Sputtering target material preparation process based on plasma spraying technology
A preparation process and plasma technology, which are applied in metal material coating process, sputtering coating, ion implantation coating, etc., can solve the problem that the target size is difficult to enlarge, the target particles fall off, the furnace pressure and temperature uniformity are difficult to solve. control issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
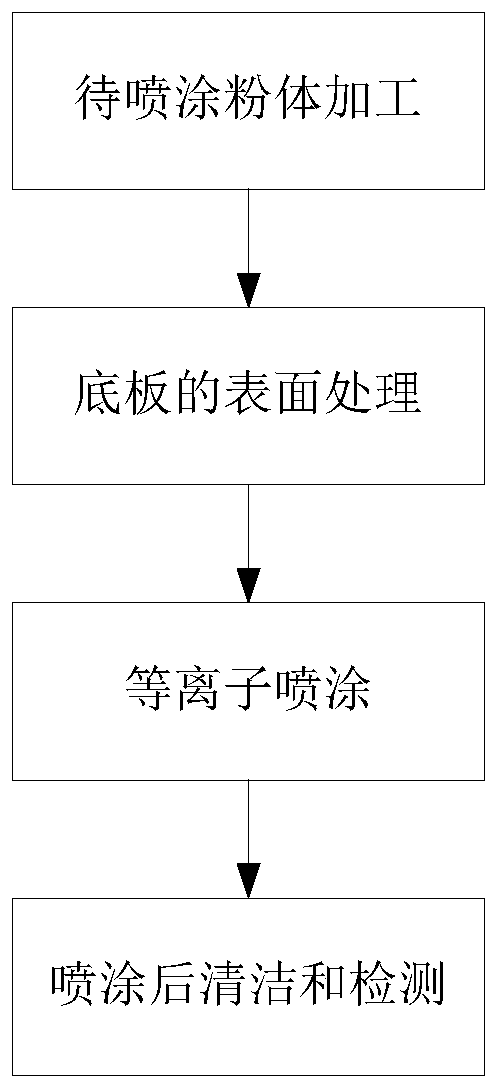
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, the sputtering target preparation process based on plasma spraying technology disclosed by the present invention includes the following steps:
[0034] Step 1, processing the powder to be sprayed to a particle size range for plasma spraying;
[0035] Step 2, the surface of the bottom plate is subjected to a surface treatment satisfying plasma spraying;
[0036] Step 3, using a plasma spraying machine to spray the powder to be sprayed prepared in step 1 on the surface of the bottom plate after surface treatment in step 2;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com