Preparation for direct writing forming 3D printing bioink, and 3D printing method capable of adopting direct writing forming 3D printing bioink
A 3D printing and bio-ink technology, applied in 3D object support structures, additive manufacturing, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of easy fiber dispersion and poor stability, achieve high biocompatibility, adjustable viscosity, and improve survival rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] A method for preparing direct writing 3D printing bio-ink includes the following steps:
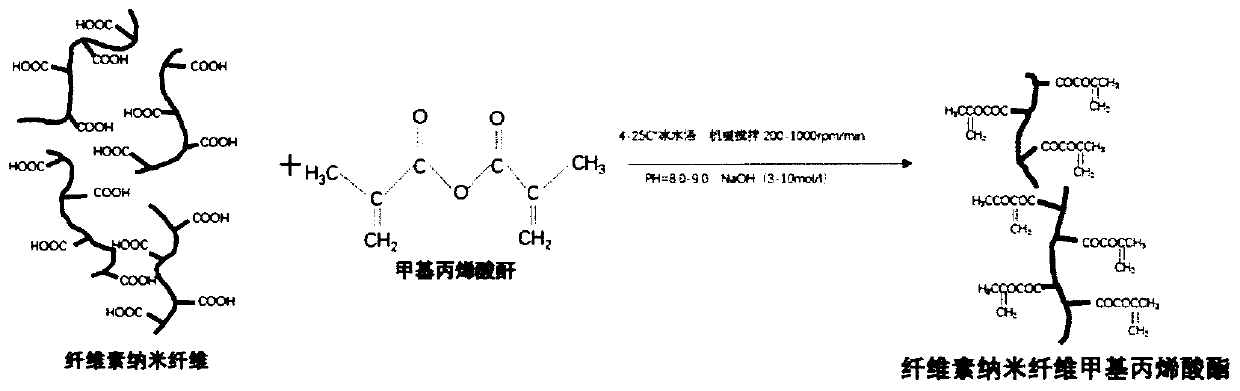
[0043] S1, Preparation of cellulose nanofiber methacrylate freeze-dried fiber
[0044] Disperse 1 to 5 g of cellulose nanofiber powder in deionized water at 4 to 50° C., rotate at a speed of 200 to 1000 r / min, and mechanically stir for 30 to 120 minutes to achieve uniform dispersion. Stir for 12-24 hours in a water bath at 4-25°C to obtain a cellulose nanofiber dispersion with a mass percentage of 1 to 5%. According to the quality of the cellulose nanofiber powder, add 1-20 times the volume of methacrylic anhydride liquid in the dispersion liquid at a rate of 0.5-1mL / min. After reacting for 2-3h, add 3-10mol / L of hydroxide With sodium solution, adjust the pH value of the mixed solution to the range of 8.0-9.0, and continue to react for 12-24 hours to obtain the cellulose nanofiber methacrylate precursor. The cellulose nanofiber methacrylate precursor is clamped with a 5000-14000 molec...
Embodiment 2
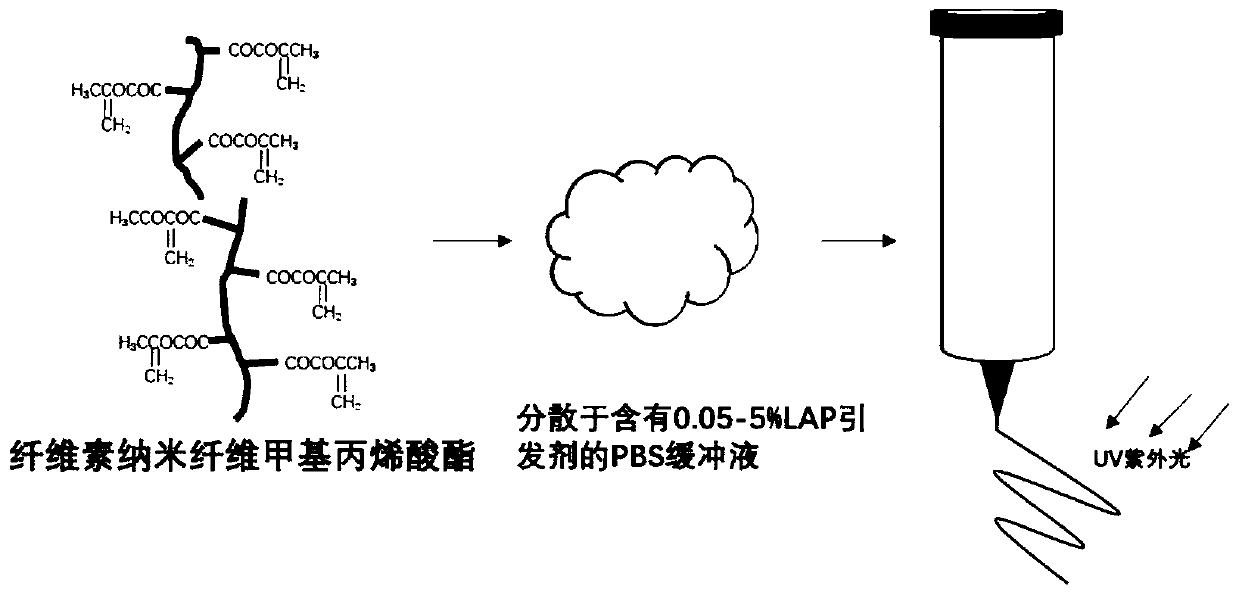
[0061] A direct-write molding 3D printing bio-ink. The preparation process is the same as that of Example 1, except that in step S1, 1g of cellulose nanofiber powder is added, and the prepared cellulose nanofiber methacrylate solution contains fiber The mass percentage of the plain nanofiber methacrylate is 1%, the mass percentage of the photoinitiator is 0.05%, the mass percentage of the PBS buffer is 98.95%, and the sum of the mass percentages of the above components is 100%.
[0062] The LAP photoinitiator used in the present invention has an improved polymerization reaction kinetic mechanism, so that the polymer hydrogel or other polymer materials can encapsulate biological cells under lower initiator concentration and longer wavelength light. Under the action of blue light, LAP quickly initiates the curing of the photosensitive hydrogel material. Compared with ultraviolet light initiators, blue light does less damage to biological cells, thereby increasing the survival rate ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] A direct-write molding 3D printing bio-ink. The preparation process is the same as that in Example 1, except that in step S1, 5g of cellulose nanofiber powder is added, and the prepared cellulose nanofiber methacrylate solution contains fiber The mass percentage of the plain nanofiber methacrylate is 5%, the mass percentage of the photoinitiator is 0.5%, the mass percentage of the PBS buffer is 94.5%, and the sum of the above-mentioned components is 100%.
[0065] The cellulose nanofiber used in the invention is a natural polymer material, which has the characteristics of adjustable viscosity, structural orientation, wide sources, and good mechanical properties. Grafting olefin groups into the cellulose nanofiber system makes it obtain the photocurable properties of synthetic polymers. The blue light initiates photocuring to prepare stable cellulose nanofiber methacrylate hydrogel.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| percent by volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com