Specific targeted breast cancer cell mesoporous silicon nanometer drug loading system and preparation method thereof
A breast cancer cell and nano-drug loading technology, which is applied in the research and development and preparation of cancer cell-targeted drugs, can solve problems such as limiting the effect of clinical treatment, and achieve the effects of efficient chemotherapy drug delivery, good stability, and accelerated drug release
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: Preparation and characterization of specific targeted drug-loaded MSN system
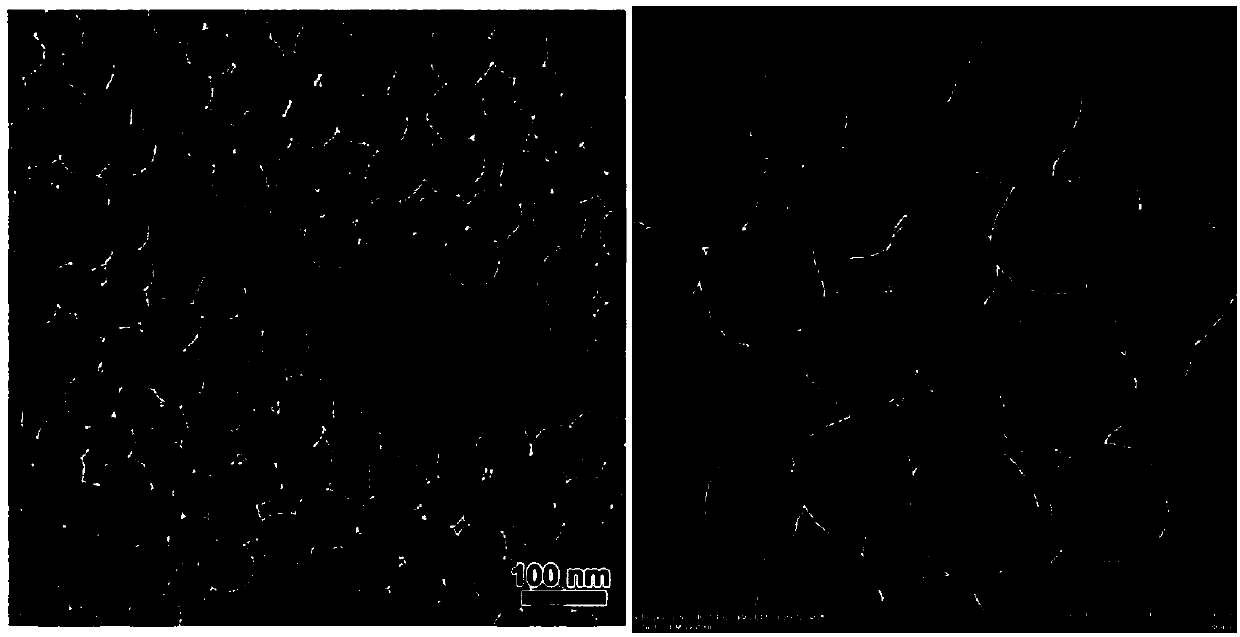
[0026] Weigh 0.3198g CTAB + 2.815ml EtOAc + 545.0ml H2O + 9.695ml NH4OH, stir to fully dissolve CTAB, add (0.72mlTEOS + 0.88ml APTES) mixture (mixed by pipetting more than 20 times), and react at 22°C for 24h; Centrifuge at 13000rpm for 30min, wash with ultrasonic ethanol twice, and react the obtained sample + (240ml ethanol + 480ul concentrated HCL) at 60°C for 3h. Using the method of chemical synthesis, different experimental conditions were changed to synthesize mesoporous silica nanoparticles with different sizes and particle diameters. The nanoparticles were examined by scanning electron microscopy. The results of electron microscopy showed that the mesoporous silica particles were uniform and the pore size was the same. Evenly distributed (such as figure 1 shown).
[0027] According to the principle that the surface of mesoporous silica is rich in amino groups, YSA and D4 s...
Embodiment 2
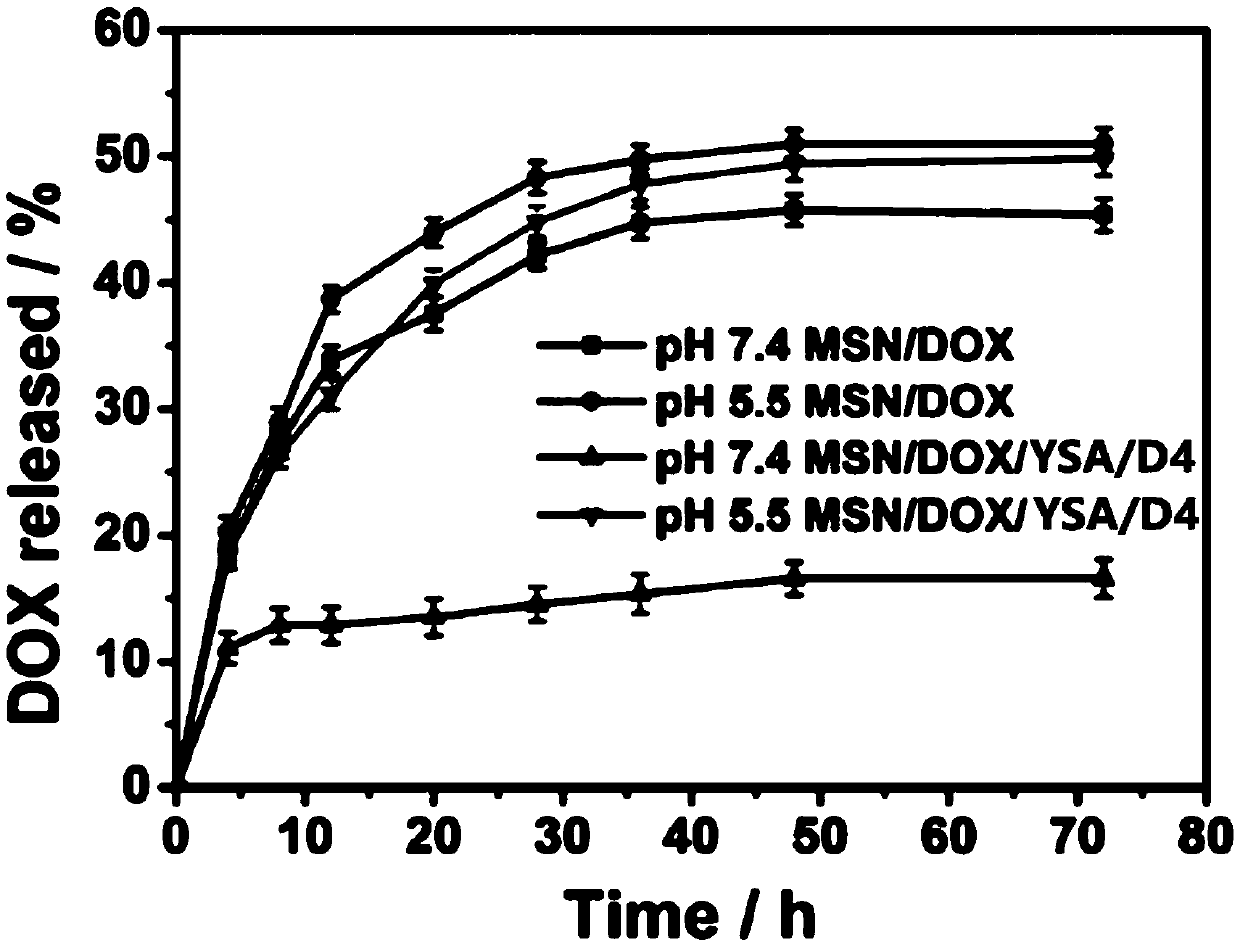
[0029] Example 2: In vitro slow-release experiment of specifically targeting highly expressed EGFR drug-loaded MSN system
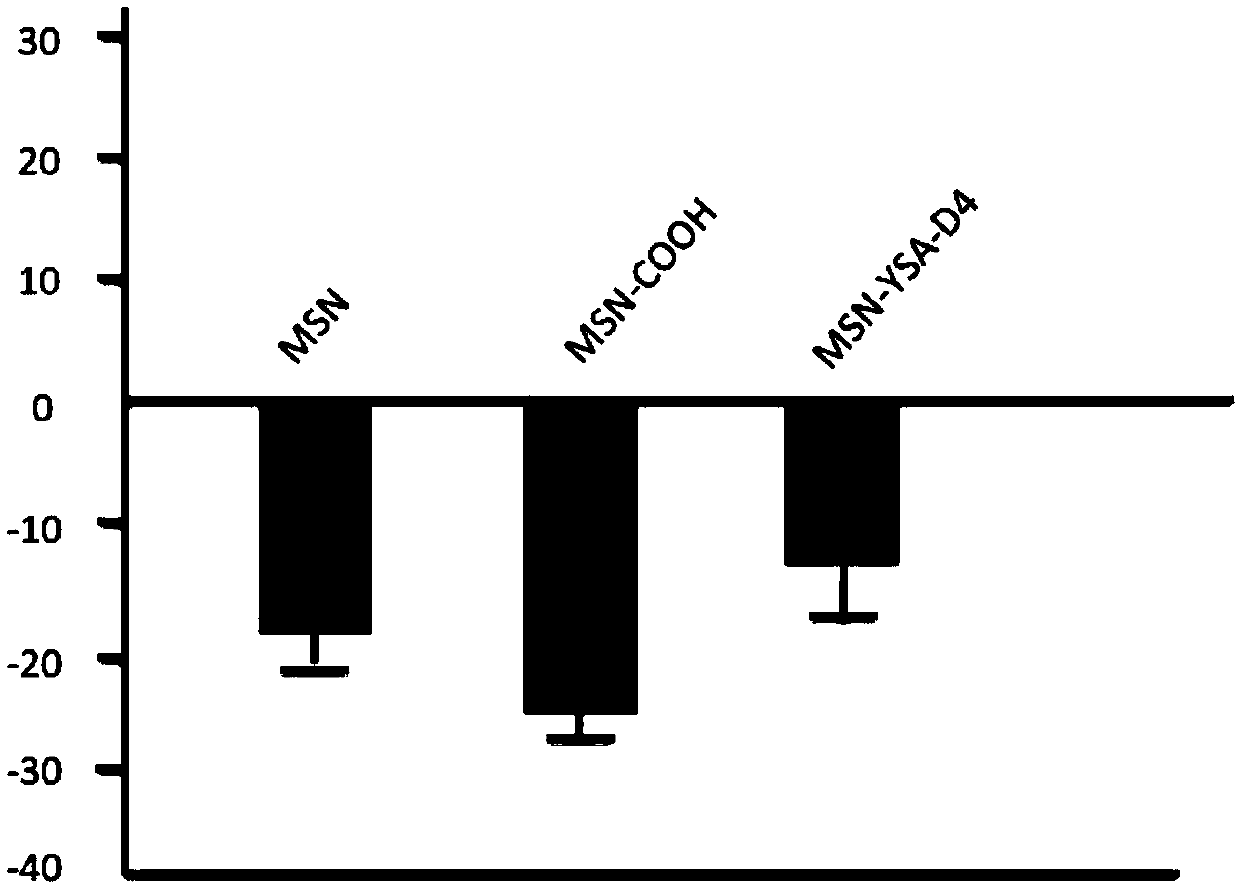
[0030] To confirm the loading efficiency of doxorubicin by the same weight of mesoporous silica (MSN) nanomaterials under different pH conditions. The specific operation is briefly described as follows: Dissolve 2 mg of mesoporous silica material and 0.5 mg of doxorubicin in 1 mL of phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with different pH values, shake and mix overnight at room temperature, and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 30 minutes , and the supernatant was taken to measure the loading efficiency of the same concentration of doxorubicin in the mesoporous silica in solutions with different pH values by spectrophotometer. In a neutral alkaline (pH7.4) environment similar to normal human body fluids, the drug loading capacity of mesoporous silica is the largest, and the drug content in the centrifuged supernatant is the lowest. When the solution is acidic (pH5...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: The in vitro uptake experiment of breast cancer cell MCF7 to the specific targeting drug-loaded MSN system
[0032] Doxorubincin (DOX), also known as doxorubicin, is the most commonly used tumor chemotherapy drug. This chemotherapy drug can be used for acute leukemia, malignant lymphoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, bone and soft tissue sarcoma, nephritis Cell tumor, bladder cancer, thyroid cancer, prostate cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, testicular cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, etc. The chemotherapeutic drug has good water solubility, and the most important thing is that the drug emits red fluorescence under ultraviolet irradiation, and the fluorescence intensity can be observed with a fluorescence microscope to judge the nanoparticles entering the cells.
[0033]When breast cancer MCF7 cells were subcultured for 24 hours and the fusion rate between cells reached about 80%, we added mesoporous silica nanomaterials loaded...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com