Method for efficiently separating and instantaneously converting protoplast of artemisia annua L.
A protoplast and instantaneous transformation technology, applied in the field of plant biology, can solve problems affecting the progress of scientific research of Artemisia annua, improve the efficiency of scientific research and shorten the experimental period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
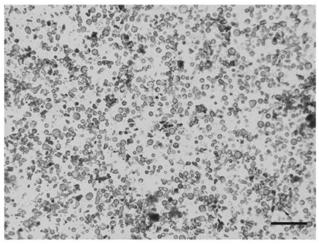
[0070] This embodiment relates to a method for isolating protoplasts of Artemisia annua, comprising the following steps:
[0071] Preparation of protoplasts:
[0072] (1) Select young Artemisia annua seedlings that have grown vigorously for 2-3 weeks. At this time, each seedling has 4-6 leaves. Use tape to tear off the lower epidermis of the leaves and put them into the enzymatic hydrolysis solution, and put about 30-40 leaves. . Vacuumize in the dark for 30-40min, and put it in a horizontal shaker for 4-6h in the dark for enzymatic hydrolysis. The enzymolysis solution is: 1.65% cellulase R10, 0.44% resolase R10, 0.4mol / L mannitol, 0.02mol / L potassium chloride, 0.02mol / L MES with pH 5.7, placed in a water bath at 55°C for 10min (to inactivate the protease and increase the solubility of the enzyme solution), after cooling down to room temperature, add 0.01mol / L calcium chloride, 0.1% BSA, set the volume to 20mL, stir well and filter it into a petri dish with a 0.45μm filter ...
Embodiment 2
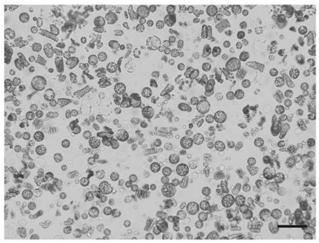
[0082] This embodiment relates to a method for transient transformation of Artemisia annua protoplasts mediated by PEG, comprising the following steps:
[0083] (1) Preparation of the expression vector plasmid: the vector used is pCambia1300-GFP, which was purchased from CAMBIA Company in Australia. The Tiangen Endotoxin-Free Plasmid Extraction Kit was used for plasmid extraction, and the extracted plasmid concentration was adjusted to about 1 μg / μL for later use;
[0084] (2) Add 10 μL of plasmid DNA (1 μg / μL) to 200 μL of protoplast-MMG suspension, flick the bottom of the tube to mix;
[0085] (3) Add 220 μL of 40% PEG4000 solution, flick the bottom of the tube to mix, and place in the dark at 23°C for 20-25 minutes;
[0086] (4) Add 880 μL of W5 solution to stop the transformation, flick the bottom of the tube to mix;
[0087] (5) Centrifuge at 1000rpm for 3min, discard the supernatant, add 1ml of W5 solution to resuspend the protoplasts, and culture at 23°C for 12-16h und...
Embodiment 3
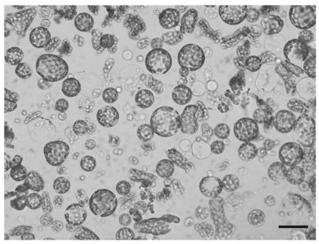
[0091] This example relates to the transient expression of reporter genes LUC and REN in protoplasts of Artemisia annua.
[0092] Isolation of protoplasts:
[0093] Same as the method for protoplast isolation in Example 2.
[0094] Transient transformation method of Artemisia annua protoplasts mediated by PEG:
[0095] Expression vector plasmid preparation: the vector used is pGreenII 0800-ALDH1 pro -LUC, pGreenII 0800 vector obtained from Promega, ALDH1 pro It is the promoter of the key enzyme gene ALDH1 in the last step in the synthesis of artemisinin. Its NCBI accession number is proALDH1 (KC118525.1). The plasmid is extracted with the Tiangen Endotoxin-free Plasmid Extraction Kit, and the concentration of the extracted plasmid is adjusted to It is about 1 μg / μL for use.
[0096] (1) Add 6 μL of pGreenII 0800-ALDH1 pro - Add LUC plasmid (1 μg / μL) to 200 μL protoplast-MMG suspension, flick the bottom of the tube to mix;
[0097] (2) Add 220 μL of 40% PEG4000, flick the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com