Plant root-knot nematode biocontrol bacterium as well as preparation and application thereof
A biological control agent and nematode technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as poor implementation of root-knot nematode disease, low economic value and income, and difficulty in accepting idle land, etc., to achieve strong pathogenicity or kill Elimination effect, not easy to produce drug resistance, fast cultivation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
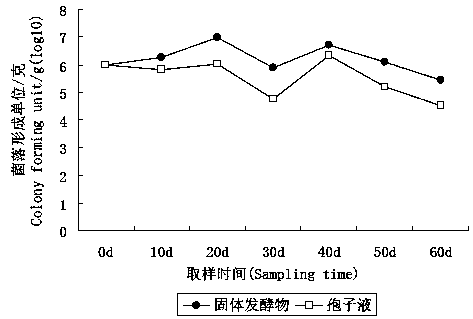
[0035] Example 1: Porphyridium lavender strain Pt362 Cultivation and domestication
[0036] Original strain of Porphyridium lavender Pl36-1 It was isolated from root-knot nematodes by Wang Mingzu in Hubei Province in 1991 and stored in the Phytopathological Nematode Laboratory of Huazhong Agricultural University. In 1991, he published an article in Acta Phytopathology as "Preliminary Research Report on Root-knot Nematode Egg Parasitic Fungi". Pt362 It is a mutant strain obtained by T-DNA insertion genetic transformation mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It was deposited in the China Type Culture Collection on November 25, 2016, and its deposit number is CCTCC NO: M2016682 (see Patent Document CN 106967613A).
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Porphyridium lavender strain Pt362 Determination of egg parasitism and larval lethality of root knot nematodes
[0038] Separate root knot nematode eggs from the roots of diseased tomato plants, disinfect the surface with 1% sodium hypochlorite for 3 minutes and wash 3 times with water. Place the disinfected eggs on top of the hyphae that have been grown on water agar (WA) plates for 2 days. 50 oocysts per dish, sealed and cultured in the dark in a 28°C incubator for 9 days, and observed the parasitic status of the eggs under a microscope. The parasitic observation of egg particles was treated with lactic acid glycerin solution. About 2 minutes after treatment, the edges of the eggs infected by Porphyridium spp. were transparent, and the uninfected ones were still dark. Repeat four times, and only the eggs were used as a blank control.
[0039] Porphyridium lavender strain Pt362 Parasitic root knot nematode eggs such as figure 1 Shown.
[0040] The specific test r...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Porphyridium lavender strain Pt362 Spore determination
[0051] Porphyridium lavender Pt362 After culturing on a PDA plate at 28°C for 3 days, use a punch (0.5cm in diameter) to take out the agar block with hyphae on the edge, and transfer it to a petri dish (9cm in diameter) containing quantitative PDA (20mL / dish) ) In the center, inoculate one piece per petri dish to start the strain ( Pl36-1 Strain) is the control, and each strain is repeated 4 times. After incubating at 28°C for 10 days, a spore suspension of P. lavender was prepared, and the spore concentration was determined by counting with a hemocytometer.
[0052] The specific test results are shown in Table 3.
[0053] Table 3 Spore production of Porphyridium lavender
[0054] .
[0055] The determination of spore production of the purple lavender strain showed that: Pt362 Spore production can reach 5.3×10 8 spores / dish; strain Pl36-1 Spore production can reach 3.2×10 6 spores / dish.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com