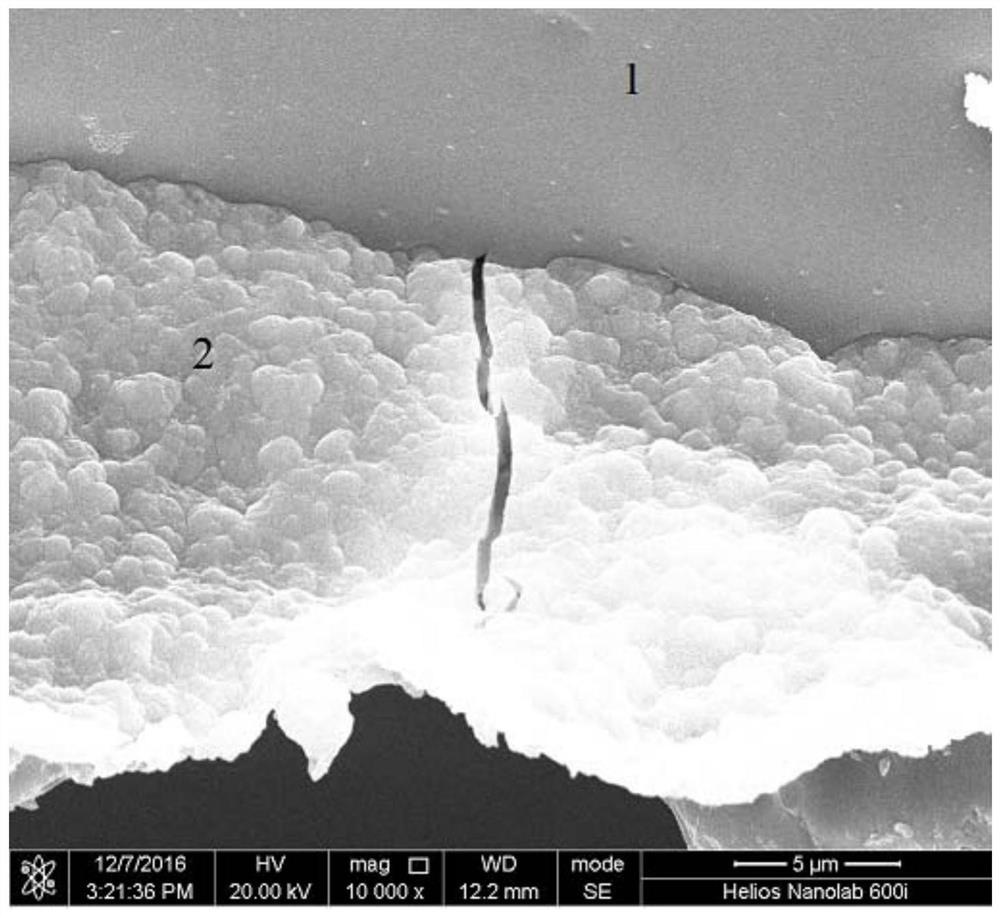
A SEM in-situ tensile test method for studying the interface fracture behavior of metal substrate and ceramic film layer
An in-situ stretching and metal matrix technology, applied in the direction of applying stable tension/pressure to test material strength, preparation of test samples, and measurement devices, can solve the problem that is not suitable for revealing the fracture of brittle film layers and plastic matrix systems Process and mechanism analysis and other issues, to achieve visual representation and wide applicability, energy saving, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
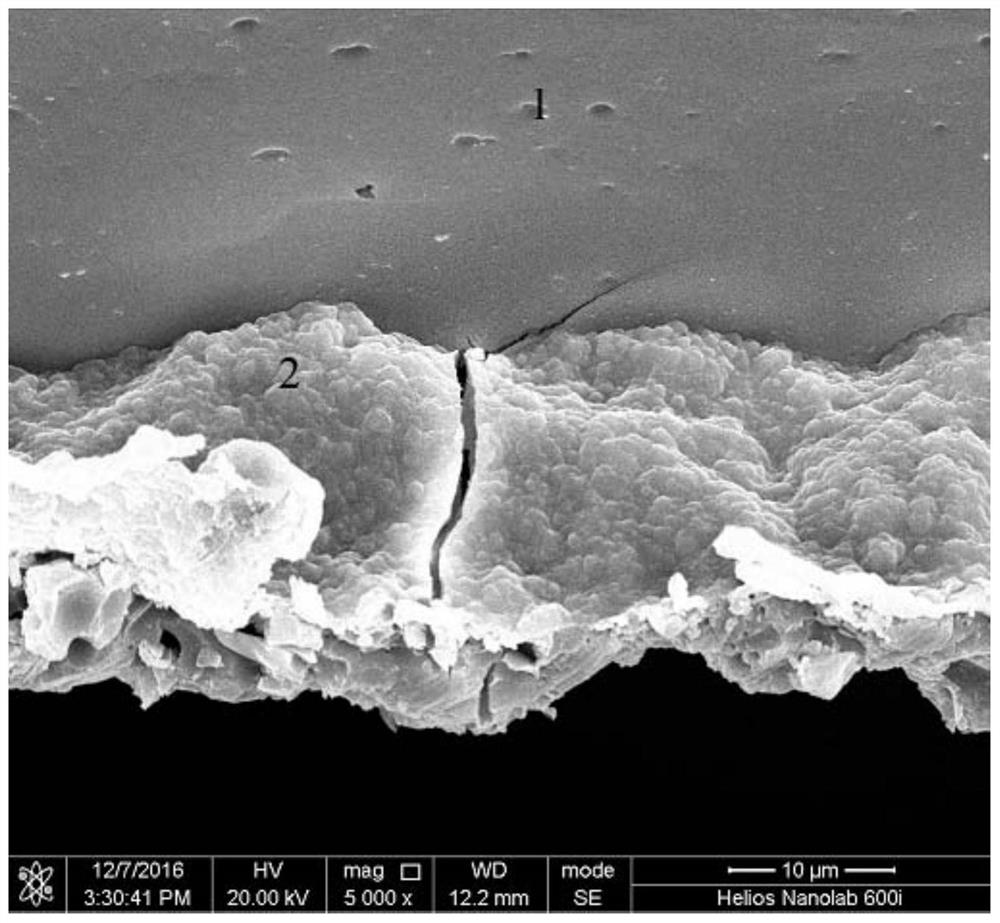
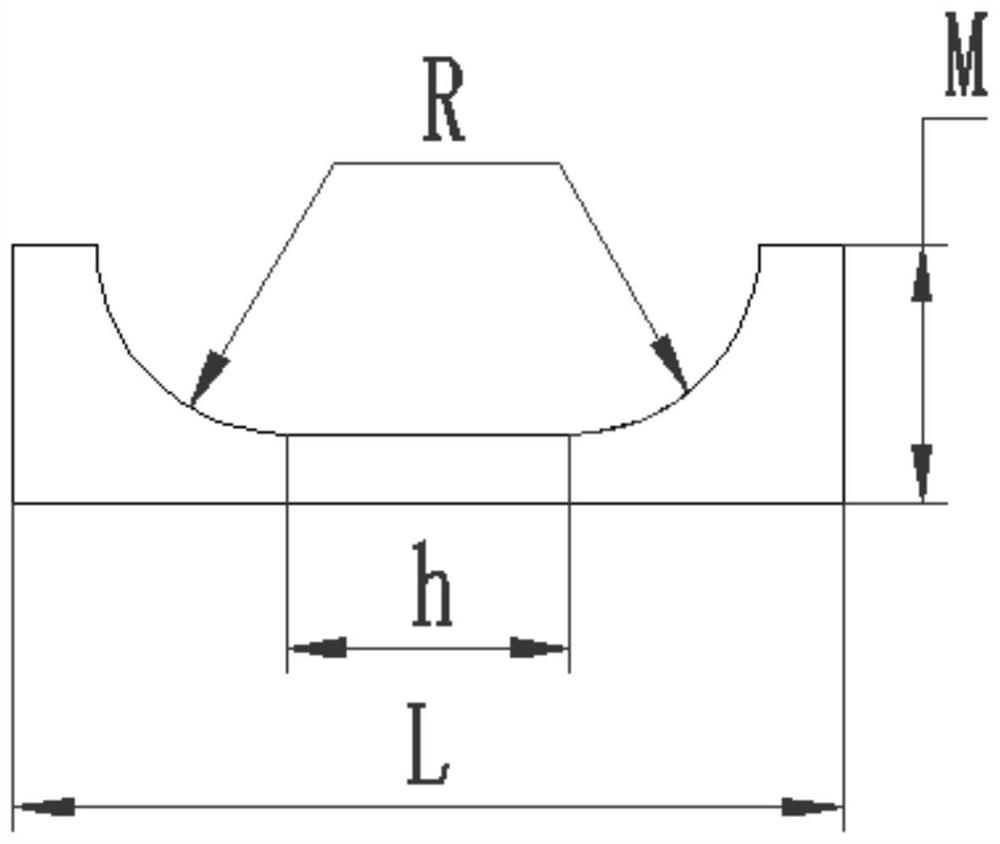
[0023] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Specifically, this embodiment is a SEM in-situ tensile test method for studying the fracture behavior of the metal substrate and the ceramic film layer interface, which is completed according to the following steps:
[0024] 1. Preparation of in-situ tensile specimens:
[0025] Open a U-shaped notch in the middle of one side of the long-side section of the plastic metal substrate covered with a ceramic film layer to obtain an SEM in-situ tensile sample;
[0026] The shape of the plastic metal substrate covered with a ceramic film layer is rectangular, the thickness is 0.2mm-5mm, the length is L=20mm-40mm, and the width is M=5mm-15mm;
[0027] The length of the straight section of the bottom edge of the U-shaped notch is h=10mm-30mm, the depth is equal to the radius of the transition fillet, the radius of the transition fillet is R=5mm-10mm, and the length of the opening is (h+2R)mm;
[0028] 2. Sample processing:
[...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0040] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 or 2 is: in step 2, use 600#, 800# for the long side section of the opposite side of the U-shaped notch in the SEM in-situ tensile sample. , 1200# and 2000# sandpaper for polishing. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0041] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and one of the specific embodiments one or two is: in step three, the sample clamping part in the test bench is adjusted, so that the gold-sprayed side of the SEM in-situ tensile sample after spraying gold is positive After aligning the scanning electron microscope lens, mark several positions on the gold-sprayed side by focusing the electron beam. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com