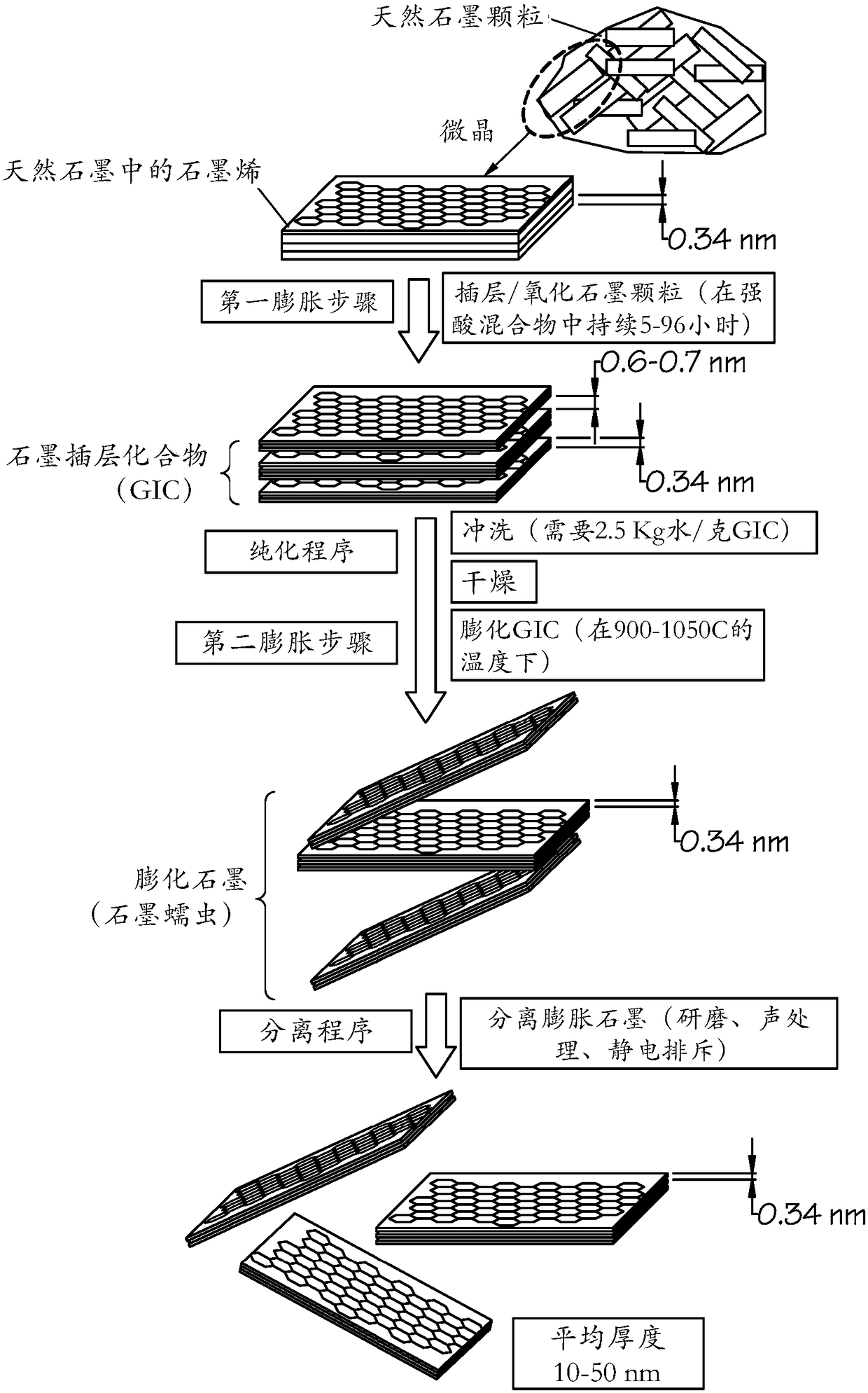
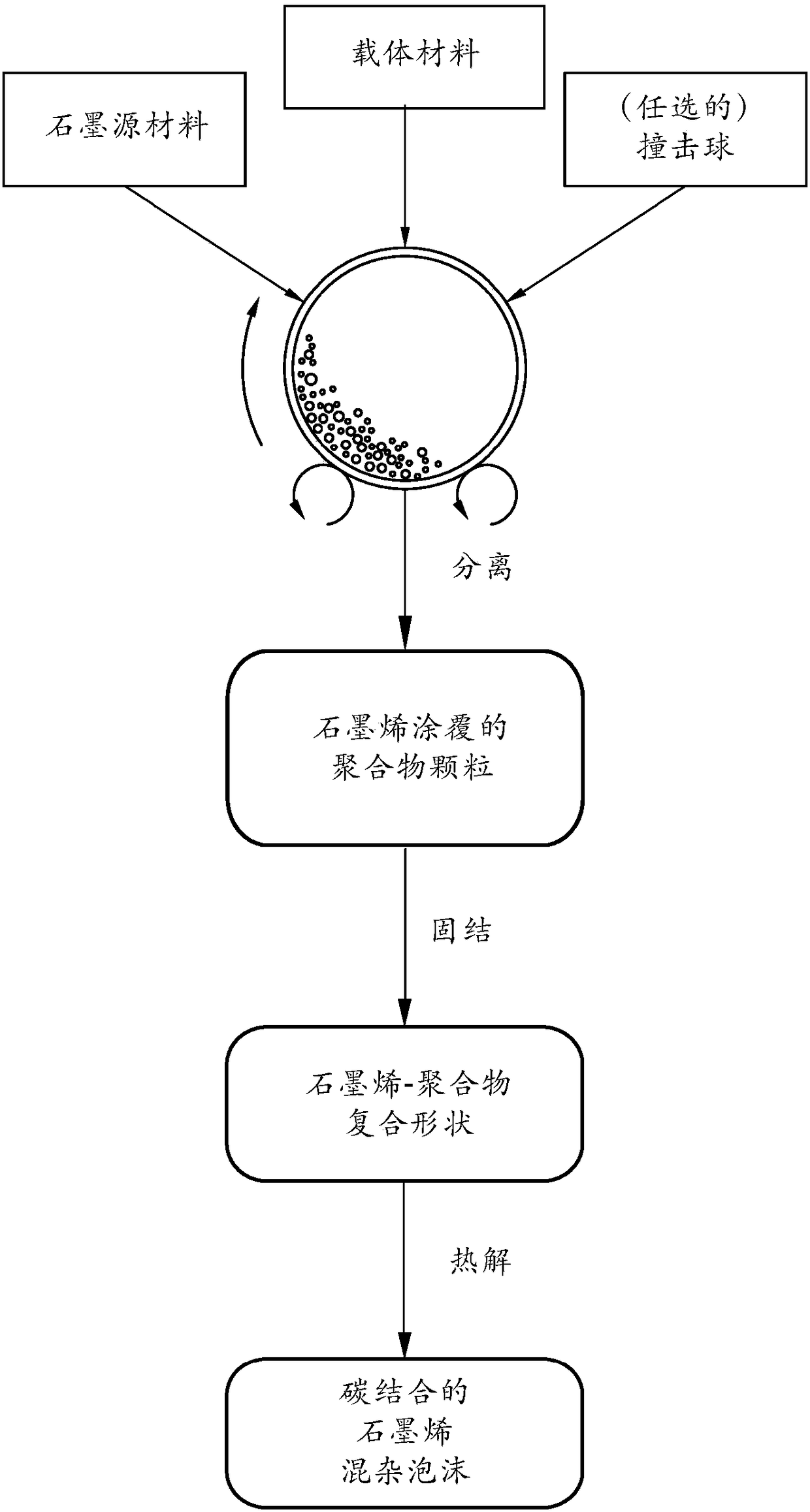
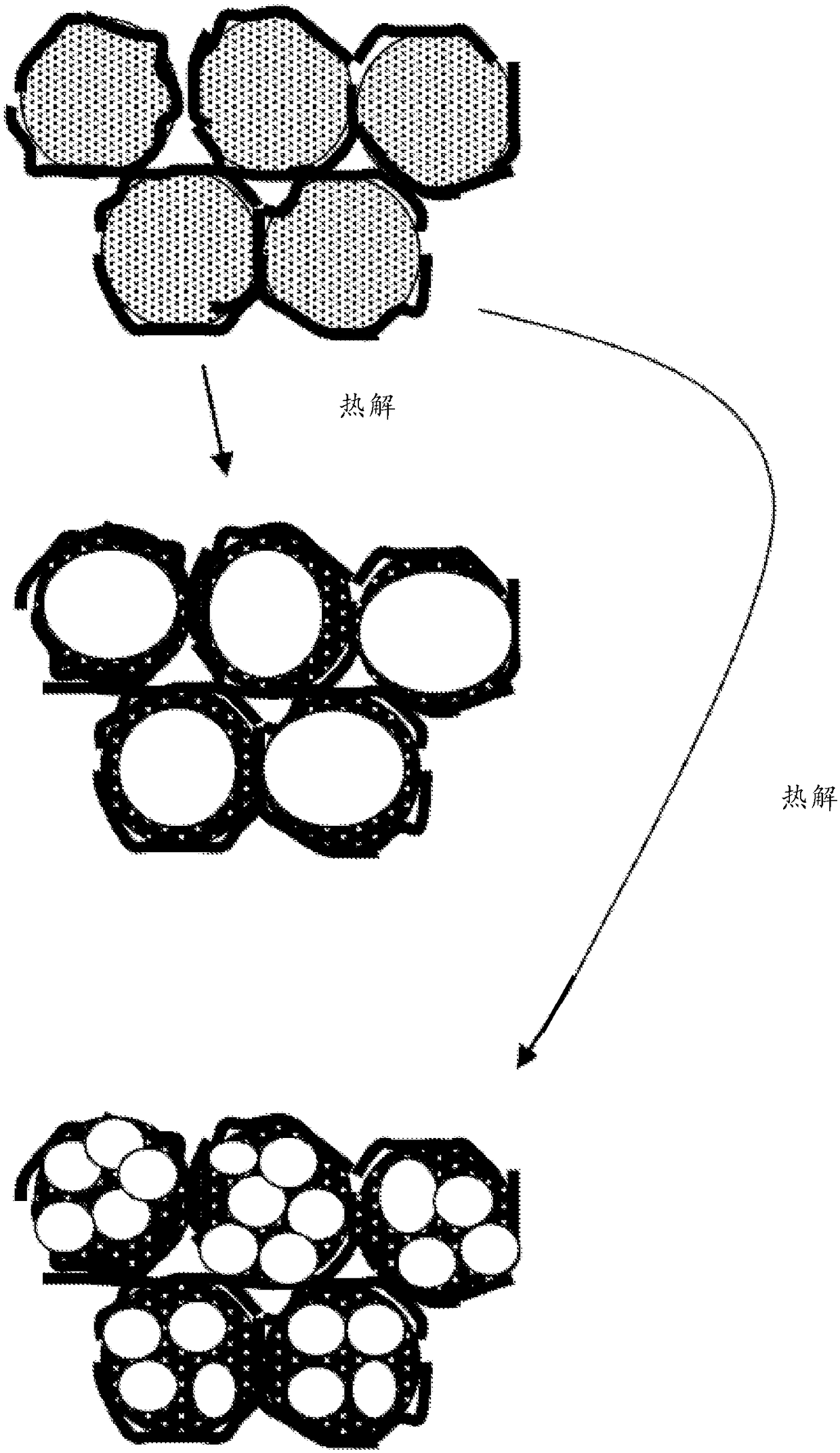
Graphene-Carbon Hybrid Foam
A graphene, graphene sheet technology, applied in other chemical processes, ceramic products, applications, etc., can solve problems such as expensive, unrealistic and highly undesirable for industrial-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0143] Example 1: Production of graphene-carbon foams from flake graphite via a solid polymer support based on polypropylene powder
[0144] In the experiment, 1 kg of polypropylene (PP) pellets, 50 g of flake graphite, 50 mesh (average particle size 0.18 mm; Asbury Carbons, Asbury NJ) ) and 250 grams of magnetic steel balls are placed in a high energy ball mill container. The ball mill was operated at 300 rpm for 2 hours. The vessel lid was removed and the stainless steel ball was removed via the magnet. The polymeric support material was found to be coated with a black graphene layer. The support material was placed on a 50 mesh screen and a small amount of raw flake graphite was removed.
[0145] The coated support material samples were then immersed in tetrachlorethylene for 24 h at 80 °C to dissolve the PP and allow the graphene sheets to disperse in the organic solvent. After solvent removal, isolated graphene sheet powders (mostly few-layer graphene) are recovered. ...
example 2
[0148] Example 2: Graphene-carbon hybrid foam using expanded graphite (thickness >100 nm) as graphene source and ABS as polymer solid support particles
[0149] In the experiment, 100 grams of ABS pellets as solid carrier material particles were placed in a 16 oz plastic container along with 5 grams of expanded graphite. The container was placed in an acoustic mixing unit (Resodyn Acoustic mixer company) and processed for 30 minutes. After processing, the support material was found to be coated with a thin layer of carbon. A small sample of the support material was placed in acetone and subjected to ultrasonic energy to accelerate the dissolution of the ABS. The solution was filtered using an appropriate filter and washed four times with additional acetone. Following washing, the filtrate was dried in a vacuum oven set at 60°C for 2 hours. The sample was examined by light microscopy and found to be graphene. The remaining pellets were extruded to produce graphene-polymer s...
example 3
[0150] Example 3: Production of graphene-carbon hybrid foams from mesocarbon microspheres (MCMB as graphene source material) and polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fibers (as solid support particles)
[0151] In one example, 100 grams of PAN fiber segments (2 mm long, as carrier particles), 5 grams of MCMB (China Steel Chemical Co., Taiwan) and 50 grams of zirconia beads were placed in Vibrating ball mill and process for 2 hours. After the process was complete, the vibratory mill was then turned on, and the support material was found to be coated with a black coating of graphene sheets. Zirconia particles of significantly different sizes and colors were manually removed. The graphene-coated PAN fibers were then compacted and melted together to form several composite films. These films were subjected to heat treatment at 250°C for 1 hour (in room air), at 350°C for 2 hours, and at 1,000°C for 2 hours (under an argon atmosphere) to obtain graphene-carbon foam layers. Half of the carboni...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com