Bone-imitation composite material scaffold and preparation method thereof
A composite material and bone-like technology, which is applied in medical science, tissue regeneration, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete degradation, large difference in bone modulus, and weak osteogenic performance, so as to achieve easy production, popularization and application, The effect of good biocompatibility and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
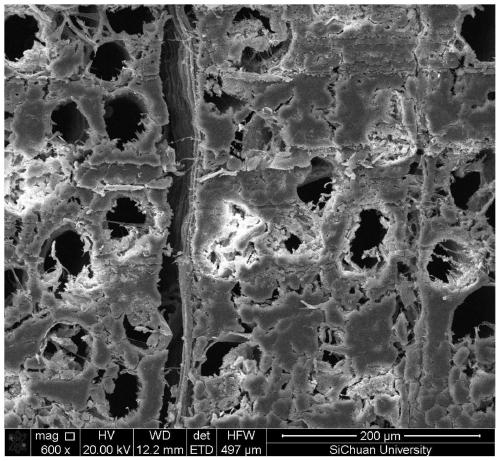
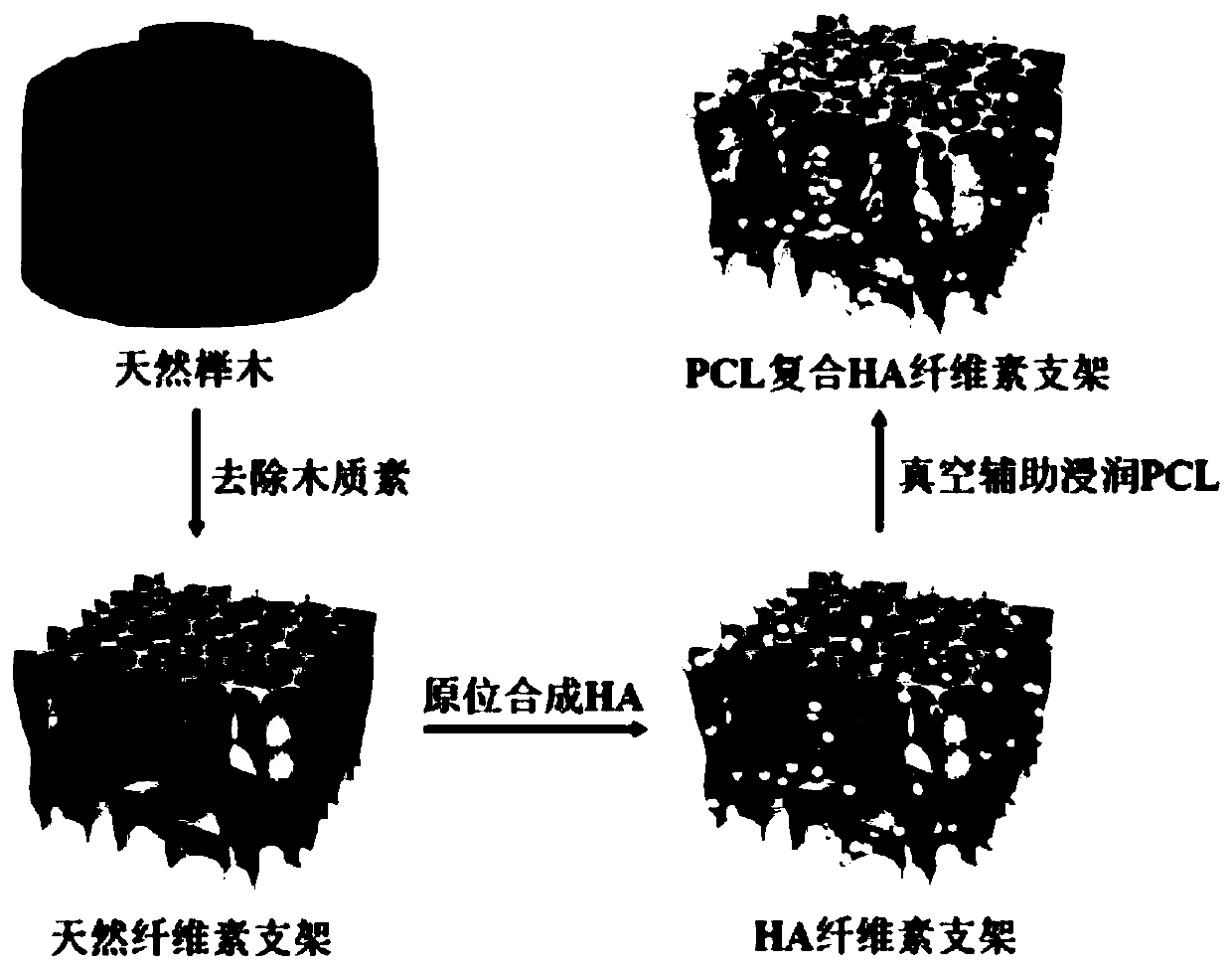
[0037] (1) Preparation of natural cellulose scaffold material
[0038] Measure 100 mL of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, weigh 3.5 g of sodium chlorite into the buffer solution, stir evenly to dissolve it, and prepare a lignin removal solution. Immerse the beech wood chips in the lignin removal solution, and stir slowly at 60°C for 36 hours, then take out the wood chips, rinse with deionized water for 5 minutes, soak and ultrasonicate for 5 minutes, repeat three times, and then soak in deionized water for 24 hours. The wood chip samples were taken out, rinsed with deionized water, and freeze-dried for 12 hours.
[0039] (2) Fabrication of HA cellulose scaffolds
[0040] Prepare 0.5mol / L calcium nitrate solution, adjust the pH to 11 with ammonia water, put the natural cellulose stent into 50mL calcium nitrate solution, soak for 8 hours, take out the stent sample; then prepare 0.5mol / L diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution , adjust the pH to 11 with ammonia water,...
Embodiment 2
[0045] (1) Preparation of natural cellulose scaffold material
[0046]Measure 100 mL of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, weigh 10 g of sodium chlorite into the buffer solution, stir evenly to dissolve it, and prepare a lignin removal solution. Immerse the pine wood chips in the lignin removal solution, and stir slowly under the condition of 70°C for 24 hours, then take out the wood chips, rinse with deionized water for 10 minutes, soak and ultrasonicate for 10 minutes, repeat three times, and then soak in deionized water for 24 hours. The wood chip samples were taken out, rinsed with deionized water, and freeze-dried for 18 hours.
[0047] (2) Fabrication of HA cellulose scaffolds
[0048] Prepare 0.2mol / L calcium nitrate solution, adjust the pH to 11 with ammonia water, put the natural cellulose stent into 60mL calcium nitrate solution, soak and react for 12h, take out the stent sample; then prepare 0.2mol / L diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution , adjust the pH ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] (1) Preparation of natural cellulose scaffold material
[0054] Measure 100 mL of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution, weigh 10 g of sodium chlorite into the buffer solution, stir evenly to dissolve it, and prepare a lignin removal solution. Immerse the beech wood chips in the lignin removal solution, and stir slowly at 70°C for 24 hours, then take out the wood chips, rinse with deionized water for 10 minutes, soak and ultrasonicate for 10 minutes, repeat three times, and then soak in deionized water for 24 hours. The wood chip samples were taken out, rinsed with deionized water, and freeze-dried for 18 hours.
[0055] (2) Preparation of PCL composite HA cellulose bone-like composite scaffold
[0056] Dissolve 5g of polycaprolactone and 5g of nano-hydroxyapatite in 40g of 1,4-dioxane solution, and stir vigorously at 40°C until the polycaprolactone is completely dissolved and the nano-hydroxyapatite is fully dispersion. Place the natural cellulose stent prepare...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com