Comprehensive utilization method for recycling industrial hazardous wastes
A technology for resource utilization and hazardous waste, applied in chemical instruments and methods, selenium/tellurium compounds, photographic technology, etc., can solve the problems of single solution of metal lead recovery technology, waste of secondary resources of copper smelting smoke, etc., and achieve easy governance. , The effect of high equipment utilization and stable product quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
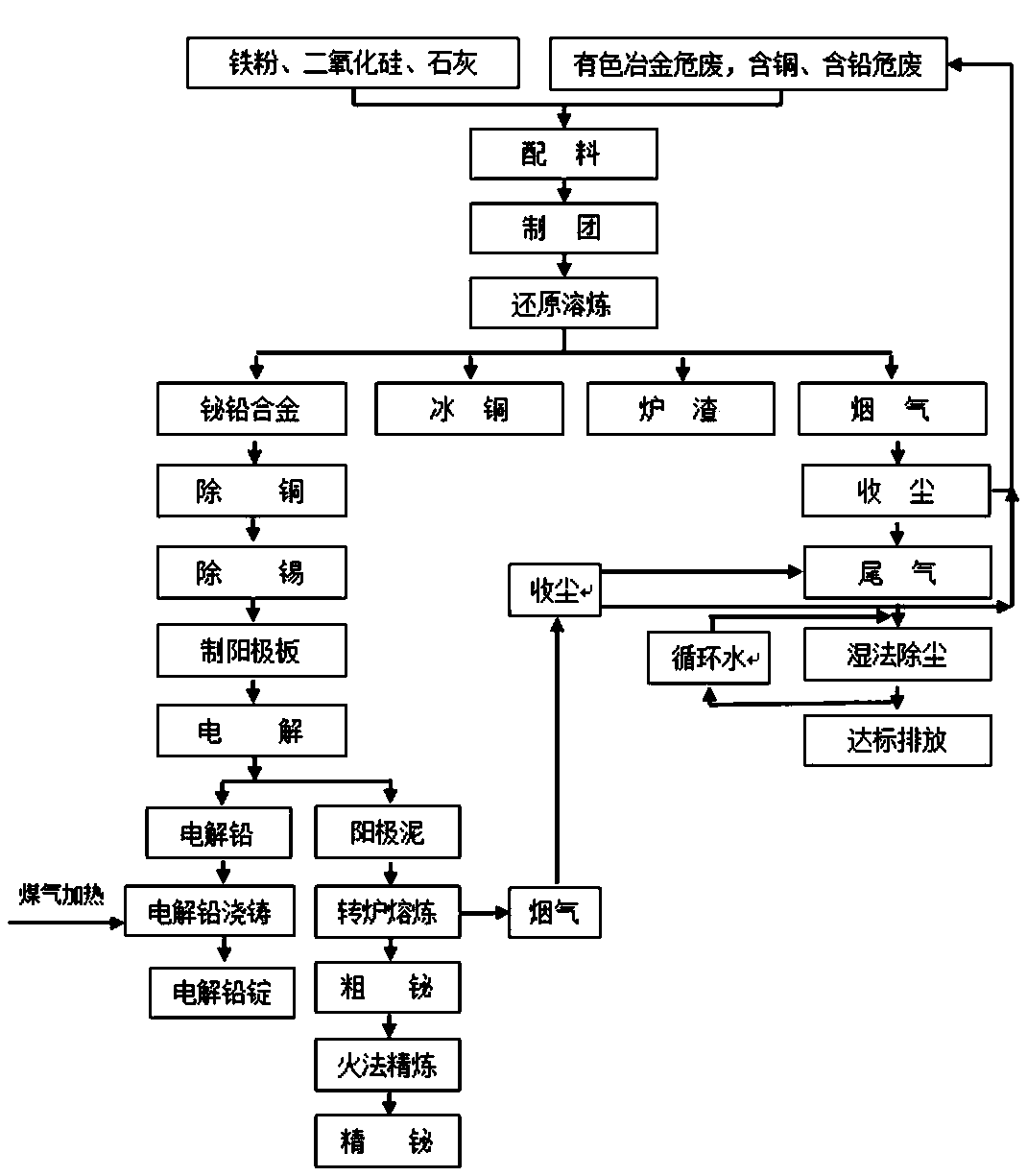
[0034] see figure 1 , a method for comprehensive utilization of industrial hazardous waste resources, comprising the following steps;
[0035] (1) Ingredients: a) According to the chemical composition of non-ferrous metallurgical hazardous waste, copper-containing hazardous waste, and lead-containing hazardous waste, use non-ferrous metallurgical hazardous waste or copper-containing hazardous waste or lead-containing hazardous waste to make charge, and the prepared charge contains Bismuth (Bi) 1-10%, tin (Sn) 0.5-5%, copper (Cu) 1-10%, lead (Pb) 8-20%; b) Add iron, silicon and Calcium material, the material ratio is: iron: silicon: calcium = 20-40: 15-25: 10-20, the silicon is silicon dioxide, and the calcium is lime.
[0036] (2) Group making: Press the prepared charge in the pellet making machine into charge balls or charge bricks with a relative density of 50-60%. The diameter of the charge balls is φ10-15cm; the size of the charge bricks is 6 ×12×24cm, the prepared furna...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is: (1) Ingredients: a) According to the chemical composition of non-ferrous metallurgical hazardous waste, copper-containing hazardous waste and lead-containing hazardous waste, non-ferrous metallurgical hazardous waste and copper-containing hazardous waste and / or Hazardous lead waste is mixed in a certain proportion to make charge, and the prepared charge contains bismuth (Bi) 1-10%, tin (Sn) 0.5-5%, copper (Cu) 1-10%, lead (Pb) 8-20% %; b) According to the chemical composition of the charge, iron, silicon and calcium materials are added in proportion, and the material ratio is: iron: silicon: calcium = 20-40: 15-25: 10-20.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com