Cobalt-chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy powder for biomedical 3D printing and preparation method thereof
A 3D printing, biomedical technology, applied in 3D printing, metal processing equipment, additive manufacturing, etc., can solve problems such as powder adhesion, achieve high bulk density, fast scanning speed, good wear resistance and corrosion resistance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] A preparation method of cobalt-chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy powder for biomedical 3D printing, comprising the following steps:
[0029] Step 1 Melting: Co: 60-78%, Cr: 20-30%, W: 3.0-7.0%, Mo: 2.0-6.0%, Si: ≤1.0%, Be: ≤0.02%, Cd: ≤0.02%, Ni: ≤0.1%, the rest is impurity raw materials, metal cobalt, chromium, tungsten, molybdenum, silicon are added to the vacuum induction furnace for melting, the surface oxide scale is removed and put into vacuum self-consumption remelting to obtain cobalt Chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy ingots, and then the ingots are processed to obtain cobalt-chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy rods;
[0030] Step 2 Vacuum pressure holding gas protection: transfer the cobalt-chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy rod into the feeding chamber of the plasma rotary electrode atomization equipment, vacuumize the whole set of equipment and fill it with inert gas argon and helium;
[0031] Step 3 Atomization and condensation: start the water circulation...
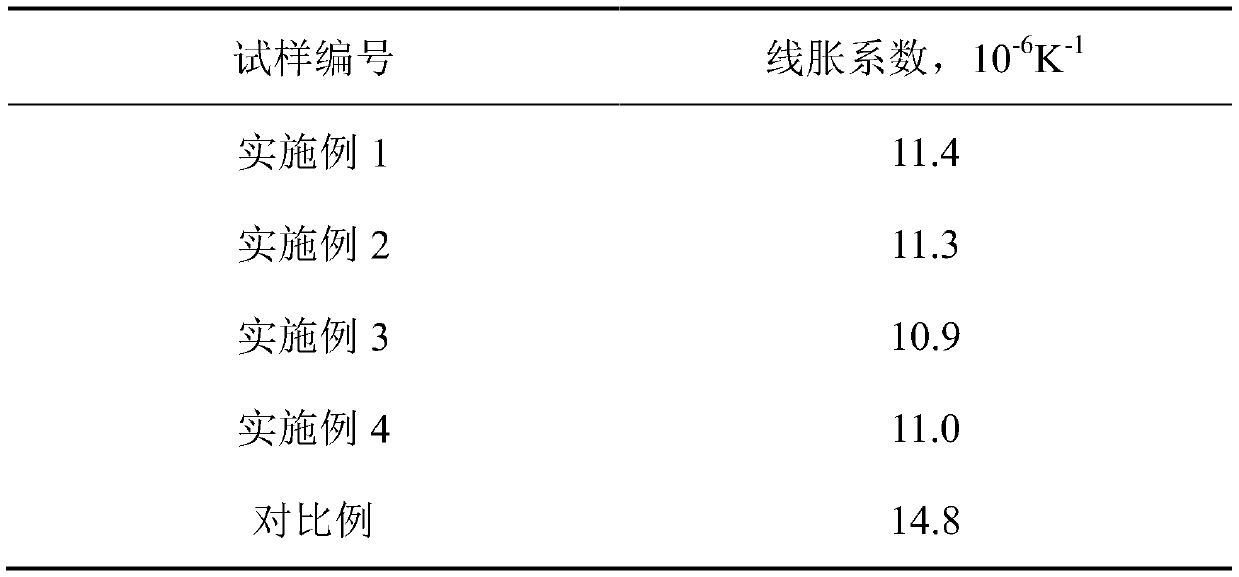
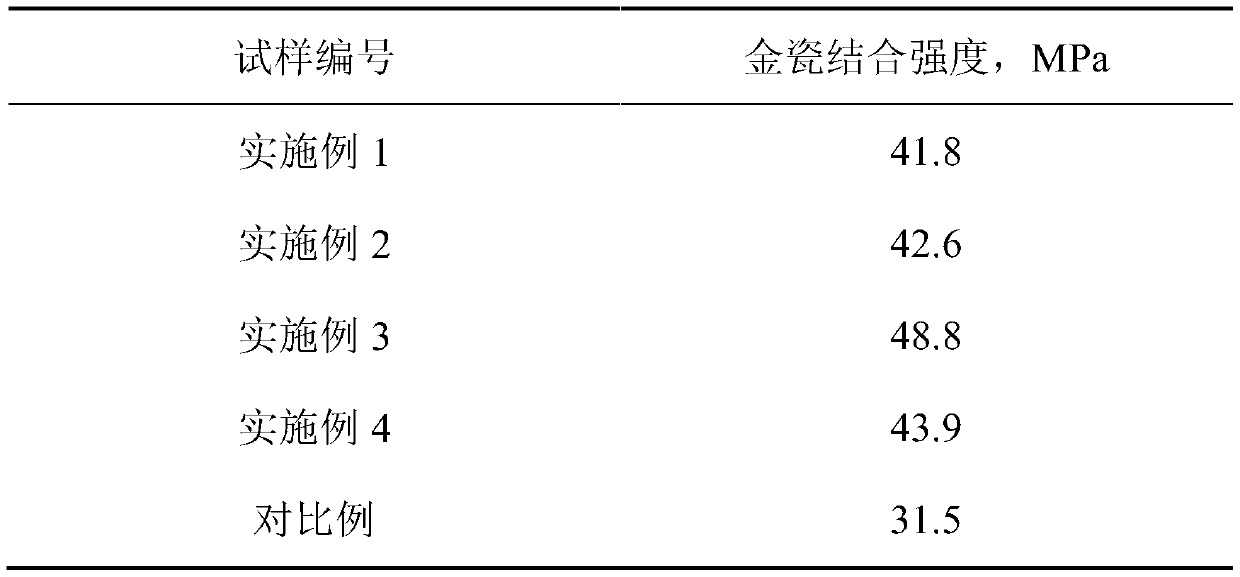
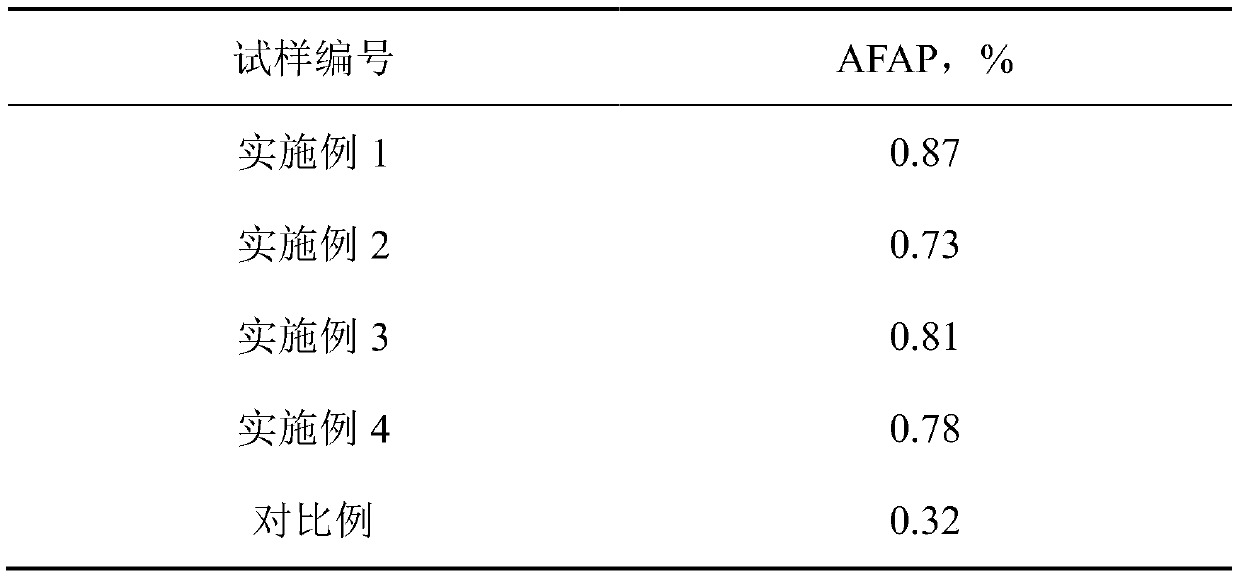
Embodiment 1
[0048] Specific steps: Step 1 Add metal cobalt, chromium, tungsten, molybdenum, and silicon to the vacuum induction furnace for melting, remove the surface oxide skin and put it into vacuum self-consumption remelting to obtain a cobalt-chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy ingot, and then process the ingot After treatment, a cobalt-chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy rod is obtained, and the weight percentage of each component of the alloy material is Co: 63.9%, Cr: 24.7%, W: 5.4%, Mo: 5.0%, Si: 1.0%, Be: -5 %, Cd: -5 %, Ni: -5 %, the balance is impurities; step 2 transfers the cobalt-chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy bar into the feeding chamber of the plasma rotary electrode atomization equipment, and vacuumizes the whole set of equipment to 5×10 -5 Within Pa and filled with inert gas argon and helium; step 3 start the water circulation system and atomization function, turn on the power of the plasma generator, and then ignite the plasma gun. Rotate the cobalt-chromium-tungsten-...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Specific steps: Step 1 Add metal cobalt, chromium, tungsten, molybdenum, and silicon to the vacuum induction furnace for melting, remove the surface oxide skin and put it into vacuum self-consumption remelting to obtain a cobalt-chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy ingot, and then process the ingot After treatment, the cobalt-chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy rod is obtained, and the weight percentage of each component of the alloy material is Co: 62.3%, Cr: 26.0%, W: 5.9%, Mo: 5.1%, Si: 0.82%, Be: -5 %, Cd: -5 %, Ni: -5 %, the balance is impurities; step 2 transfers the cobalt-chromium-tungsten-molybdenum alloy bar into the feeding chamber of the plasma rotary electrode atomization equipment, and vacuumizes the whole set of equipment to 5×10 -5 Within Pa and filled with inert gas argon and helium; step 3 start the water circulation system and atomization function, turn on the power of the plasma generator, and then ignite the plasma gun. Rotate the cobalt-chromium-tungst...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com