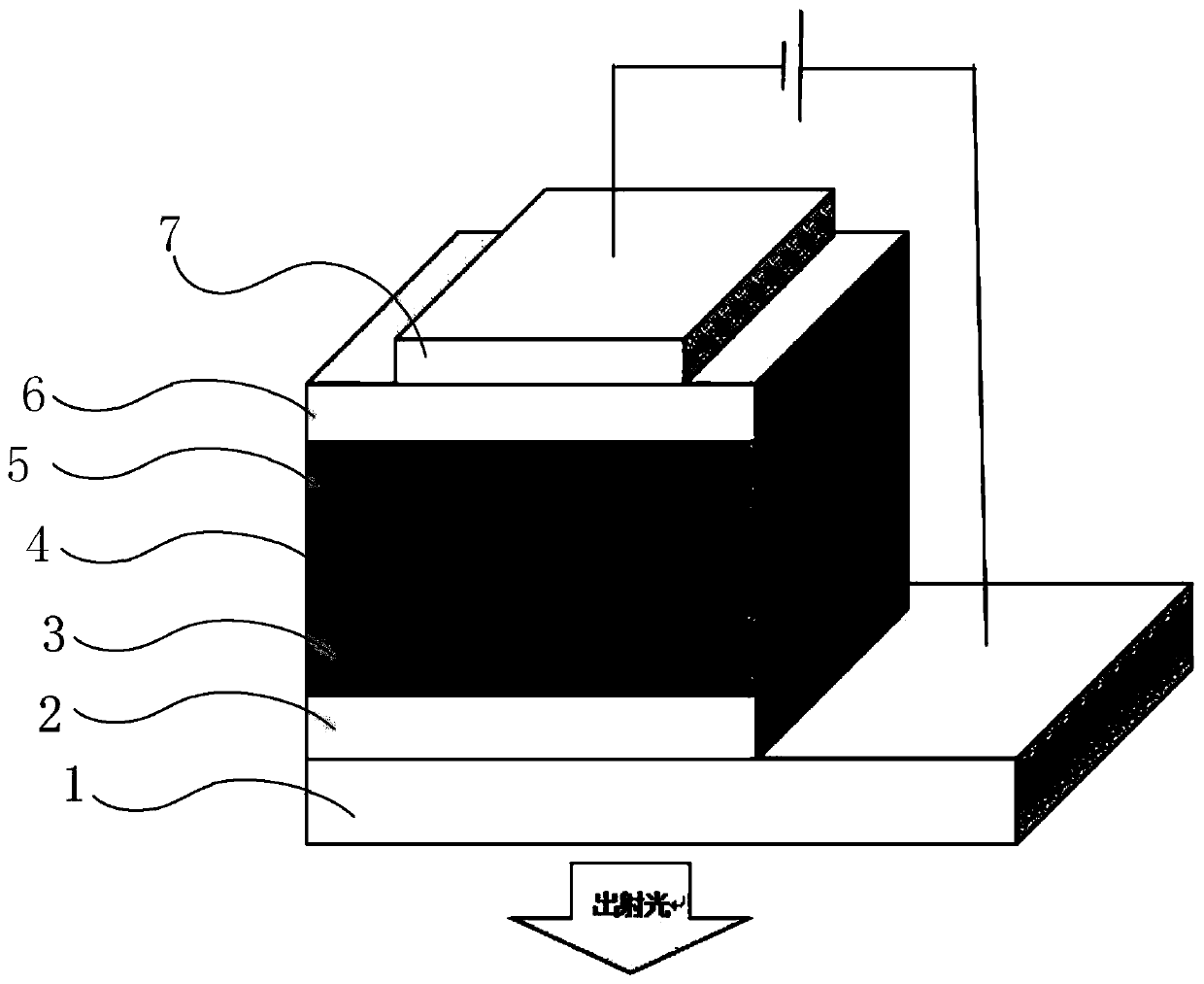
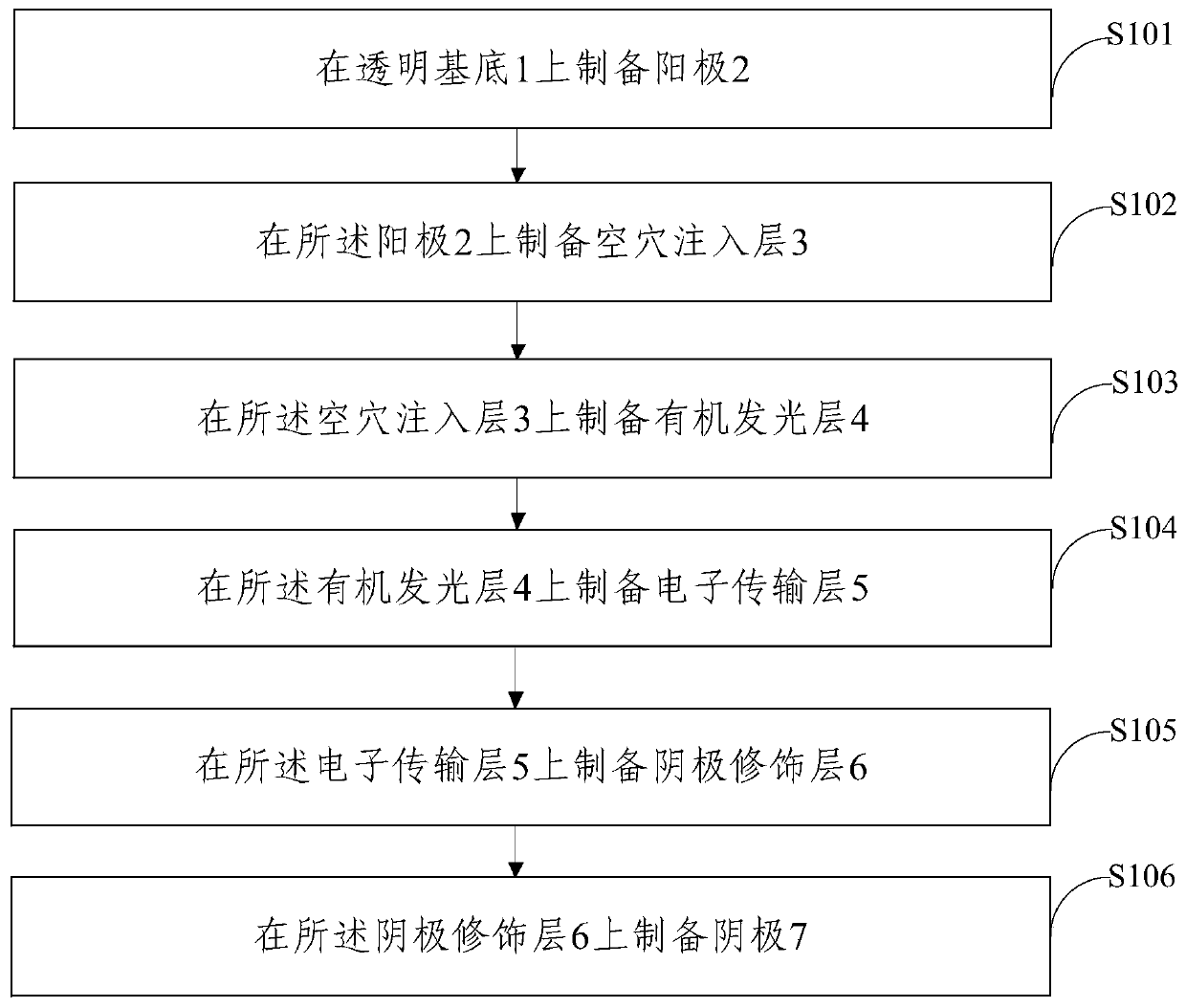
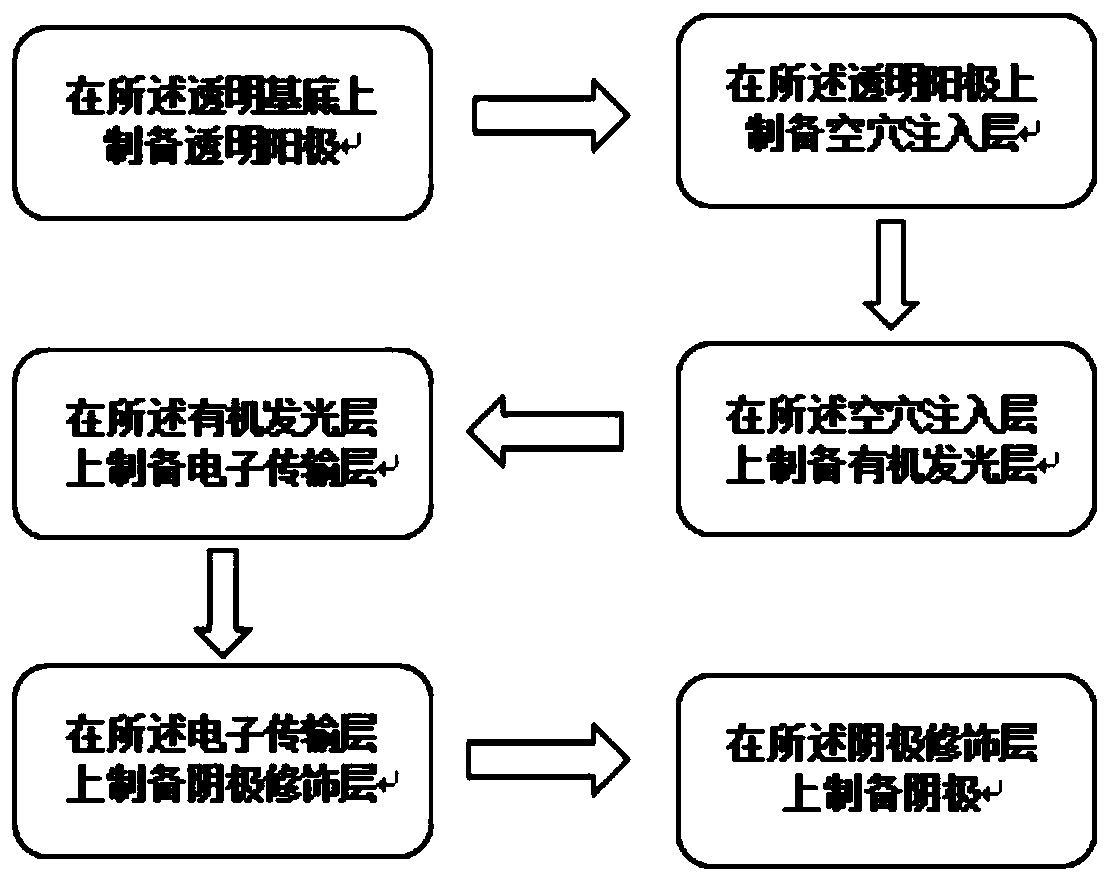
[0051] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing an organic electroluminescence device, see figure 2 ,include:
[0052] S101: preparing an anode 2 on a transparent substrate 1;
[0053] In this step, indium tin oxide is plated on the transparent substrate 1; the substrate 1 is respectively soaked in substrate detergent, deionized water, and absolute ethanol, and the soaked substrate 1 is cleaned by an ultrasonic cleaner; Drying the cleaned substrate 1 with nitrogen gas, and treating the dried substrate 1 with oxygen plasma for 3 minutes to obtain an anode 2;
[0054] Among them, the transparent substrate is a hard substrate or a flexible substrate, the hard substrate is glass, silicon dioxide or quartz, and the flexible substrate is polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene naphthalate or polyimide .
[0055] It should be noted that the ultrasonic cleaning in step S101 can effectively remove organic matter and impurities on the surface of the s...
Embodiment 4
[0090] On the basis of Example 3, the light-emitting material of the organic light-emitting layer 4 is selected from SpiroAC-TRZ, and the specific preparation process is: the blue light TADF material 10-(4-(4,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-triazin-2 -yl)phenyl)-10H-spiro[acridine-9,9'-fluoren e](SpiroAC-TRZ) was dissolved in chloroform (CF): chlorobenzene (CB) at a volume ratio of 1:1 in a mixed solvent at 10 mg / ml , heated and stirred for 6 hours, wherein the heating temperature was 60 degrees Celsius. Dissolve the bipolar small molecule host material 3′-bis(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl (mCBP) at 10 mg / ml in chloroform (CF): chlorobenzene (CB) In a mixed solvent with a volume ratio of 1:1, heat and stir for 6 hours, wherein the heating temperature is 60 degrees Celsius. The obtained blue-light SpiroAC-TRZ solution and the host material CzSi solution were miscible at a volume ratio of 1:10, heated and stirred for 12 hours to obtain 300 microliters of a light-emitting layer solution with...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Luminescence peak | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com