Probe combination for detecting hereditary hearing loss and application thereof
A probe and gene detection technology, which is applied in the fields of biomedicine and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of false positive or false negative, and achieve the effect of improving accuracy and overcoming allelic tripping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Capture probe set of hereditary deafness-related genes:
[0032] The genes that can be captured by the capture probe set (liquid phase capture probe) include:
[0033] Group 1: Coding regions and splicing sites of hereditary deafness-related genes GJB2, GJB3 and SLC26A4:
[0034] Group 2: SNPs within 2MB regions upstream or downstream of 3 genes
[0035] SNP screening principles: selecting data from the Thousand Genomes Project
[0036] (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / variation / tools / 1000genomes / ), the minimum allele frequencies of CHB (Northern Han Chinese) and CHS (Southern Han Chinese) within 2 Mb upstream and downstream of each gene above are greater than 0.1 high-frequency mutation sites, remove polynucleotides (polyN) and polymorphic sites with GC content > 70% in the upstream and downstream 50bp sequences of the site, and select unique to compare to the human genome hg19, obtained after screening SNP loci.
[0037] The first group and the second group ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2 target gene detection method
[0039] 1. Library construction and sequencing
[0040] 1. Sample DNA Preparation
[0041] Samples can be DNA extracted from blood or saliva, or single cells or a small number of cells, DNA products obtained through single-cell whole genome amplification (WGA);
[0042] 2. Sample DNA Fragmentation
[0043] About 50ng of genomic DNA and / or single-cell WGA products were disrupted by ultrasound (covaris), resulting in DNA fragments with a main length of 200-250bp.
[0044] 3. Genomic library construction using KAPA reagents
[0045]The library can be constructed using the commercially available reagent KAPA Hyper Prep Kit (KAPA, KK8504). The main steps include: end repair of the fragmented DNA and adding A to the tail, linker ligation and purification (the linker contains the Index sequence, and each sample uses Linkers containing different index sequences are connected, and the linker sequence is a T overhang), and finally a ...
Embodiment 3
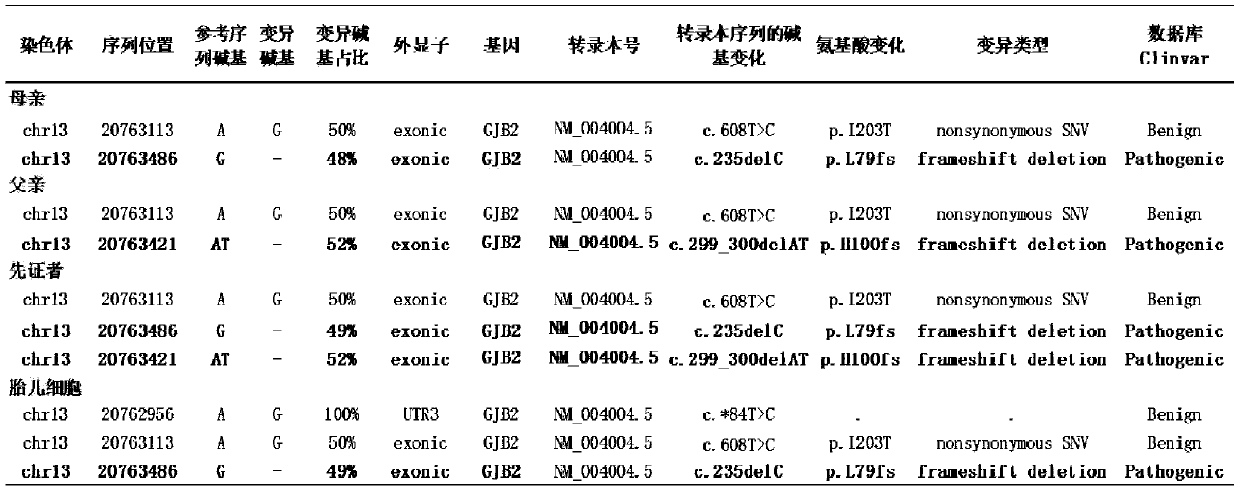
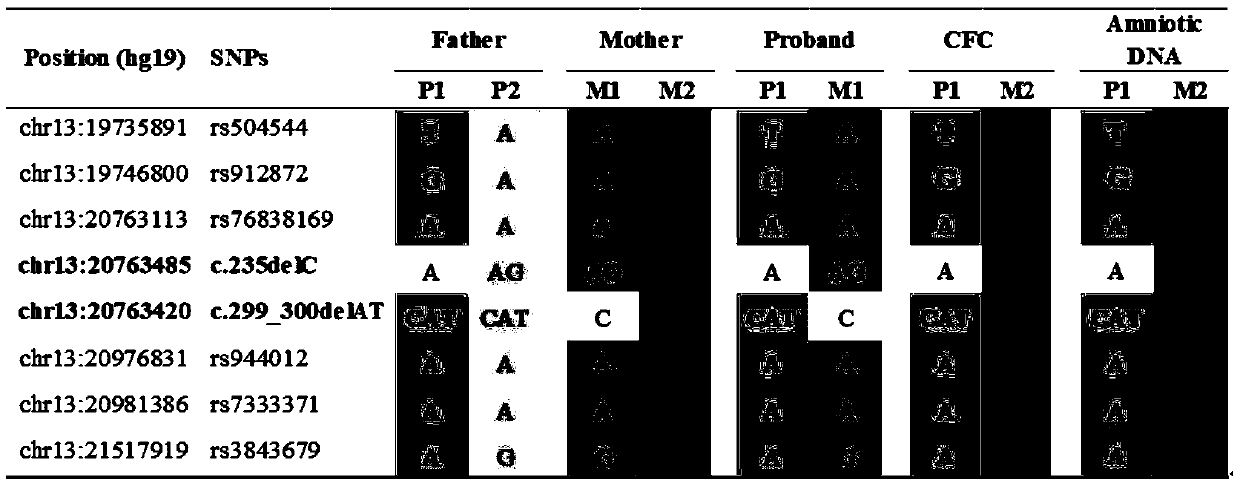
[0055] Example 3 Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis of deafness gene GJB2
[0056] 1. Sample collection: Collect a family with GJB2 gene-related hereditary deafness (the pregnant woman is heterozygous for GJB2 c.299delAT, the father of the fetus is heterozygous for GJB2 c.235delC, the proband is compound heterozygous for GJB2 c.299delAT and GJB2 c.235delC) Pregnant women collect 16ml of peripheral blood within 10-14 weeks of pregnancy to capture fetal cells in peripheral blood; the biological father, pregnant woman, and proband patient collect saliva for genomic DNA extraction.
[0057] 2. According to the method of Example 1, use the probe combination of the present invention to carry out library construction and on-machine sequencing, and perform data analysis.
[0058] 3. The results of data analysis are as follows:
[0059] (1) Data quality control:
[0060]
[0061] For genomic DNA, the coverage rate of the coding region of the detected gene region is 100%, and only a f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com