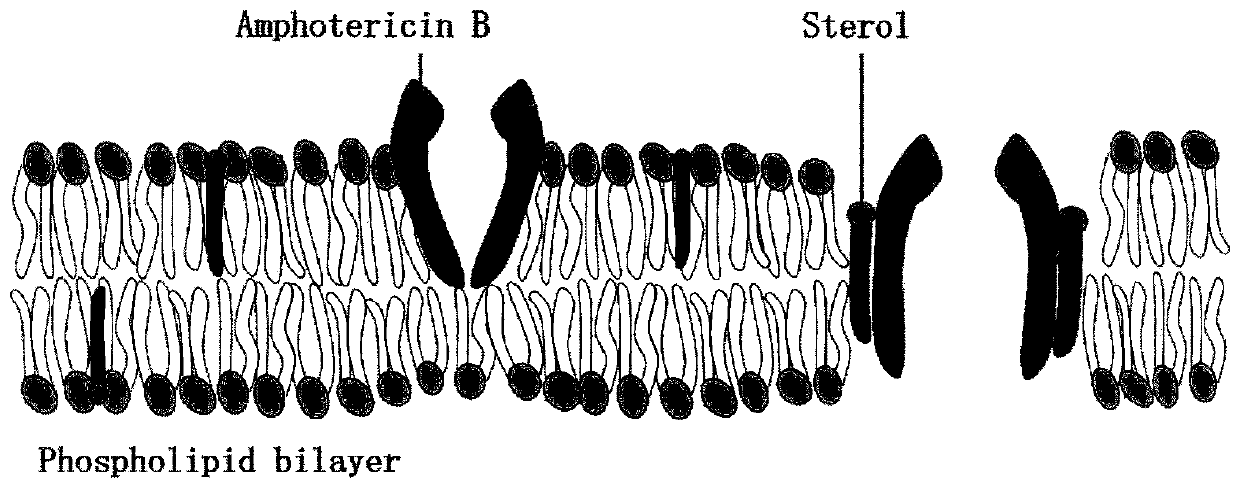
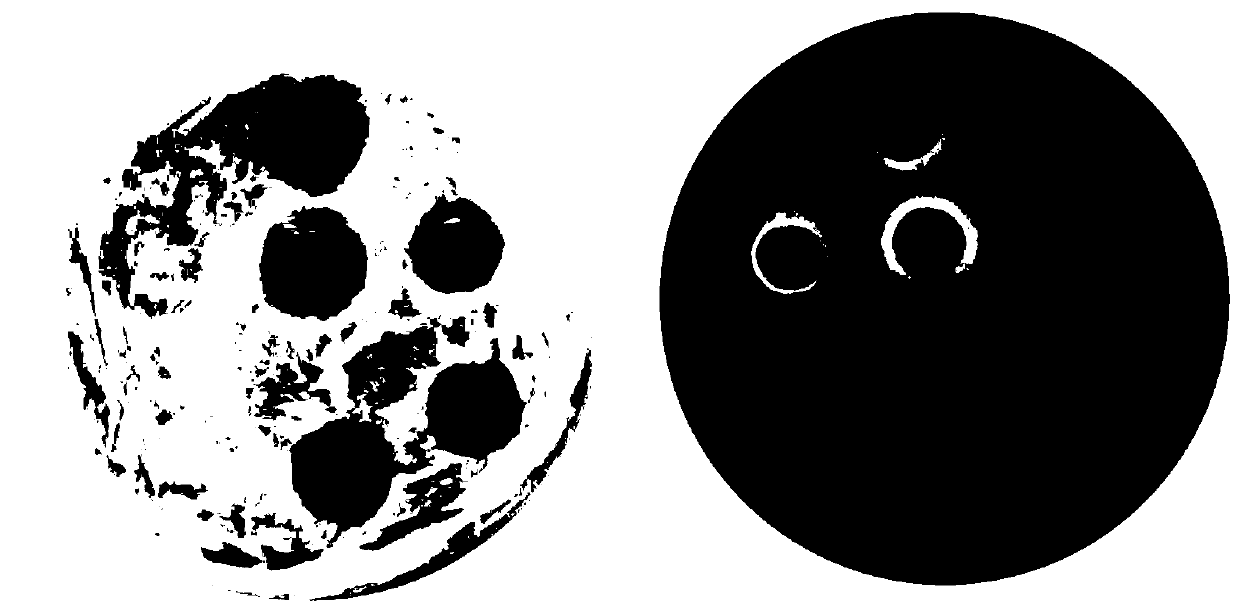
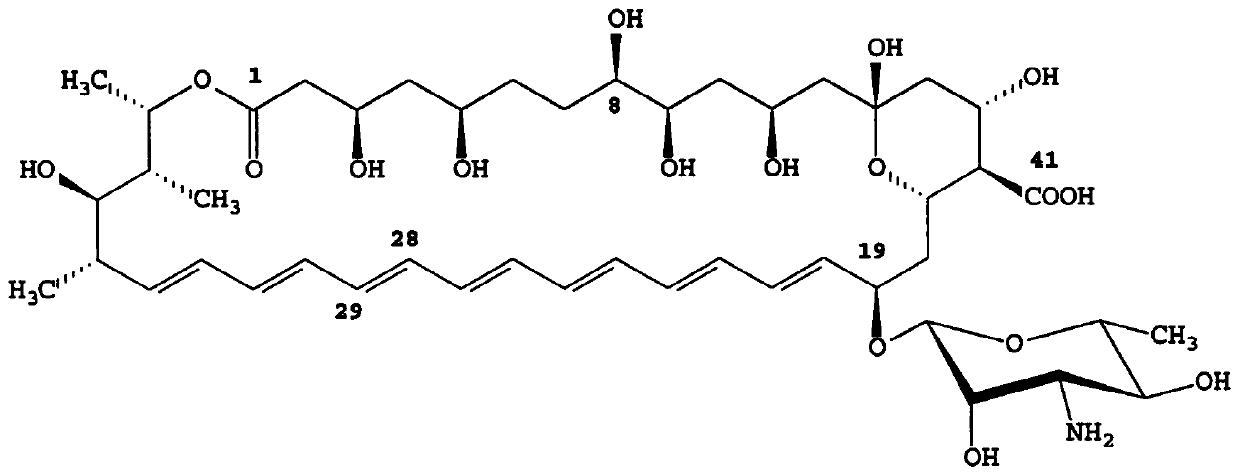
Method for screening high-yield amphotericin B streptomyces nodosus through high-throughput mutagenesis and strain
A technology for amphotericin and mutagenesis screening, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, etc., can solve the problem of V-shaped pore not penetrating the cell membrane, etc., to improve the efficiency of screening or verification and the overall yield The effect of raising and lowering costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1: Construction of high-throughput screening method
[0053] (1) Spread or streak the mutagenized spores and the control strain Streptomyces nodosum N3 (ATCC14899) on the GYM solid medium, and culture at 26° C. for 7 days until a single colony can be observed. Using a sterile toothpick or pipette tip, prick a single colony and streak a new GYM solid medium plate. After numbering, culture at 26°C for 4-7 days for preservation. The plates after the retention treatment were used for the inhibition zone experiment.
[0054] (2) Using yeast X33 (preserved in the laboratory) as a sensitive strain, pick a single colony on the GYM solid medium, culture it in the GYM liquid medium for 24 hours, take 100 μL and spread it on the GYM solid medium. On the plate that has been preserved in (1), use a sterile puncher or a pipette tip to pick out agar blocks containing a single colony, place them upside down on the GYM solid medium that has been coated with yeast, and number t...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2: the mutagenic strain of high AmB production
[0056] (1) Streptomyces nodosus N3 (ATCC14899) was inoculated on a GYM plate and cultured at 26°C for 7 days, and the gray-black spores were taken, and the surface spores were eluted into 10 mL of sterile water with a cotton swab, and washed The spore suspension was filtered with a syringe containing cotton, and the filtered spores were centrifuged at 12000rpm for 5min to remove the supernatant, added 10mL of sterile water to resuspend, centrifuged at 12000rpm for 5min to elute again, and resuspended with 5mL of sterile water as spore suspension.
[0057] (2) NTG-UV mutagenesis method: take 10mL of diluted spore suspension and place it under a UV lamp (15W, 254nm) at 20cm for 1min, inoculate it in GYM medium, and incubate at 26°C for 24-32h in the dark , collect the cells after mutagenesis, and treat them with NTG. The treatment method: use 50mM PBS buffer solution containing 5mg / mL NTG per 1mL of cell suspens...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Embodiment 3: Shake flask fermentation produces AmB
[0065] (1) Preparation of seed liquid: streak the Streptomyces nodosum mutagen (i.e. CCTCC NO: M 2017426) with high amphotericin B production prepared in Example 2 onto a GYM plate, culture at 26°C for 4 days, and select a single colony , inoculated into the seed medium, cultured at 26° C., 220 rpm for 48 hours, to obtain seed liquid.
[0066] The seed medium was prepared as follows: peptone 20g, NaCl 8g, glucose 15g, yeast powder 10g, CaCO 3 1g, add water to make up to 1L, pH 7.0, sterilize at 121°C for 20min.
[0067] (2) Fermentation culture
[0068] Load 100mL of fermentation medium into a 500mL shake flask, inoculate the seed solution at a volume concentration of 4% during fermentation, and ferment and cultivate at 26°C and 220rpm for 144 hours. The AmB production in the fermentation broth can reach 12g / L.
[0069] Fermentation medium composition: glucose 70g / L, beef extract 8g / L, soybean protein powder 8g / L,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com