Organic-inorganic composite solid electrolyte material and preparation method and application thereof
A solid electrolyte, inorganic electrolyte technology, applied in electrolytes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient manufacturing process and overall structure design, influence of battery electrochemical performance, lack of solid electrolyte, etc., and achieve good room temperature ionic conductivity. , the effect of improving safety and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
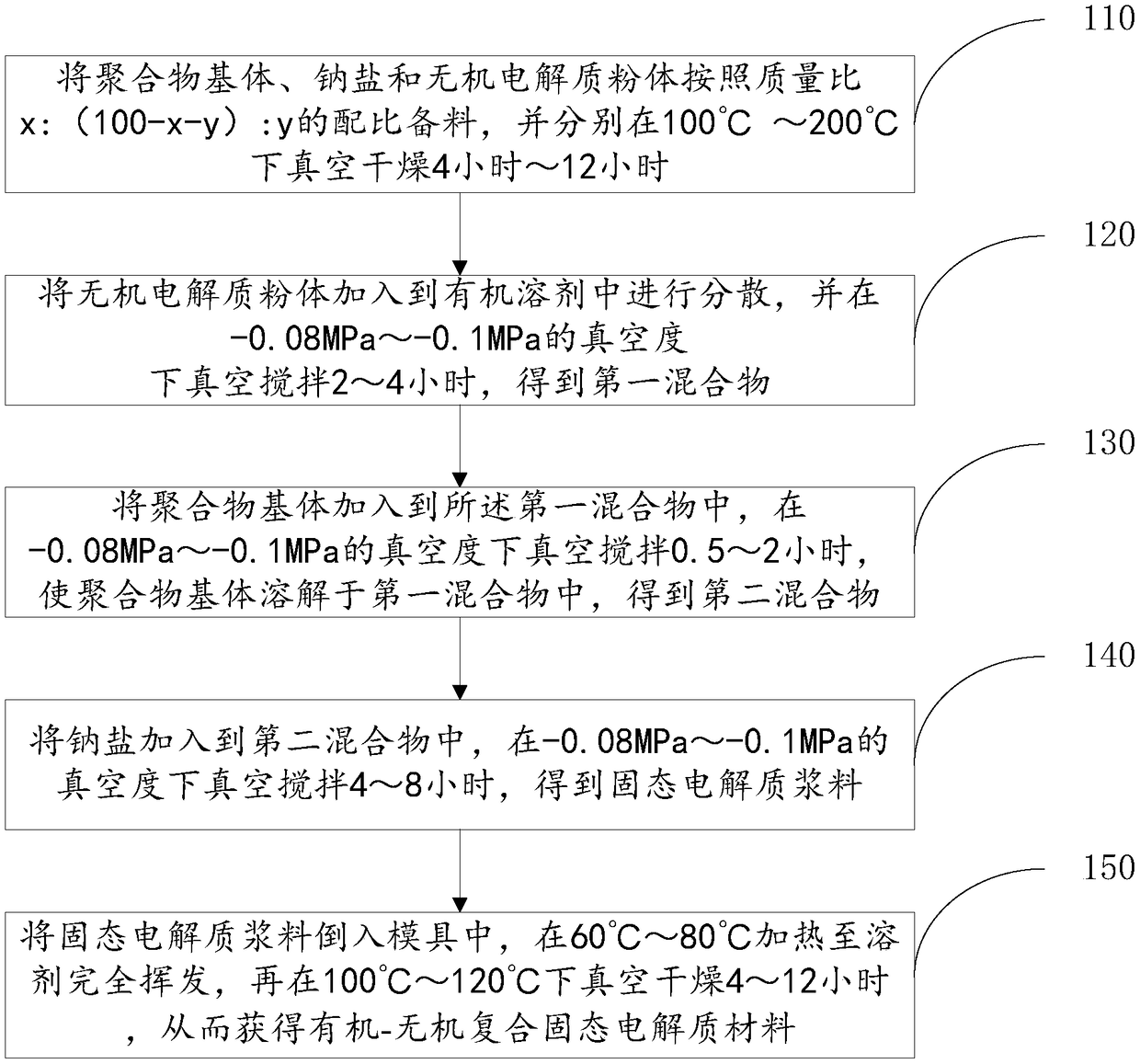
[0026] The preparation method of the organic-inorganic composite solid electrolyte material provided by the embodiment of the present invention, its main process is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0027] Step 110, preparing the polymer matrix, sodium salt and inorganic electrolyte powder according to the mass ratio x:(100-x-y):y, and vacuum drying at 100°C-200°C for 4 hours-12 hours;
[0028] Among them, x≥60, y≥5, and x+y<100;
[0029] The polymer matrix includes one or more combinations of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP) and polypropylene carbonate (PPC), among which PVDF The molecular weight of PVDF-HFP is 50,000-120,000; the molecular weight of PPC is 50,000-100,000.
[0030] The sodium salt is sodium perchlorate (NaClO 4 ) and / or sodium bistrifluoromethanesulfonylimide (NaTFSI).
[0031] The inorganic electrolyte powder has a NASICON structure, and the compound formula is:
[0032...
Embodiment 1
[0042]The inorganic electrolyte with a particle diameter of 5 μm was dispersed and stirred in NMP for 2 hours. Subsequently, PVDF and NaTFSI were added to the mixture and stirred evenly to form a uniform slurry. The solid content of the slurry is 15%, PVDF accounts for 10% of the total mass, NaTFSI accounts for 4% of the total mass, and the mass of the inorganic electrolyte accounts for 1%. The prepared slurry was coated on a grinding tool, heated and dried, and then vacuum-dried for 12 hours after the solvent evaporated completely to obtain a solid electrolyte material.
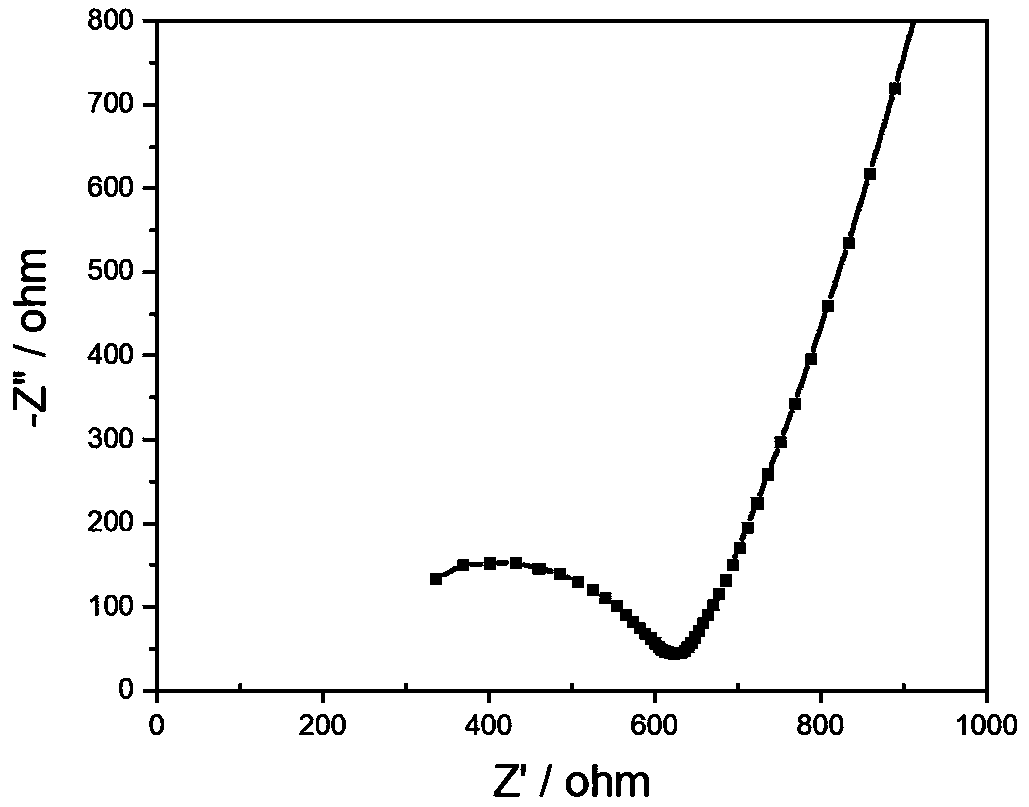
[0043] The real object of the solid electrolyte material prepared in Example 1 is as follows: figure 2 shown. image 3 It is the AC impedance spectrum measured at room temperature 25°C for the solid electrolyte material of the embodiment of the present invention, and the calculated conductivity is 2×10 -4 S / cm.
Embodiment 2
[0045] The inorganic electrolyte with a particle diameter of 200 nm was dispersed and stirred in NMP for 2 hours. Subsequently, PVDF, PVDF-HFP and NaTFSI were added into the mixture and stirred evenly to form a uniform slurry. The solid content of the slurry is 12%, the polymer matrix accounts for 8% of the total mass, wherein the mass ratio of PVDF to PVDF-HFP is 5:5, NaTFSI accounts for 3% of the total mass, and the mass of inorganic electrolyte accounts for 2%. The prepared slurry was coated on a grinding tool, heated and dried, and then vacuum-dried for 12 hours after the solvent evaporated completely to obtain a solid electrolyte material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com