Non-calcium ion dependent alpha- amylase with extreme halophilic and surfactant resistance and gene and application thereof
A surfactant and amylase technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of limited research on halophilic α-amylase, and achieve high enzyme activity and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: α-amylase gene amySL3 clone
[0033] Haloalkaliphiles Alkalibacterium Genomic DNA extraction of sp. SL3: A α-amylase-producing microorganism was isolated from the sediment of Gan'an Dabusu Saline-Alkali Lake in Jilin Province using the screening medium with starch as the only carbon source, and it was identified as halophilic by 16S Alkaliphiles, named Alkalibacterium sp. SL3. The bacterial genome extraction kit (DP302) from Tiangen Company was used to extract the genomic DNA of the halophilic and alkalophilic bacteria, and the specific operation was carried out in accordance with the instructions of the kit.
[0034] according to Alkalibacterium According to the sequence comparison results of α-amylase protein from genus origin, two conserved region sequences were found and degenerate primers were designed and synthesized amy -F and amy -R (Table 1):
[0035] PCR amplification was carried out using the total genomic DNA of the above-mentioned halop...
Embodiment 2
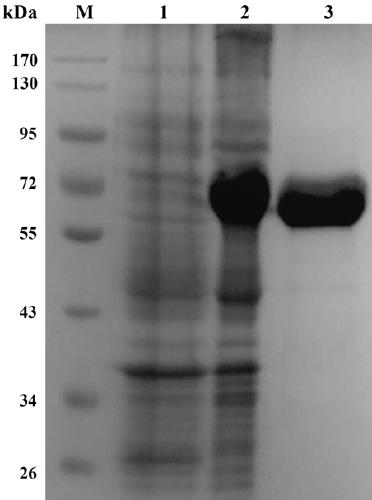
[0044] Example 2 Preparation of recombinant α-amylase.
[0045] Introduced at the 5' and 3' ends of the gene, respectively Sac I and xho I restriction site AmySL3-m- F and AmySL3-m- R is a pair of primers (see Table 1), and the genomic DNA of halophilic and alkalophilic bacteria is used as a template for PCR amplification. The parameters of the PCR reaction were: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 50°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 1.5 min, 30 cycles, and incubation at 72°C for 5 min. The expression vector pET28a (+) was double digested ( Sac I+ xho I), while the gene encoding α-amylase amySL3 double digestion ( Sac I+ xho I), the excised gene fragment encoding α-amylase is connected with the expression vector pET28a (+), and the gene containing α-amylase is obtained amySL3 recombinant plasmid pET28a-amySL3 And transform Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli strain BL21 / amyS...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 Determination of the properties of recombinant α-amylase AmySL3
[0048] 1. Activity analysis of recombinant amylase
[0049] The activity of recombinant α-amylase was determined by 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) method: the specific method was as follows: at pH 7.5, 45°C, 1 mL of reaction system included 100 μL of appropriate diluted enzyme solution , 900 μL substrate (1 wt% soluble starch), 4M NaCl, reacted for 10 min, added 1.5 mL DNS to terminate the reaction, boiled water for 5 min. After cooling, the OD value was measured at 540 nm. One enzyme activity unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme required to release 1 μmol of reducing sugar per minute under given conditions.
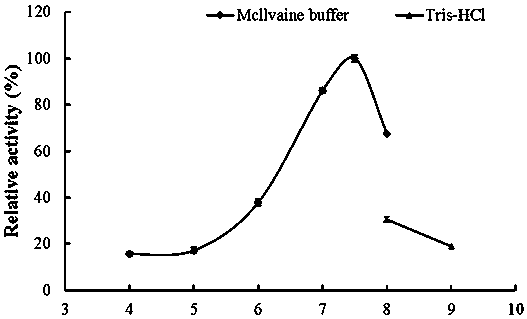
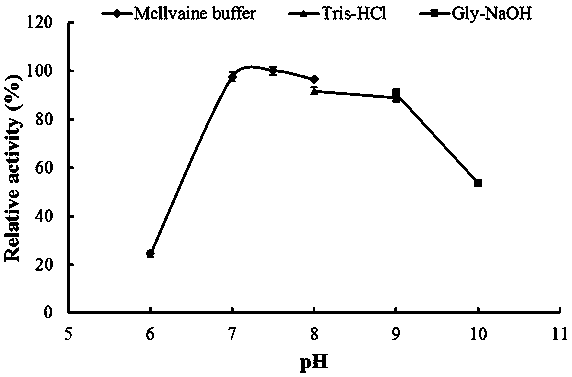
[0050] 2. Determination of optimum pH and pH stability of recombinant α-amylase AmySL3
[0051] Optimum pH determination: The purified recombinant α-amylase AmySL3 was subjected to an enzymatic reaction at 37°C in a 0.1M pH4.0–9.0 buffer. Determination of the pH stability of th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com