Lactobacillus plantarum DNB1 and extracellular polysaccharide and application thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and extracellular polysaccharides, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems that lactic acid bacteria cannot regulate intestinal flora and anti-oxidation at the same time, and application limitations, and achieve significant in vitro anti-oxidation ability, high survival rate, and good tolerance affected by performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1 Isolation and identification of Lactobacillus plantarum DNB1
[0057] 1. Strain isolation and screening
[0058] Take 10mL to 90mL sterile physiological saline solution of grapefruit peel natural fermentation liquid under aseptic conditions, pipette evenly, and dilute to a suitable concentration according to 10 times gradient, take 100μL of the diluted bacterial solution, and spread it evenly with a coating stick. Spread on MRS solid medium, and incubate upside down in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 48h. Pick a single colony with the typical characteristics of lactic acid bacteria (round, milky white, neat edges, raised), and repeatedly streak and separate on the MRS solid medium to obtain a single colony;
[0059] Pick a single colony with a sterile bamboo stick, pull it out gently, measure the length of the colony's string, and select the strain with the largest string length as the target strain.
[0060] 2. Identification of the target stra...
Embodiment 2
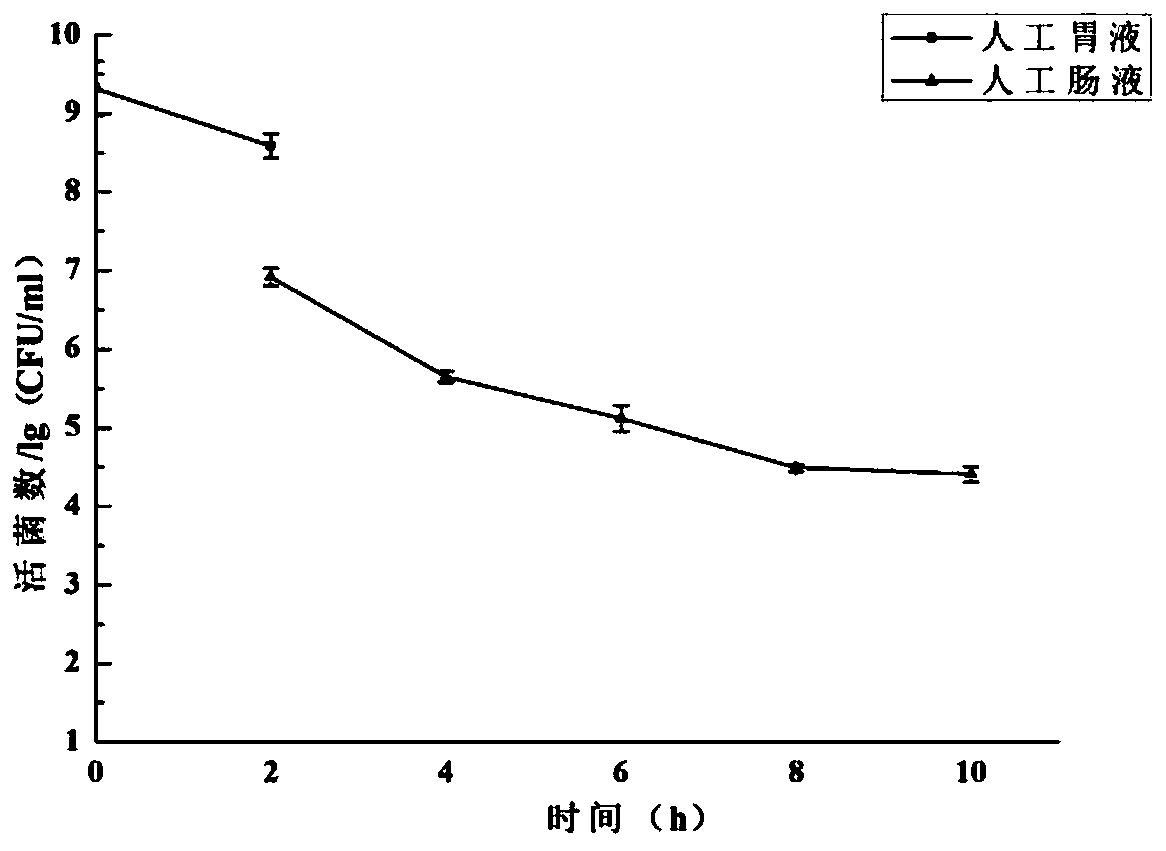
[0074] The acid and bile salt resistance performance measurement of embodiment 2 Lactobacillus plantarum DNB1
[0075] 1. Determination of acid tolerance of Lactobacillus plantarum DNB1
[0076] The acid resistance of lactic acid bacteria is one of the necessary conditions to ensure their survival through gastric juice into the intestinal tract, so the tolerance of lactic acid bacteria to acid is an important indicator.
[0077] (1) Experimental method
[0078] Inoculate Lactobacillus plantarum DNB1 into MRS liquid medium, activate 3 times, culture in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for 24 hours, collect the cells by centrifuging at 3000r / min and 4°C for 10 minutes, wash the cells with an equal volume of sterile saline Centrifuge twice under the same conditions, pour out the supernatant, and suspend the bacteria in an equal volume of sterile saline to prepare the bacteria solution to be tested;
[0079] Inoculate the bacteria solution to be tested into MRS liquid me...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Example 3 The extraction and yield determination of Lactobacillus plantarum DNB1 exopolysaccharide
[0105] 1. Experimental method
[0106] (1) Extraction of exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus plantarum DNB1
[0107] The extraction method of the extracellular polysaccharide of Lactobacillus plantarum DNB1 comprises the following steps:
[0108] S1. Inoculate Lactobacillus plantarum DNB1 in MRS liquid medium at an inoculum size of 3% (v / v), culture in a 37°C constant temperature incubator for 24h, and after continuous activation for 3 times, centrifuge at 4°C and 10000r / min for 10min Remove the bacteria and impurities in the fermentation liquid to obtain the fermentation liquid;
[0109] S2. Add 80% trichloroacetic acid solution to the fermentation broth so that the final concentration of trichloroacetic acid in the solution is 4% (m / v). After placing it in a refrigerator at 4°C for 7h, centrifuge at 4°C and 10000r / min for 15min Remove the protein precipitate to obt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com