Method for preparing high light oil selectivity hydrocracking catalyst
A hydrocracking and catalyst technology, applied in the direction of physical/chemical process catalysts, molecular sieve catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low octane number of naphtha, reduce selectivity, maintain stability, reduce Effects of deep cracking reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: Preparation of Y molecular sieve Z1
[0033] Prepare 2000mL of 3wt% dilute nitric acid solution, add 500g of Y molecular sieve Z0 to it, stir vigorously at 50°C for 4h, settle for 2-3h, pour out most of the upper liquid, centrifuge the remaining solid and a small amount of liquid, and centrifuge the solid Add 250mL deionized water, stir and wash, and centrifuge. Repeat centrifugation and washing for 3 times, and finally the molecular sieve solid obtained by centrifugation is first dried at 150°C for 8 hours, and then calcined at 500°C for 4 hours in an air atmosphere to obtain acid-treated molecular sieve Z1.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: Preparation of Y molecular sieve Z2
[0035] Prepare 1000mL, 1mol / L ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) ethanol solution, add 200g Y molecular sieve Z0 to it, stir vigorously at room temperature for 4 hours, settle for 2-3 hours, pour out most of the upper liquid, and carry out the remaining solid and a small amount of liquid After centrifugation, the centrifuged solid was added to 200 mL of ethanol, stirred, washed, and centrifuged. Repeat centrifugation and washing for 3 times, and finally the molecular sieve solid obtained by centrifugation is dried in a vacuum oven at 80°C for 6h, and then calcined at 500°C for 4h in an air atmosphere to obtain the treated molecular sieve Z2.
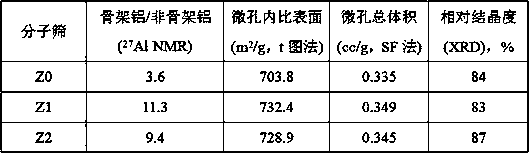
[0036] The properties of commercial Y molecular sieve Z0 and Y molecular sieves Z1 and Z2 prepared in Examples 1 and 2 are compared in Table 1.
[0037] Table 1 Performance comparison of different molecular sieves
[0038]
[0039] Depend on 27According to the character...
Embodiment 3
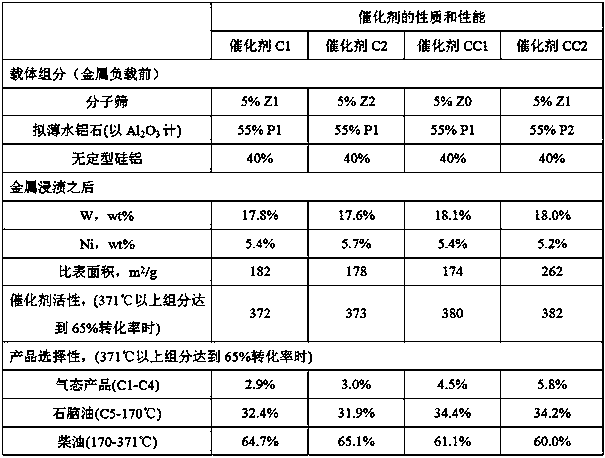
[0040] Example 3: Preparation of hydrocracking catalyst C1 (Z1+P1 (acid gel index 90%))
[0041] Weigh 110 g of pseudo-boehmite P1 (dry basis, unless otherwise specified, all weights of the following raw materials are dry basis), 80 g of imported amorphous silica-alumina, and 10 g of molecular sieve Z1, and fully mix the three solid powders Finally, add the pre-prepared dilute nitric acid solution (3.3g, 67wt% concentrated nitric acid diluted with 200 g deionized water), knead vigorously for 15 minutes, extrude through a 2.5mm orifice plate, and dry at 120°C for 6h. Calcined in air at 500°C for 4h to obtain the catalyst carrier. Then impregnate the carrier with a mixed aqueous solution of ammonium metatungstate and nickel nitrate in equal volume to load 18% W and 5.4% Ni (theoretical weight), and then dry it at 120°C for 4 hours, then dry it at 500°C in an air atmosphere Calcined for 4h, the resulting catalyst was marked as C1.
[0042] Implementation 4: Preparation of hydro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com