A lithium battery electrode material α-fe 2 o 3 The preparation method of nanosphere
An electrode material, nanosphere technology, applied in battery electrodes, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, negative electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of capacity fading, poor capacity, etc. The effect of the chemical window
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The lithium ion battery electrode material α-Fe of the present embodiment 2 o 3 The preparation method of nanosphere, concrete steps are as follows:
[0024] (1) Dissolve potassium chlorate and ferrous sulfate in deionized water to obtain a mixed solution, wherein the concentration of potassium chlorate is 1mol / L, and the concentration of ferrous sulfate is 0.5mol / L;
[0025] (2) Adjust the pH value of the solution to 10 by using coconut acid diethanolamide with a concentration of 0.25 mol / L, place the mixed solution in a high-pressure reactor, heat it at 140°C for 12 hours, and then take out the reactor;
[0026] (3) Repeated ultrasonic washing with deionized water for 30 min, and separated the precipitated product;
[0027] (4) The precipitated product is dried and calcined at 350°C for 5 hours under an oxygen atmosphere to obtain the final dark brown powder product α-Fe, an electrode material for lithium-ion batteries 2 o 3 nanospheres.
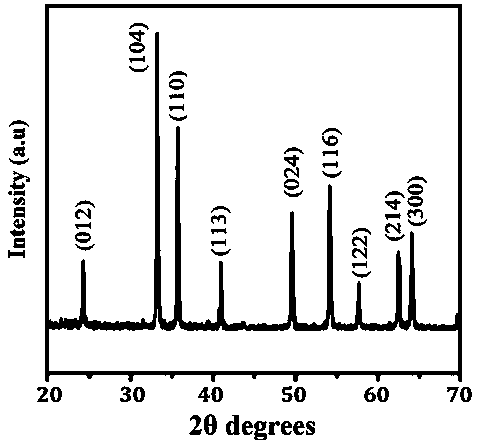
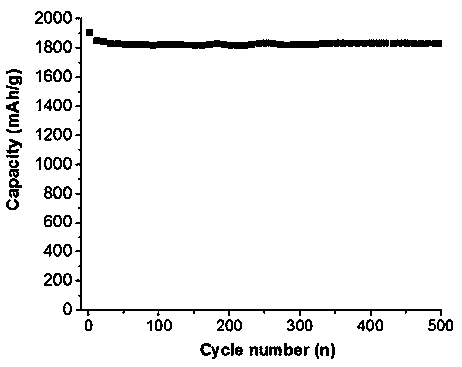
[0028] figure 1 is the...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The lithium ion battery electrode material α-Fe of the present embodiment 2 o 3 The preparation method of nanosphere, concrete steps are as follows:
[0033] (1) Dissolve potassium chlorate and ferrous sulfate in deionized water to obtain a mixed solution, wherein the concentration of potassium chlorate is 0.8mol / L, and the concentration of ferrous sulfate is 0.4mol / L;
[0034] (2) Adjust the pH value of the solution to 10 by using coconut acid diethanolamide with a concentration of 0.2mol / L, put the mixed solution in a high-pressure reactor, heat it at 120°C for 14 hours, and then take out the reactor;
[0035] (3) Repeated ultrasonic washing with deionized water for 50 min, and separated the precipitated product;
[0036] (4) The precipitated product is dried and calcined at 300°C for 6 hours under an oxygen atmosphere to obtain the final dark brown powder product α-Fe, an electrode material for lithium-ion batteries 2 o 3 nanospheres.
Embodiment 3
[0038] The lithium ion battery electrode material α-Fe of the present embodiment 2 o 3 The preparation method of nanosphere, concrete steps are as follows:
[0039] (1) Dissolve potassium chlorate and ferrous sulfate in deionized water to obtain a mixed solution, wherein the concentration of potassium chlorate is 1.2mol / L, and the concentration of ferrous sulfate is 0.6mol / L;
[0040] (2) Adjust the pH value of the solution to 10 by using coconut acid diethanolamide with a concentration of 0.3mol / L, place the mixed solution in a high-pressure reactor, heat it at 150°C for 10 hours, and then take out the reactor;
[0041] (3) Repeated ultrasonic washing with deionized water for 20 min, and separated the precipitated product;
[0042] (4) The precipitated product is dried and calcined at 400°C for 4 hours under an oxygen atmosphere to obtain the final dark brown powder product α-Fe, an electrode material for lithium-ion batteries2 o 3 nanospheres.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| discharge efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com