Solid-state electrolyte, preparation method thereof, and solid-state battery containing the solid-state electrolyte
A technology of solid electrolyte and electrolyte powder, which is applied in the direction of non-aqueous electrolyte battery, electrolyte battery manufacturing, solid electrolyte, etc. It can solve problems such as high addition of nano-inorganic powder, poor mechanical properties of solid electrolyte, and difficult breakthrough in room temperature conductivity. Achieve the effects of reducing the risk of fire and explosion, good room temperature ionic conductivity, and improving safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
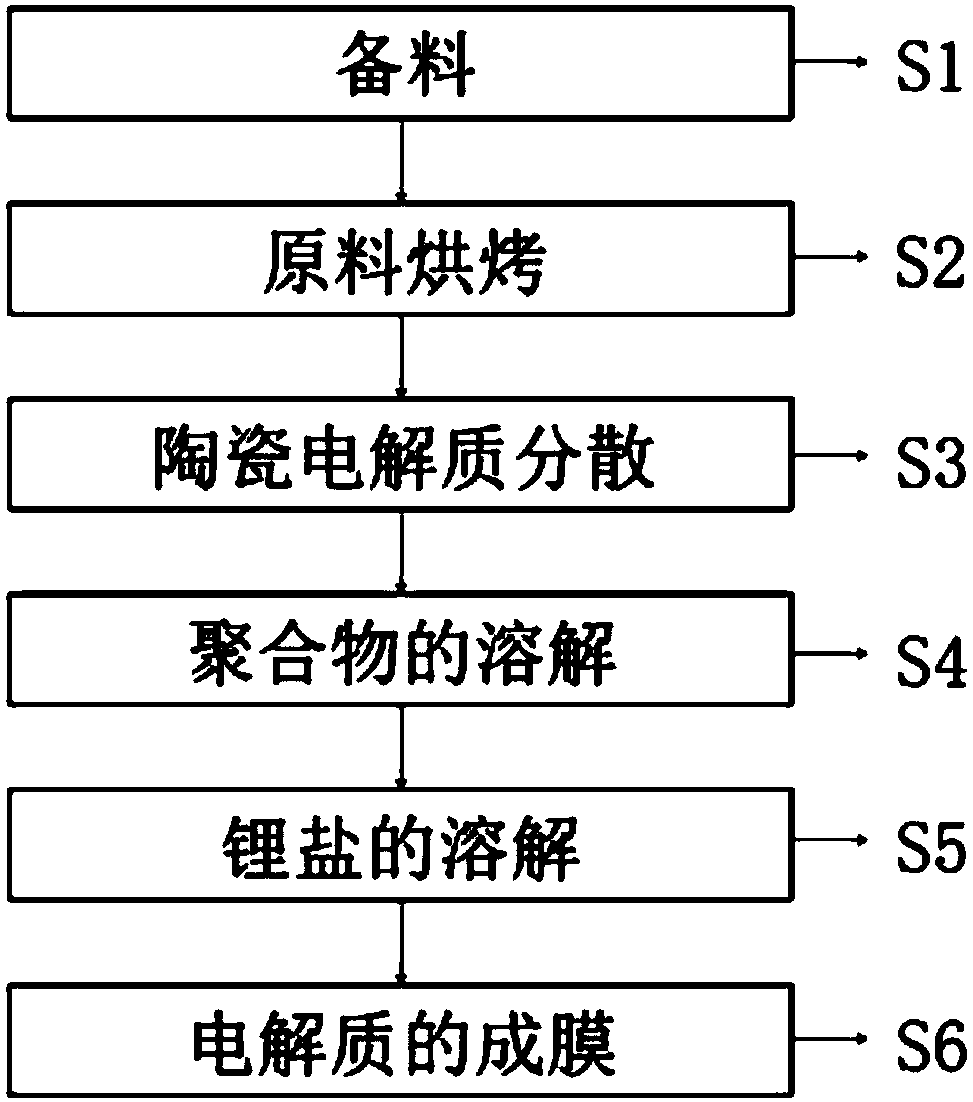
[0038] Another object of the present invention, such as figure 1 Shown, the preparation method of solid-state electrolyte, this method is based on above-mentioned any one described solid-state electrolyte, comprises the following steps:
[0039] S1, material preparation: prepare the required materials according to the following mass ratio: the mass ratio of polymer matrix, lithium salt and inorganic ceramic electrolyte powder x:(100-x-y):y (wherein x≥60, y≥5);
[0040] S2. Drying of raw materials: vacuum-dry the polymer matrix, lithium salt, and inorganic ceramic electrolyte powder at high temperature. The drying time and temperature are not particularly limited, and those skilled in the art can choose according to actual needs; The material matrix, lithium salt, and inorganic ceramic electrolyte powder are vacuum-dried at 100°C to 200°C for 4h to 12h;
[0041] S3. Dispersion of inorganic ceramic electrolyte powder: uniformly disperse the inorganic ceramic electrolyte powder in...
Embodiment 1
[0048] Embodiment 1, making solid electrolyte
[0049] The inorganic ceramic electrolyte was dispersed in NMP (N-methylpyrrolidone). Subsequently, PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride), PVDF-HFP (poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)) and LiTFSI (lithium bistrifluoromethanesulfonimide) were added to the mixture to form a uniform slurry. The solids content of the slurry was 15%. Based on the weight of the solid electrolyte, the polymer matrix accounted for 65%, of which the weight ratio of PVDF to PVDF-HFP was 5:5, LiTFSI accounted for 25%, and the inorganic ceramic electrolyte accounted for 10wt%. The prepared slurry is coated on the foil by a coating machine, and the solid electrolyte is obtained by vacuum drying after the solvent is completely evaporated.
[0050] The physical figure of the solid electrolyte prepared in embodiment 1 is as follows figure 2 As shown, the solid electrolyte has good mechanical properties and can be wound.
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2, making solid electrolyte
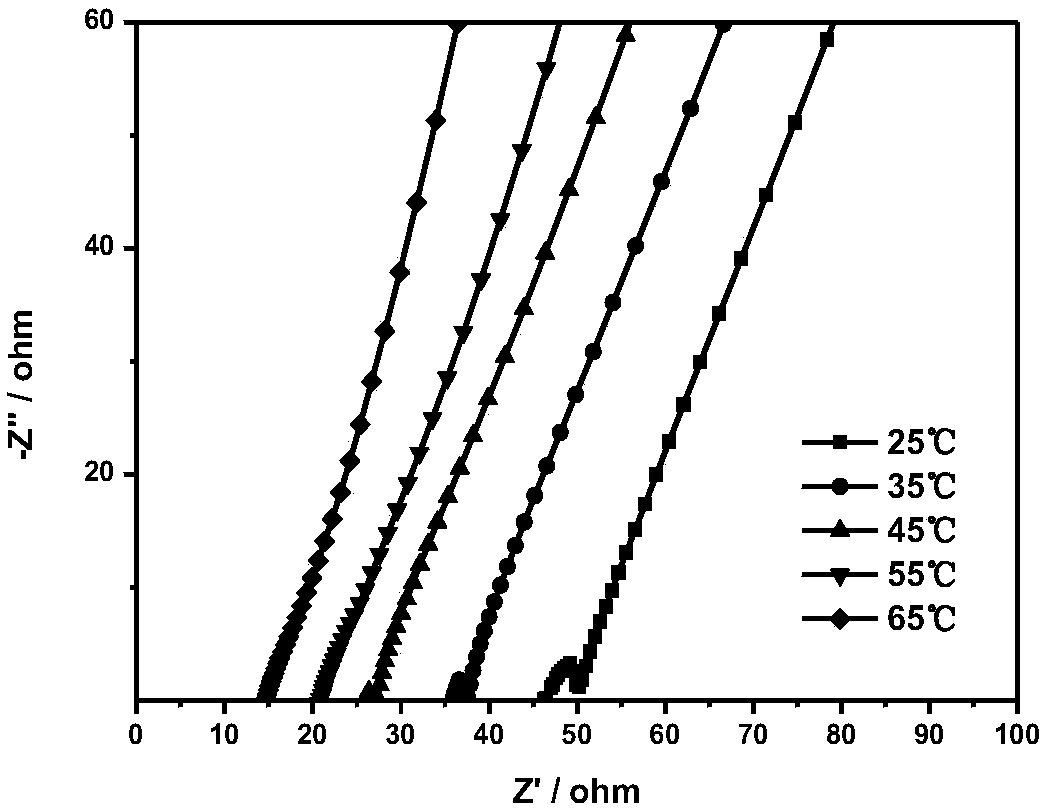
[0052] Disperse the inorganic ceramic electrolyte in NMP. Subsequently, PVDF, PVDF-HFP and LiTFSI were added into the mixture and stirred evenly to form a uniform slurry. The solids content of the slurry was 12%. Based on the weight of the solid electrolyte, the polymer matrix accounts for 85%, of which the weight ratio of PVDF to PVDF-HFP is 5:5, LiTFSI accounts for 10wt%, and the inorganic ceramic electrolyte accounts for 5%. The prepared slurry is coated on the foil by a coating machine, and after the solvent is completely volatilized, it is vacuum-dried to obtain a solid electrolyte, such as image 3 Shown is the AC impedance spectrum of the solid electrolyte.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com