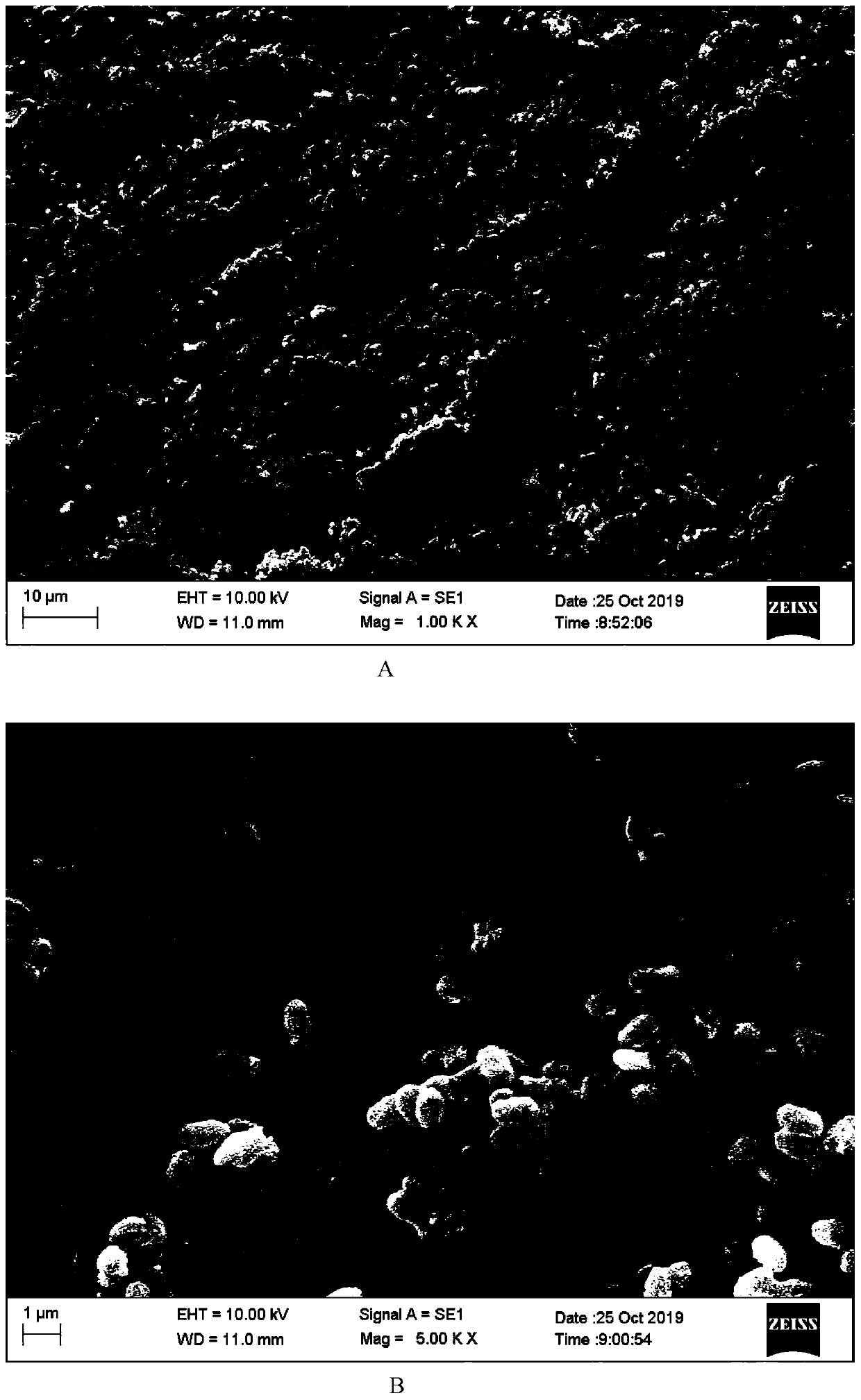
Pu'er tea leaf endophytic bacillus and application thereof
A Bacillus and leaf technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of fungi resistance, single compound can not achieve extensive bacteriostasis, etc., and achieve the effect of easy control and mild conditions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1 Isolation and Identification of Antifungal Endophytic Bacteria (Endophytic Bacillus in Pu'er Tea Tree Leaves)
[0065] (1) Pretreatment of fresh Puer tea tree leaves: The collected fresh and complete Puer tea tree leaves of the same age (from Menghai County, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan Province) were transported to the laboratory within 24 hours and subjected to surface disinfection operations, as follows: In the aseptic operation bench, soak the fresh and complete Pu'er tea tree leaves in 75% (volume fraction) ethanol solution for 15 seconds, then rinse them with sterile water and dry them with sterile cotton; content) Soak in sodium hypochlorite solution for 15 seconds, rinse with sterile water and dry with sterile cotton; repeat the above surface disinfection operation three times. The last flushing water was spread on potato dextrose agar medium (PDA medium), and then cultured at 37°C for 2 weeks. If no microorganisms appeared, the leaf surface was considered to...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2 Preparation of lipopeptides from Bacillus velezensis FZ06
[0076] (1) Strain activation: Under sterile conditions, take 1 ring of Bacillus velezensis FZ06 from a glycerol cryopreservation tube and insert it into PDA medium, and activate and culture at 36-38°C for 24 hours;
[0077] (2) Seed solution culture: Under sterile conditions, take 1 mL of activated Bacillus velezensis FZ06 and transfer it into 100 mL liquid LB medium, and culture it on a shaking table at 36-38°C and 160 rpm for 24 hours to obtain a seed solution;
[0078] (3) Fermentation culture: Under aseptic conditions, take 20 mL of the seed liquid obtained in step (2) and insert it into 2 L of liquid LB medium, and culture it on a shaker at 36-38 ° C and 160 rpm for 72 hours to obtain a fermentation liquid;
[0079] (4) Acid precipitation separation and washing: Centrifuge the fermentation broth in a low-temperature high-speed centrifuge at 4°C and 10,000rpm for 10 minutes to remove bacteria, the...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3 Structural identification of lipopeptides prepared from Bacillus velezensis FZ06
[0083] Redissolve 50 mg of the lipopeptide powder obtained in Extraction Example 2 in 50 mL of anhydrous methanol, and then dilute 1000 times with anhydrous methanol, and perform ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray-secondary mass spectrometry UPLC-ESI-MS / MS structure Determination, the specific analysis conditions are as follows:
[0084] Chromatographic separation conditions: chromatographic column: Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEHC18 column (2.1mm×100mm, 1.7μm); column temperature: 30°C; flow rate: 0.4mL / min; mobile phase: A - ultrapure water containing 0.1% formic acid, B—Acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid; Gradient elution conditions: 0-0.5min, 60%A; 0.5-3.5min, 60-20%A;. 3.5~4min, 20%A; 4~6min, 20~5%A; 6~7min, 5~2%A; 7~10min, 2%A; 10~10.5min, 2~60%A; 10.5~15min , 60% A; injection volume: 1 μL.
[0085] Mass spectrometry conditions: Agilent G6545A QTOF ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com