Borosilicate glass ceramic curing base material, and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for solidifying borosilicate glass and ceramics, used in radioactive purification, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve the problems of lack of long-term safety and stability evaluation methods for glass solidified bodies, low containment capacity and low containment capacity of nuclear waste solidified bodies, etc. Achieve the effect of improving chemical stability and packaging capacity, minimizing volume, and effectively containing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a borosilicate glass ceramic solidified substrate, which specifically includes the following steps:
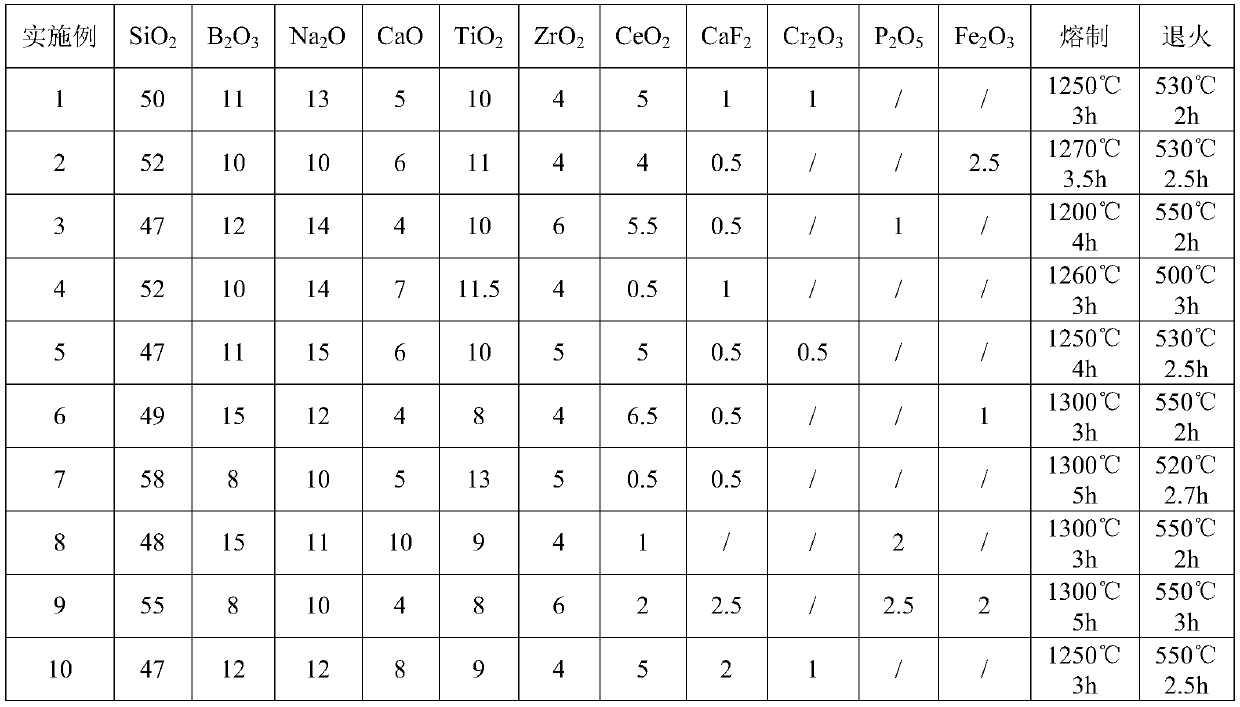
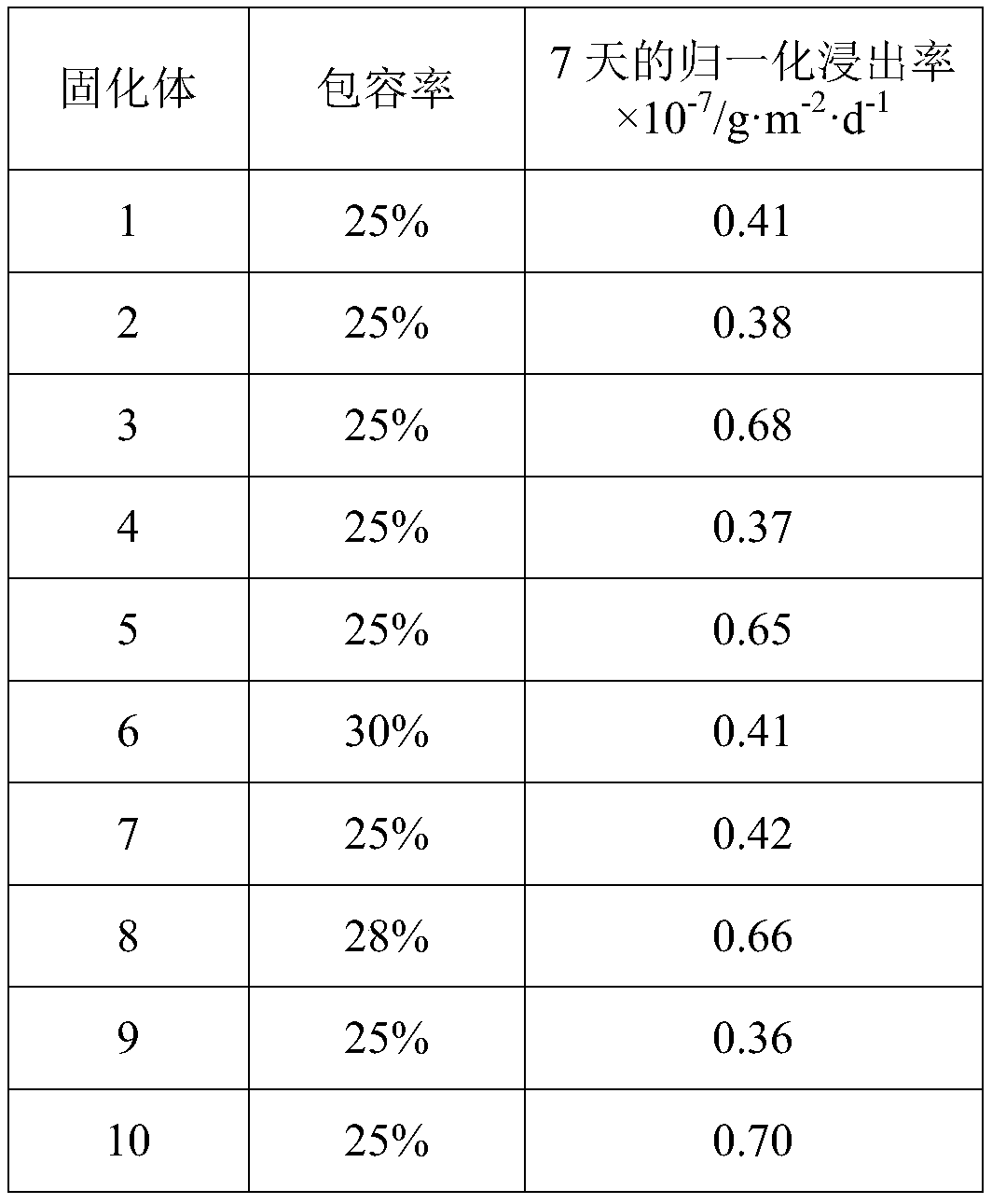
[0037] (1) select the raw material of borosilicate glass-ceramic solidified base material, by mass percentage, described raw material comprises the following components: SiO 2 50%, B 2 o 3 11%, Na 2 O 13%, CaO 5%, TiO 2 10%, ZrO 2 4%, CeO 2 5%, CaF 2 1%, Cr 2 o 3 1%;
[0038] (2) Put the raw materials into a mixer and grind them thoroughly; place them in a high-temperature furnace and melt them at 1250°C for 3 hours to completely melt the ingredients into a liquid melt; the particle size of the grinding is no more than 40 head;
[0039] (3) Pour the liquid melt into a mold preheated at 500°C, cool and shape it, put it in an annealing furnace at 530°C for 2 hours, and cool to room temperature with the furnace to obtain a silicate glass ceramic solidified substrate .
Embodiment 2
[0041] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a borosilicate glass ceramic solidified substrate, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0042] (1) select the raw material of borosilicate glass-ceramic solidified base material, by mass percentage, described raw material comprises the following components: SiO 2 53%, B 2 o 3 10%, Na 2 O 10%, CaO 7%, TiO 2 11%, ZrO 2 4%, CeO 2 4%, CaF 2 0.5%, Fe 2 o 3 2.5%;
[0043] (2) Put the raw materials into a mixer and grind them thoroughly; place them in a high-temperature furnace and melt them at 1270°C for 3.5 hours to completely melt the ingredients into a liquid melt; the particle size of the grinding is no more than 40 head;
[0044] (3) The liquid melt is poured into a preheated mold at 510°C, cooled and molded, placed in an annealing furnace at 530°C for 2.5 hours, and cooled to room temperature with the furnace to obtain a silicate glass ceramic solidified substrate .
Embodiment 3
[0046] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a borosilicate glass ceramic solidified substrate, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0047] (1) select the raw material of borosilicate glass-ceramic solidified base material, by mass percentage, described raw material comprises the following components: SiO 2 47%, B 2 o 3 12%, Na 2 O 14%, CaO 4%, TiO 2 10%, ZrO 2 6%, CeO 2 4%, CaF 2 0.5%, P 2 o 5 1%;
[0048] (2) Put the raw materials into a mixer and grind them thoroughly; place them in a high-temperature furnace and melt them at 1200°C for 4 hours to completely melt the ingredients into a liquid melt; the particle size of the grinding is no more than 40 head;
[0049] (3) Pour the liquid melt into a mold preheated at 500°C, cool and form it, put it in an annealing furnace at 550°C for 2 hours, and cool to room temperature with the furnace to obtain a silicate glass ceramic solidified substrate .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com