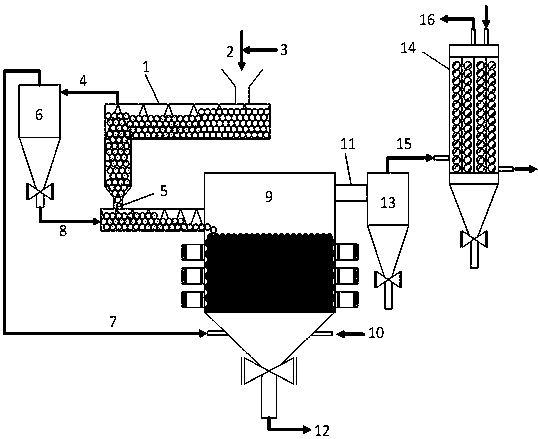
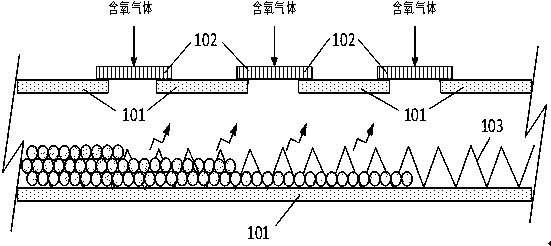
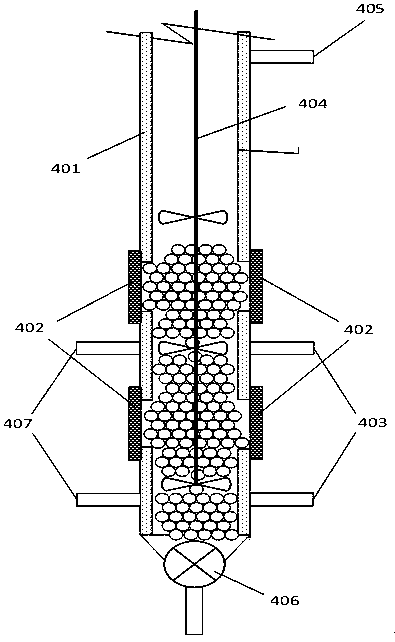
Auxiliary agent for biomass treatment and biomass gasification treatment method
A biomass treatment and treatment method technology, applied in the field of biomass processing, can solve the problems of poor quality and low yield of synthesis gas, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] According to the mass fraction, take 10% component A, 80% component B and 10% component C, wherein component A includes 1 part of oxalic acid and 0.5 part of aluminum chloride, and component B includes 1 part of ammonium borate and 1 part of carbonic acid Sodium, component C chooses manganese sulfate. First, components A, B and C are dried at 105°C respectively, and after cooling, components A and B are subjected to high-speed ball milling at 25°C at 250 rpm to obtain powdery materials of 200-400 μm, and then the above-mentioned The powdery material was uniformly added to component C in batches, and low-speed ball milling was carried out at 4°C and 60 rpm to obtain auxiliary agent A for biomass treatment.
Embodiment 2
[0057] According to mass fraction, get 20% component A, 60% component B and 20% component C, wherein component A comprises 1 part of sulfuric acid and 1 part of magnesium chloride, component B comprises 5 parts of sodium phosphate and 1 part of potassium carbonate, Component C is manganese nitrate. First, components A, B and C are dried at 105°C respectively, and after cooling, components A and B are subjected to high-speed ball milling at 25°C at 350 rpm to obtain powdery materials of 200-400 μm, and then the above-mentioned The powdered material was uniformly added to component C in batches, and low-speed ball milling was performed at 120 rpm at 4°C to obtain the auxiliary agent B for biomass treatment.
Embodiment 3
[0059] According to the mass fraction, take 15% of component A, 70% of component B and 15% of component C, wherein component A includes 1 part of citric acid and 1 part of ferric chloride, and component B includes 1 part of ammonium phosphate and 1 part of Potassium carbonate, component C selects manganese acetate. First, components A, B and C are dried at 105°C respectively, and after cooling, components A and B are subjected to high-speed ball milling at 25°C at 350 rpm to obtain powdery materials of 200-400 μm, and then the above-mentioned The powdered material was uniformly added to component C in batches, and low-speed ball milling was carried out at 4° C. at 120 rpm to obtain biomass treatment additive C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com