Polypropylene fiber reinforced lipophilic modification method
A technology of polypropylene fiber and microporous polypropylene, which is applied in fiber treatment, fiber type, textile and papermaking, etc. It can solve the problems of poor stability and inapplicability of high-efficiency lipophilic modification of polypropylene fiber, so as to reduce interfacial energy, Enhanced lipophilic performance is stable and reliable, and the effect of low material cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
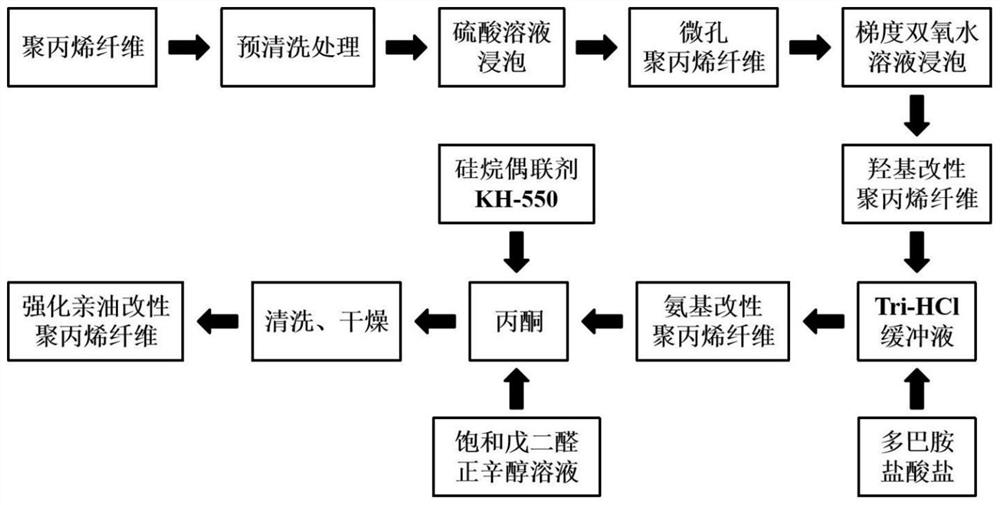
[0032] Step 1: Weigh 200g of polypropylene fiber raw material (100μm in diameter), and first perform the following pre-cleaning treatment to remove the original oily substances and other impurities on the fiber surface:
[0033] 1> Soak in 50% (volume fraction) acetone solution and 30% (volume fraction) ethanol solution successively for 1 hour;
[0034] 2>Transfer to deionized water for ultrasonic cleaning for 20 minutes, drain and set aside.
[0035]Transfer the pre-cleaned polypropylene fibers to 30% (mass fraction) sulfuric acid solution and soak for 1 hour. After sulfuric acid solution treatment, the polypropylene fibers were taken out, rinsed three times with 30% (volume fraction) ethanol solution and deionized water successively, and dried at 60° C. for 8 hours in a thermostat.
[0036] Step 2: using gradient hydrogen peroxide solution to carry out hydroxylation modification on the microporous polypropylene fiber. The specific operation process is to place the micropor...
Embodiment 2
[0041] After the polypropylene fiber raw material was pre-cleaned as described in Example 1, it was soaked in 50% (mass fraction) sulfuric acid solution for 2 hours. After being treated with sulfuric acid solution, the polypropylene fibers were taken out, rinsed three times with 30% (volume fraction) ethanol solution and deionized water successively, and dried in a thermostat at 60°C for 8 hours.
[0042] The microporous polypropylene fibers were modified by hydroxylation as described in Example 1 to obtain hydroxyl-modified polypropylene fibers.
[0043] As described in Example 1, the hydroxyl-modified polypropylene fibers were placed in 1000 mL of Tri-HCl buffer solution, 50 g of dopamine hydrochloride was added thereto, and the reaction was fully stirred (200 rpm) for 8 hours to obtain amino-modified polypropylene fibers. After the reaction, the amino-modified polypropylene fiber was washed 3 times with excess deionized water, and dried in a thermostat at 40° C. for 4 hours...
Embodiment 3
[0047] According to Example 2, the amino-modified polypropylene fiber obtained in Step 3 was added to an acetone solution containing 15% (mass fraction) of silane coupling agent KH-550 for silanization modification. The modification process was carried out under the condition of constant temperature stirring (80°C, 150rpm) for 6 hours, and a saturated glutaraldehyde n-octanol solution accounting for 1% (mass fraction) of the acetone solution was used as a crosslinking agent to realize the amination of the surface of the polypropylene fiber. Silyl graft copolymerization. Finally, the silanized modified polypropylene fiber was washed twice with 10% (volume fraction) ethanol solution and deionized water, and dried at 30°C for 12 hours in an incubator to obtain a reinforced lipophilic modified polypropylene fiber. fiber.
[0048] A large number of micropores appeared on the surface of the reinforced lipophilic modified polypropylene fiber obtained under this condition, the specif...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com