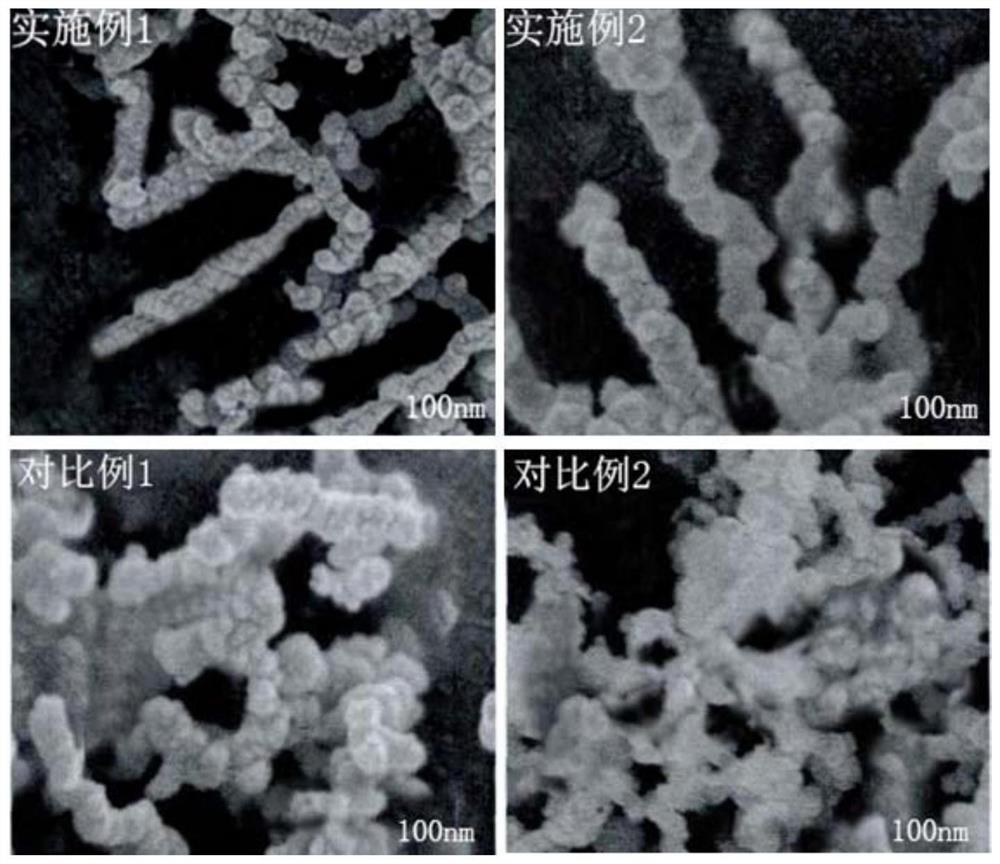
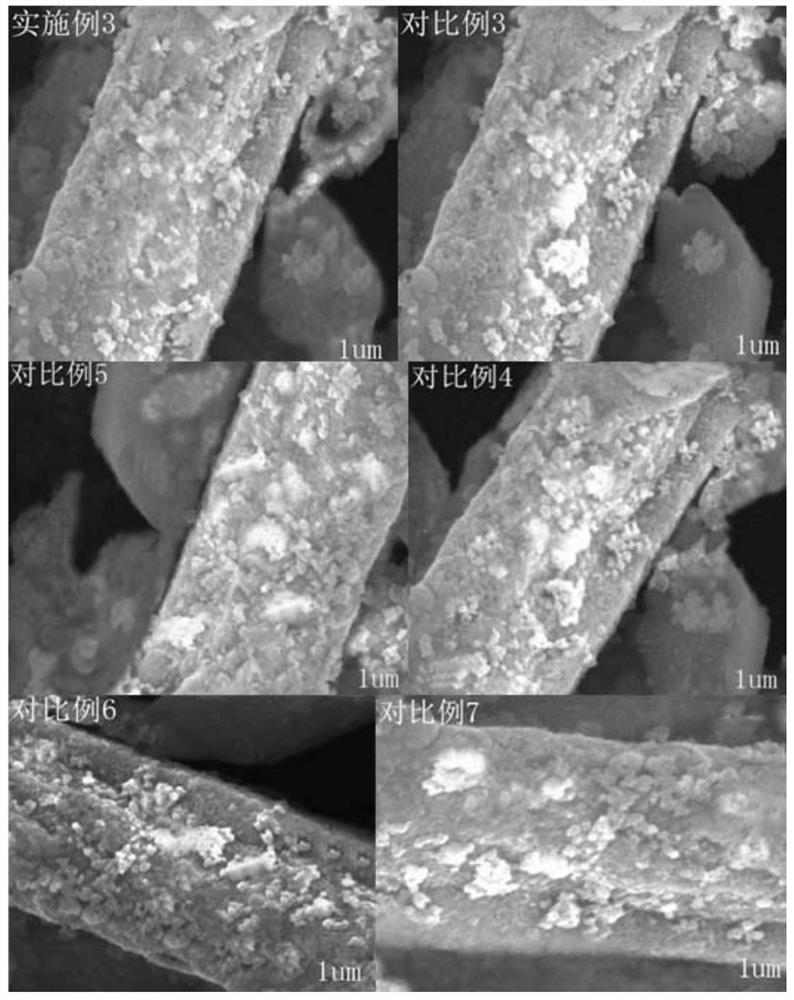
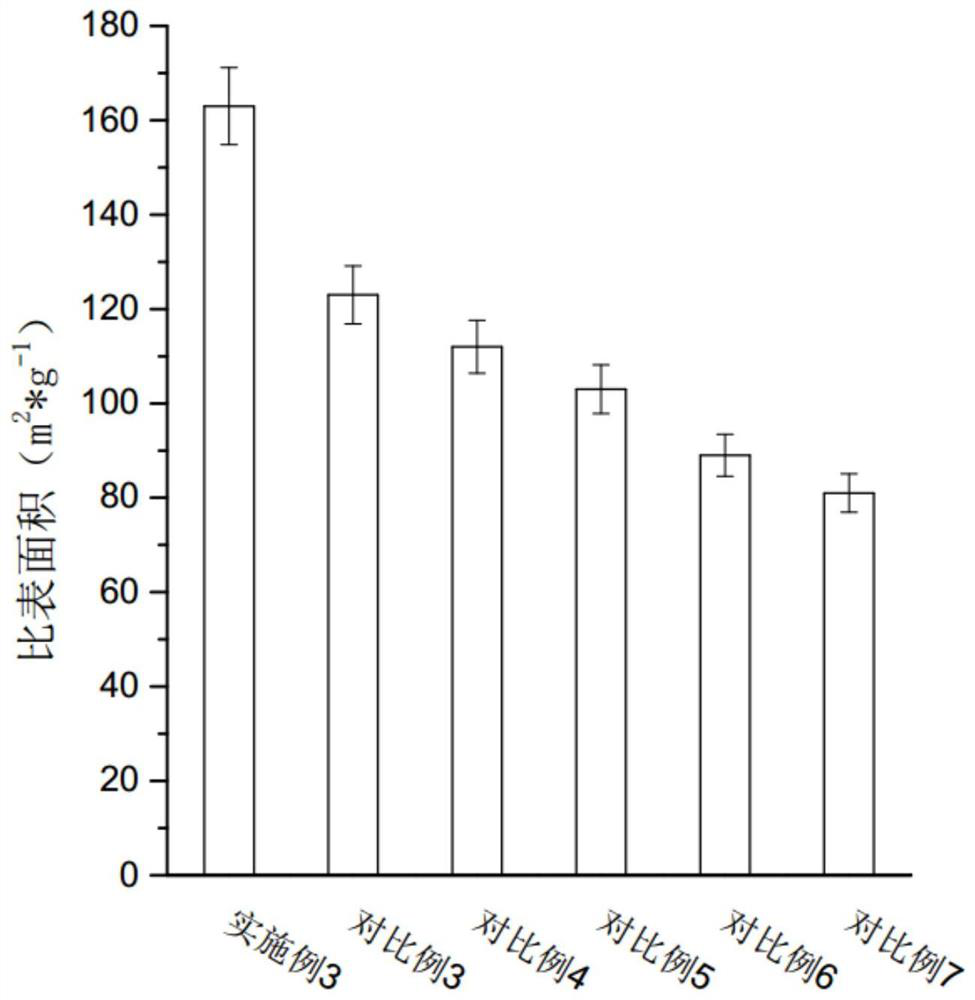
A modified nanomaterial and its application in antimony-containing wastewater treatment
A nanomaterial and modification technology, applied to the modified nanomaterial and its application in the treatment of antimony-containing wastewater, can solve the problems of reducing the reactivity, reducing the mobility, and high surface energy, and improving the dispersibility and stability. , Improve the removal effect, increase the effect of the specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0039] The invention provides a method for preparing an iron-based nanomaterial iron-based nanomaterial, which is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0040] S1, preparation of modified stabilizer;
[0041] S2. Preparation of modified nano-zero-valent iron: according to a certain mass ratio, weigh ferrous sulfate heptahydrate and loading material, dissolve in deionized water, take 100mL of loading material and ferrous sulfate mixed solution into a three-necked flask, stir , feed nitrogen, add 50mL of absolute ethanol, continue to stir for 20-30min, add dropwise the green tea extract, and slowly add the solution of step S1, then microwave radiation for 3-5min (preferably, for example 3min, 3.2min , 3.8min, 4min, 4.1min, 4.8min, 5min, etc.), continue to stir, fully react until the solution is black, and then ultrasonically treat it for 4-8min (preferably, such as 4min, 4.1min, 4.2min, 5min, 6min, 6.2 min, 6.9min, 8min, etc.), vacuum filtration, repeated was...
Embodiment 1
[0047] A method for preparing iron-based nanomaterials, comprising:
[0048] Modification of starch with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and malic acid: Add 5g of starch and 100mL of 0.4mol / L NaOH solution into a four-necked flask, heat to 75°C, and keep stirring during the period. After the starch is fully gelatinized for 1, Add ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (the mass ratio of solid starch to ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid is 1:1.8), vacuumize, reduce the pressure of the reaction system to 0.095MPa, then raise the temperature to 80°C, react for 8h, and wait for the reaction system to drop to 0.095MPa. After room temperature, acetone was added, and a thick white viscous product was obtained after settling, suction filtration and drying.
[0049] Preparation of modified nano-zero-valent iron: Mix 100mL of modified starch solution with a mass concentration of 3g / L and 100mL of 1mol / L ferrous sulfate solution, stir for 30min under the condition of nitrogen gas, and then drop i...
Embodiment 2
[0051] A method for preparing iron-based nanomaterials, comprising:
[0052] Modification of starch with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid: Add 5g of starch and 100mL of 0.4mol / L NaOH solution into a four-neck flask, heat to 75°C, and keep stirring during the period. After the starch is fully gelatinized for 1, add ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid Amine tetraacetic acid (the mass ratio of solid starch to ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid is 1:1.8), add malic acid (the mass ratio of solid starch to malic acid is 1:2.3), vacuumize, and reduce the pressure of the reaction system to 0.095MPa , and then heated to 80 ° C, the reaction 8h.
[0053] Preparation of modified nano-zero-valent iron: Mix 100mL of modified starch with a mass concentration of 3g / L and 100mL of 1mol / L ferrous sulfate solution, stir for 30min under the condition of nitrogen gas, and then drop into 100mL of 2.5mol / L Potassium borohydride solution, stirring while adding dropwise, continue to stir for 5 minutes a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com