Method for preparing hollow microneedles by ultraviolet curing process with soluble fiber as core material
A soluble, hollow microtechnology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of limiting the use range of hollow microneedle arrays, cumbersome operation steps, complex preparation processes, etc., and achieve the effects of shortening the preparation cycle, lowering the preparation environment requirements, and reducing the difficulty of forming.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] This embodiment provides a method for preparing hollow microneedles with a photoresist of c-coating type and using soluble PVA fiber as a core material by an ultraviolet curing process. The main component of this type of photoresist is polyurethane acrylate. The preparation method includes the following steps: step:
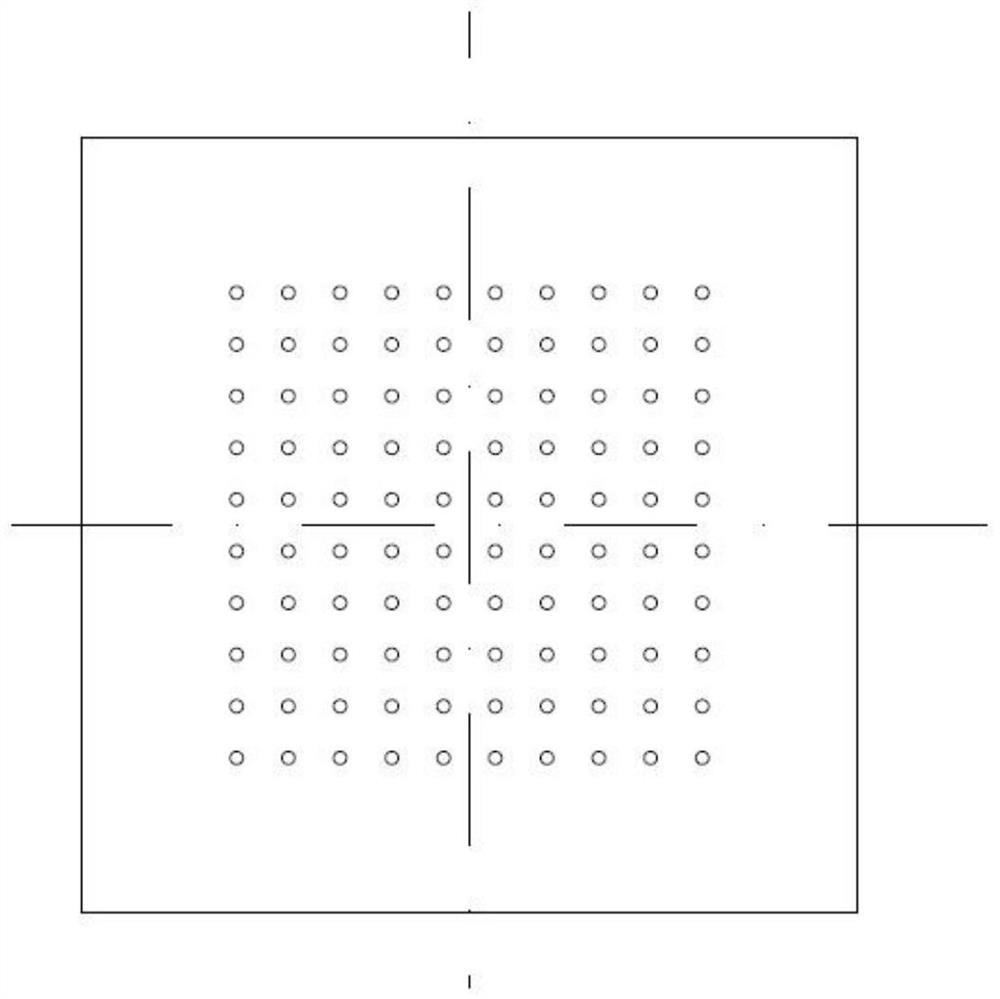
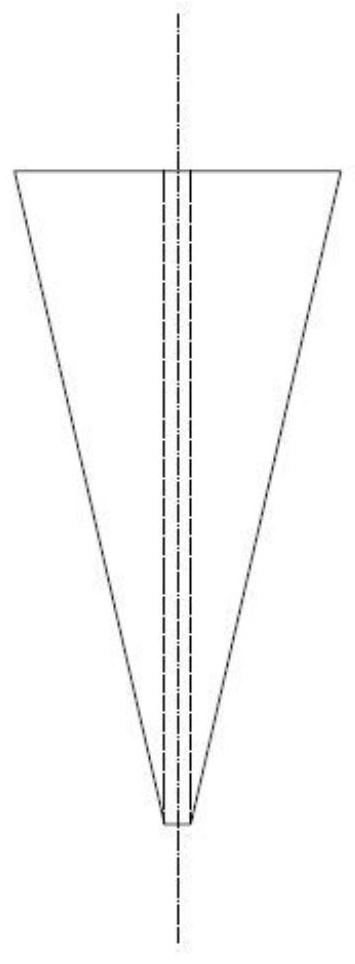
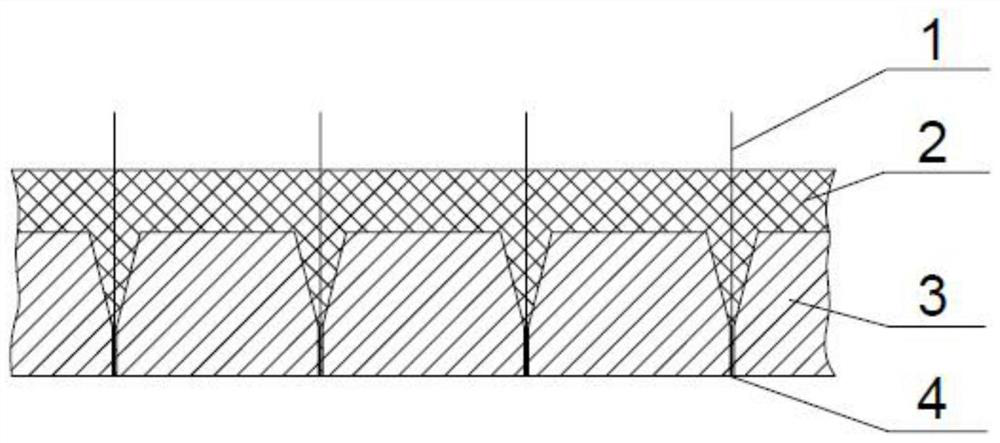
[0029] The micro-needle mold is processed on the PDMS material by using micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS). The 3 cavities of the PDMS micro-needle mold are cone arrays. The mold structure is as attached figure 1 shown. The microneedle array is arranged in 10×10, the spacing between each microneedle in the microneedle array is 1mm, and the size structure of each conical microneedle cavity of the fixed microneedle is: 500×250 μm (height × bottom diameter). In addition, a fiber fixing hole 4 is corresponding to the top of each microneedle cavity, and the fiber fixing hole 4 is a cylindrical through hole with a size of 200×20 μm.
[0030] The soluble ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] This embodiment provides a method for preparing hollow microneedles with a photoresist of GP756 type and using a soluble PVA fiber as a core material by an ultraviolet curing process. The main component of this type of photoresist is polymethyl methacrylate. The preparation method includes The following steps:
[0036] The micro-needle mold is processed on the PDMS material by using micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS). The 3 cavities of the PDMS micro-needle mold are cone arrays. The mold structure is as attached figure 1 shown. The microneedle array is arranged in 10×10, the distance between each microneedle in the microneedle array is 1 mm, and the size structure of each conical microneedle cavity is: 500×250 μm (height×bottom diameter) . In addition, a fiber fixing hole 4 is corresponding to the top of each microneedle cavity, and the fiber fixing hole 4 is a cylindrical through hole with a size of 200x20 μm.
[0037] The soluble PVA fiber 1 is prepared by an ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] This embodiment provides a method for preparing hollow microneedles with a JZ-303 type photoresist using soluble PVA fiber as a core material by an ultraviolet curing process. The main component of this type of photoresist is polymethyl methacrylate. The method includes the following steps:
[0043] The micro-needle mold is processed on the PDMS material by using micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS). The 3 cavities of the PDMS micro-needle mold are cone arrays. The mold structure is as attached figure 1shown. The microneedle array is arranged in 10×10, the distance between each microneedle in the microneedle array is 1 mm, and the size structure of each conical microneedle cavity is: 500×250 μm (height×bottom diameter) . In addition, a fiber fixing hole 4 is corresponding to the top of each microneedle cavity, and the fiber fixing hole 4 is a cylindrical through hole with a size of 200x20 μm.
[0044] The soluble PVA fiber 1 is prepared by an electrospinning proce...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com