Zinc-aluminium hydrotalcite rich in cuprous ions and preparation method and application of zinc-aluminium hydrotalcite
A zinc-aluminum hydrotalcite and cuprous ion technology, applied in the preparation/separation of ammonia, chemical instruments and methods, zinc compounds, etc., can solve the problems of poor stability, easy disproportionation reaction, application limitations, etc., to improve stability , Ease of large-scale production, and low synthesis cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Preparation of Zinc-Al Hydrotalcite 0.5%-ZnAl-LDH Rich in Cuprous Ions
[0046] 1) Prepare mixed metal precursor solution: dissolve 0.1mmol copper nitrate trihydrate, 10mmol zinc nitrate hexahydrate and 10mmol aluminum nitrate nonahydrate in 15ml deionized water;
[0047] 2) Prepare alkali precursor solution: dissolve 60mmol sodium hydroxide and 17.358mmol sodium carbonate in 15ml deionized water;
[0048] 3) Add the prepared metal precursor solution and alkali precursor solution dropwise to 15ml deionized water at the same time, and mix well to obtain a suspension;
[0049] 4) The suspension obtained in step 3) was placed on a constant temperature oil bath stirrer, and crystallized at 60° C. for 16 hours to obtain the product;
[0050] 5) Wash the product obtained in step 4) with deionized water for 10 times, dry at 60°C for 12 hours, and grind to obtain hydrotalcite nanosheets, which are zinc-aluminum hydrotalcites rich in cuprous ions, named as 0.5%- ZnAl-LDH.
[...
Embodiment 2-4
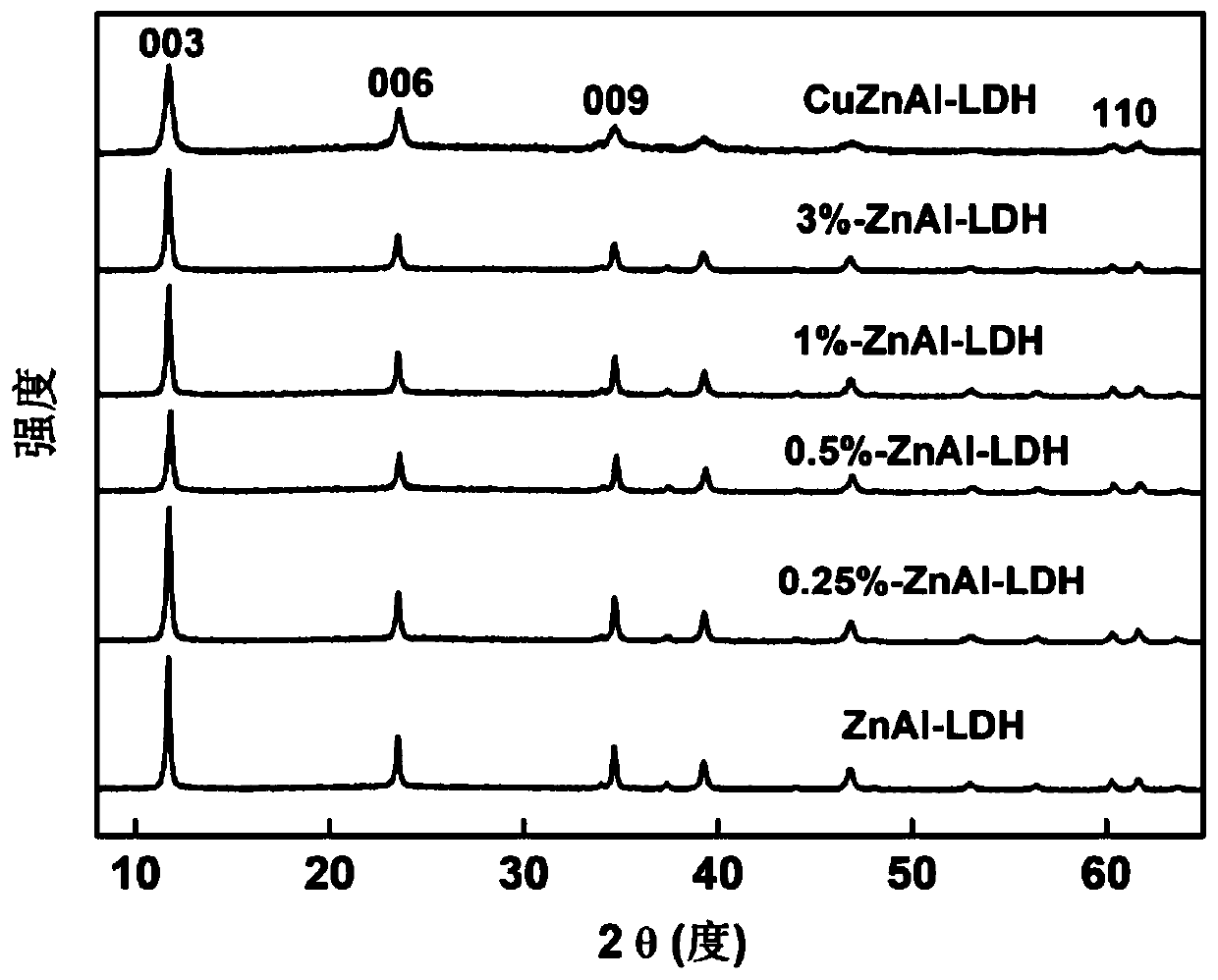
[0067] The preparation process of zinc-aluminum hydrotalcite rich in cuprous ions in Examples 2-4 is basically the same as that of Example 1, except that the amount of copper salt is changed, as shown in Table 1. The prepared hydrotalcites are respectively Named [0.25%-ZnAl-LDH, 1%-ZnAl-LDH, 3%-ZnAl-LDH], the XRD pattern of hydrotalcite is as follows figure 1 shown. The prepared zinc-aluminum hydrotalcite rich in cuprous ions is used for photocatalytic nitrogen adding water to prepare ammonia, the steps are the same as in Example 1, and the results obtained are shown in Table 1, also as Figure 4 shown.
[0068] Table 1 Photocatalytic ammonia production rate of zinc-aluminum hydrotalcites rich in different cuprous ion contents
[0069]
[0070] Combined with the ammonia production rate of the hydrotalcite prepared in Example 1, Comparative Example 1-2 and Example 2-4 for photocatalytic ammonia synthesis, it can be found that the rate of ammonia production is related to th...
Embodiment 5-9
[0072] The preparation process of the zinc-aluminum hydrotalcite rich in cuprous ions in Examples 5-9 is basically the same as in Example 1, except that the crystallization temperature is changed, as shown in Table 2. The prepared zinc-aluminum hydrotalcite rich in cuprous ions was used to photocatalyze the addition of water to nitrogen to prepare ammonia. The procedure was the same as in Example 1, and the results obtained are shown in Table 2.
[0073] Table 2 Photocatalytic ammonia production rate of cuprous ion-rich zinc-aluminum hydrotalcite prepared at different crystallization temperatures
[0074]
[0075] It can be seen from Table 2 that under full-spectrum irradiation for 1 hour, the rate of photocatalytic synthesis of ammonia is closely related to the crystallization temperature of the precursor. In a certain crystallization temperature range, the prepared copper-rich zinc-aluminum hydrotalcite can catalyze a higher rate of ammonia production. When the crystalli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com