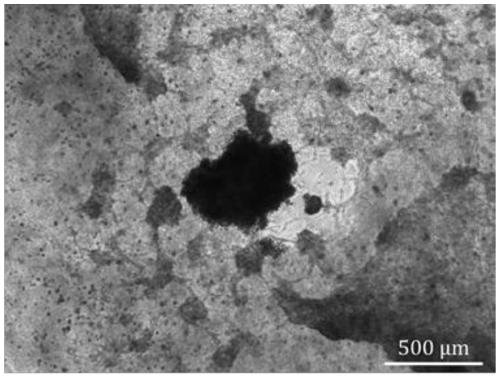
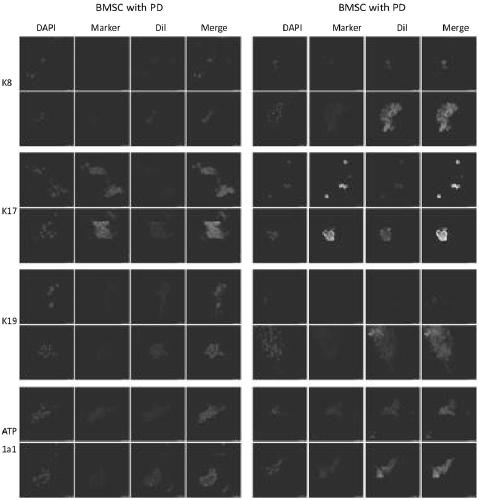
Method for constructing biological 3D printing skin microcell model containing skin appendage
A 3D printing, micro-unit technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, additive processing, etc., can solve problems such as construction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] A method for constructing a biological 3D printing skin microunit model containing skin appendages, comprising the steps of:
[0024] 1) Prepare a bio-3D printing glue block containing seed cells of sweat gland tissue, and plant hair follicles and sebaceous gland hanging drops on the bio-3D printing glue block;
[0025] 2) Inducing culture using an induction medium on the biological 3D printing block; wherein, the induction medium includes a sweat gland induction medium, a hair follicle induction medium and a sebaceous gland induction medium;
[0026] 3) After 5-10 days of induced culture, add epidermal stem cells on the surface of the bio-3D printing glue block, and perform air-liquid plane culture to form bio-3D printed skin microunits.
[0027] Wherein, the seed cells in step 1) include one or more of skin precursor cells, skin appendage precursor cells, adult stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells. The skin precursor cells, skin appendage precursor cells, adu...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The preparation of biological 3D printing glue blocks comprises the following steps:
[0032] 1.1) Collect seed cells containing sweat gland tissue, mix with printing materials evenly, and prepare bio-3D printing ink;
[0033] Among them, the printing materials include: lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer, polylactic acid, polycaprolactone, racemic polylactic acid-polydisperse methylene carbonate copolymer, nano-beta-tricalcium phosphate, nano-hydroxyapatite, nano One or more of calcium phosphate, gelatin, sodium alginate hydrogel or type I collagen hydrogel;
[0034] An example of material preparation for printing:
[0035] Weigh 3.8g of lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer, dissolve it in 10mg of dichloromethane, stir for 2 hours until the lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer is completely dissolved, and form a lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer solution; weigh 3.8g beta-tricalcium phosphate Disperse in the lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer solution and dissolve co...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The bio-3D printed skin dermis microunits prepared in Example 2 were induced and cultured;
[0049] The 3D bioprinted skin dermis microunits are placed in an incubator at 37°C for 5-10 days, preferably 7 days. The induction medium components include three types, specifically sweat gland induction medium, hair follicle induction medium and sebaceous gland induction medium. In this embodiment, the induction medium uses the same amount of sweat gland induction medium, hair follicle induction medium and sebaceous gland induction medium.
[0050] Specifically, the components of the induction medium:
[0051] Component 1, sweat gland induction medium: DMEN / E12 (1:1) added 10% v / v fetal bovine serum, 10ng / ml epidermal growth factor, 20ng / ml triiodothyronine, 0.64ng Hydrocortisone / ml, ITS 1% v / v;
[0052] Component 2, hair follicle induction medium: DMEN / E12 (1:1) added 5% v / v fetal bovine serum, 20% v / v ITS, 0.2nM / ml triiodothyronine, 20ng Basic fibroblast growth factor pe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com