Waste catalyst recycling method
A waste catalyst, alumina technology, applied in chemical recovery, chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry and other directions, can solve the problems of waste of alumina carrier, waste catalyst replacement device can not meet the reuse of waste catalyst, etc., to achieve clean and efficient extraction, Reduce the effect of excess anion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
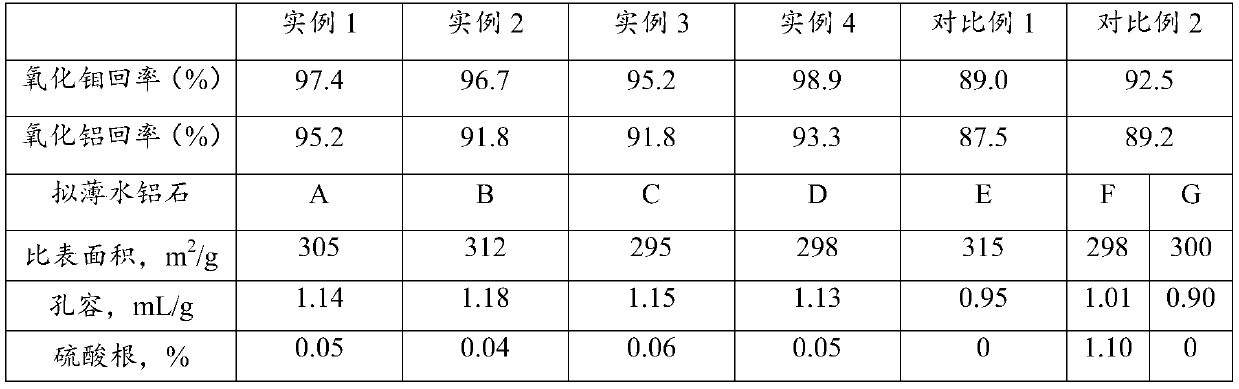
[0028] Take the molybdenum-nickel series catalyst after industrial operation for extraction and deoiling, dry, microwave treatment, and the treatment time is 5h; weigh 100g of the catalyst, crush it to 300 mesh; weigh 26.5g of sodium carbonate, mix it evenly with the spent catalyst, and roast at 600°C 4h; put the burnt solid into 400g hot water, use an autoclave to leaching at 120°C, and filter to obtain sodium molybdate solution and 74.2g solid 1; add sulfuric acid solution to the molybdate solution, and adjust the pH value to 5.2~ 7. After removing aluminum ions, continue to adjust the pH value to 1-2 to obtain 26.5g molybdic acid; mix solid 1 with 90g sodium carbonate solid, roast at 900°C, leaching in an autoclave at 120°C for 4 hours, and filter to obtain Sodium aluminate solution and 4.2g nickel oxide solid; the sodium aluminate solution was cooled to 50°C, crystallized for 24 hours, filtered to obtain sodium aluminate hydrate and dilute sodium aluminate solution; the sod...
Embodiment 2
[0030]Take the molybdenum-nickel series catalyst after industrial operation for extraction and deoiling, dry, and microwave treatment for 6 hours; weigh 100g of the catalyst, crush it to 300 mesh; weigh 26.5g of sodium carbonate, mix it with the spent catalyst, and roast at 700°C 4h; Put the burnt solid into an autoclave for leaching at 120°C, with a net water volume of 400g, filter to obtain sodium molybdate solution and 73.9g of solid 1; add sulfuric acid solution to the molybdate solution, and adjust the pH value to 5.2 ~7, after removing the aluminum ions, continue to adjust the pH value to 1~2 to obtain 26.3g of molybdic acid; mix solid 1 with 84g of sodium carbonate solid, roast at 930°C, leaching in an autoclave at 120°C for 4 hours, filter, Sodium aluminate solution and 4.1g nickel oxide solid were obtained; the sodium aluminate solution was cooled to 60°C, crystallized for 24 hours, filtered to obtain sodium aluminate hydrate and dilute sodium aluminate solution; the s...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Take the molybdenum-nickel series catalyst after industrial operation for extraction and deoiling, dry, microwave treatment, and the treatment time is 5h; weigh 100g of the catalyst, crush it to 300 mesh; weigh 26.5g of sodium carbonate, mix it evenly with the spent catalyst, and roast at 700°C 4h; Put the burnt solid into 400g of hot water, use an autoclave to leach at 120°C, and filter to obtain sodium molybdate solution and 74.1g of solid 1; add sulfuric acid solution to the molybdate solution, and adjust the pH value to 5.2~ 7. After removing aluminum ions, continue to adjust the pH value to 1-2 to obtain 25.9 molybdic acid; mix solid 1 with 84g sodium carbonate solid, roast at 930°C, leaching in an autoclave at 120°C for 4 hours, and filter to obtain aluminum sodium aluminate solution and 4.1g nickel oxide solid; the sodium aluminate solution was cooled to 60°C, crystallized for 24 hours, filtered to obtain sodium aluminate hydrate and dilute sodium aluminate soluti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com