Easy-to-disperse acrylate-coated zinc stearate composite material and preparation thereof
A technology of composite materials and zinc stearate, which is applied in the field of modified zinc stearate materials and its preparation, can solve problems such as reducing interfacial compatibility, and achieve the effects of low cost, increased application range, and excellent stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
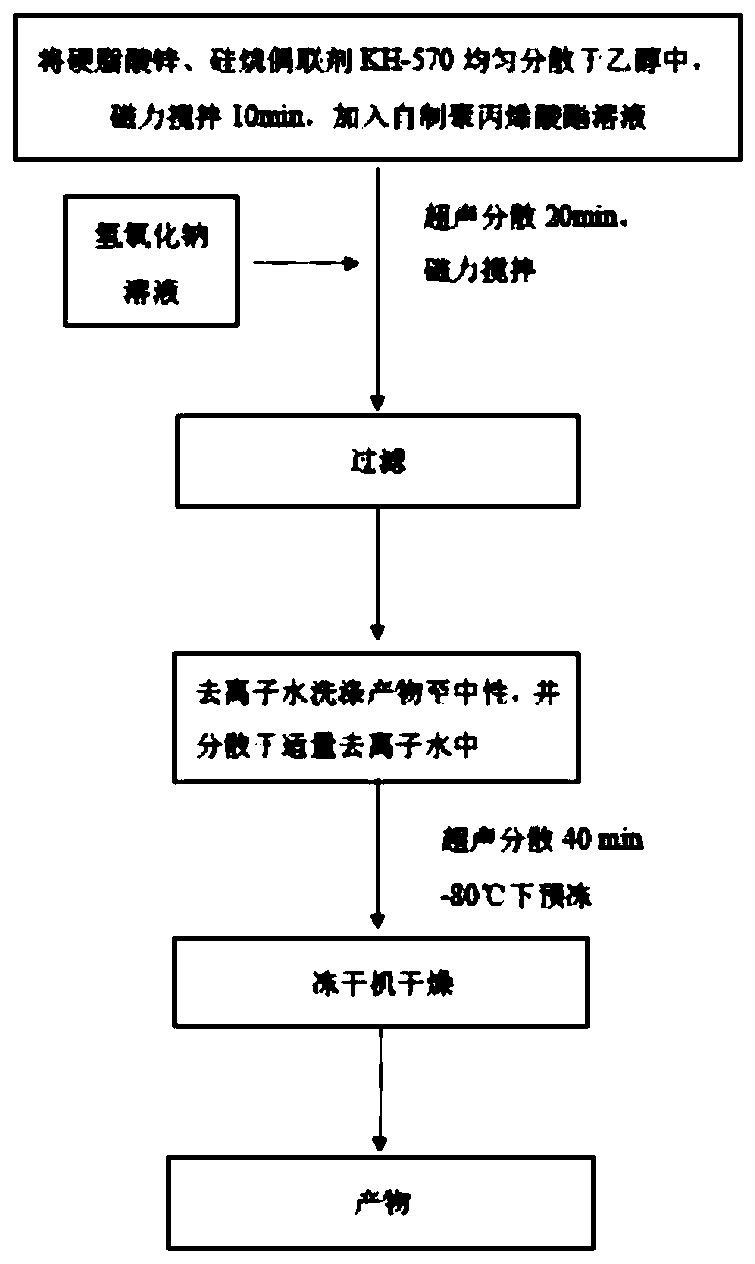
[0035] (1) Mix 5 g of commercially available zinc stearate, 0.008 g of silane coupling agent KH-570 and 75 g of ethanol in a beaker, stir magnetically for 10 min, add 2.5 g of aqueous polyacrylate solution, stir magnetically for 10 min, and disperse ultrasonically for 20 min ;
[0036] (2) Add 5 g of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass fraction of 25% into the mixed solution, and stir magnetically at 25° C. for 15 min.
[0037] (3) The mixed solution was filtered, and the white precipitate was collected, and fully washed with deionized water until neutral.
[0038] (4) The collected product was dispersed in 15 g of deionized water, ultrasonically dispersed for 30 min; pre-frozen at -80° C., dried by a lyophilizer, and collected.
[0039] figure 1 The flow chart of the product process.
Embodiment 2
[0041] (1) Mix 5 g of commercially available zinc stearate, 0.008 g of silane coupling agent KH-570 and 75 g of ethanol in a beaker, stir magnetically for 10 min, add 5.0 g of aqueous polyacrylate solution, stir magnetically for 10 min, and disperse ultrasonically for 20 min ;
[0042] (2) Add 5 g of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass fraction of 25% into the mixed solution, and stir magnetically at 25° C. for 15 min.
[0043] (3) The mixed solution was filtered, and the white precipitate was collected, and fully washed with deionized water until neutral.
[0044](4) The collected product was dispersed in 15 g of deionized water, ultrasonically dispersed for 30 min; pre-frozen at -80° C., dried by a lyophilizer, and collected.
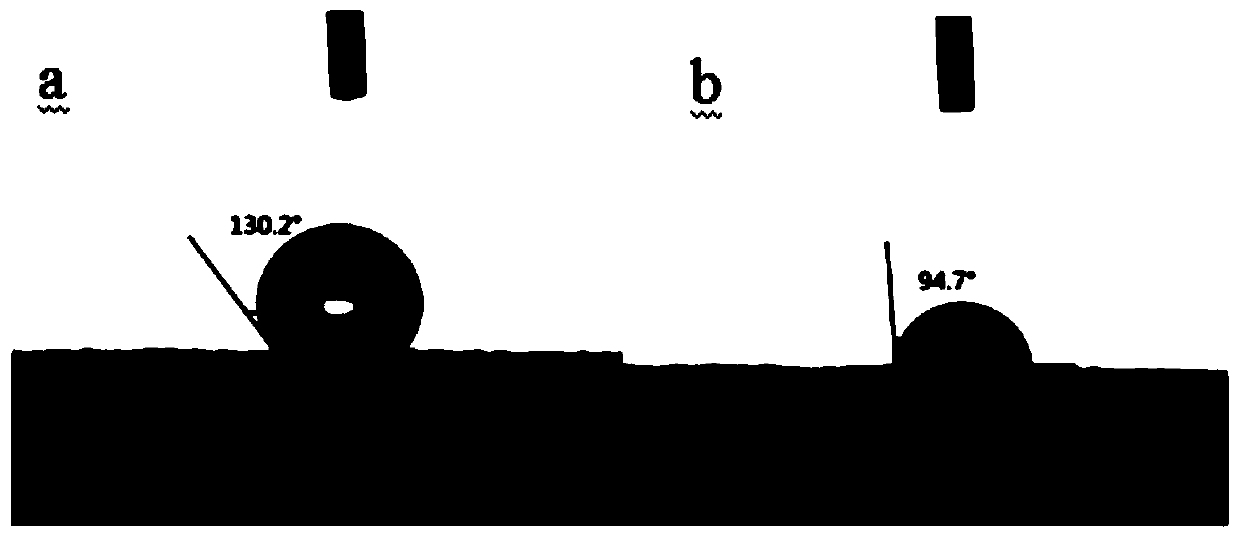
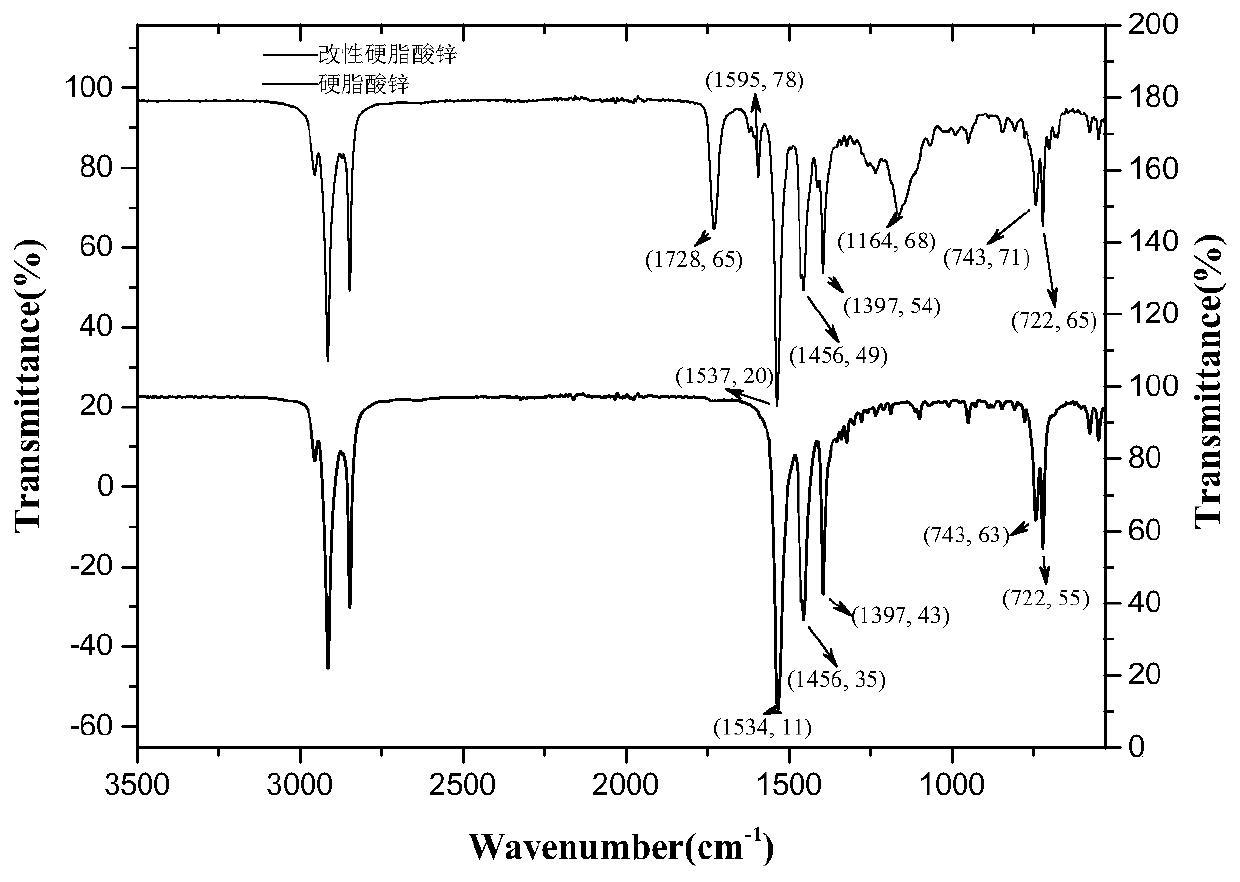
[0045] Such as figure 2 In , the contact angle of the product decreases, indicating that it has a certain degree of hydrophobicity; image 3 In the infrared spectrum, except for the characteristic peak of zinc stearate, at 1728cm -1 The stretch...
Embodiment 3
[0047] (1) Mix 5 g of commercially available zinc stearate, 0.008 g of silane coupling agent KH-570 and 75 g of ethanol in a beaker, stir magnetically for 10 min, add 7.5 g of aqueous polyacrylate solution, stir magnetically for 10 min, and disperse ultrasonically for 20 min ;
[0048] (2) Add 5 g of sodium hydroxide solution with a mass fraction of 25% into the mixed solution, and stir magnetically at 25° C. for 15 min.
[0049] (3) The mixed solution was filtered, and the white precipitate was collected, and fully washed with deionized water until neutral.
[0050] (4) The collected product was dispersed in 15 g of deionized water, ultrasonically dispersed for 30 min; pre-frozen at -80° C., dried by a lyophilizer, and collected.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com