Method for producing monosaccharide from edible mushroom bran
A technology for edible fungi and monosaccharides, applied in the field of monosaccharide production, can solve the problems of difficult separation of xylose and glucose, difficult industrial production, low hemicellulose content, etc., and achieve large-scale industrial production with mild process conditions. , the effect of efficient processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
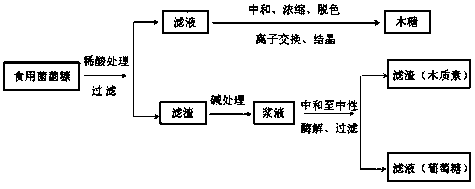
[0019] Step 1, acid hydrolysis: air-dry and crush the bran of various edible fungi such as Pingru, Coprinus comatus, and Golden Needle to about 10 mesh. ℃ for 30 minutes, after filtration, the filtrate and liquid residue were obtained;
[0020] The content of xylose in the measured filtrate is about 13g / L, and the conversion rate of hemicellulose can reach more than 92%. The filtrate is neutralized, concentrated, decolorized, ion-exchanged and crystallized to prepare food-grade xylose. The xylose output can reach 100g / kg fungus chaff, and further products such as xylitol and furfural can be produced.
[0021] Step 2, alkali hydrolysis: add the filter residue to a sodium hydroxide solution with a mass concentration of 5% at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10, treat at 60°C for 60 minutes, neutralize with acid to neutral, and measure the cellulose content;
[0022] Step 3, enzymatic hydrolysis: add commercial cellulase ( CTec2, produced by Danish Novozymes Enzyme Preparation Com...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Step 1, acid hydrolysis: air-dry and crush the bran of various edible fungi such as Pingru, Coprinus comatus, and Flammulina to about 10 meshes, and add them to a sulfuric acid solution with a mass concentration of 2% according to a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:15, 120 ℃ for 60 minutes, after filtration, the filtrate and liquid residue were obtained; the content of xylose in the filtrate was determined to be about 9g / L, and the conversion rate of hemicellulose could reach 90%. The filtrate prepares food-grade xylose through neutralization, concentration, decolorization, ion exchange and crystallization, and the output of xylose can reach 98g / kg bacterium chaff.
[0025] Step 2, alkali hydrolysis: add the filter residue to a sodium hydroxide solution with a mass concentration of 2% at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:15, treat at 60°C for 100 minutes, neutralize with acid to neutral, and measure the cellulose content;
[0026] Step 3, enzymatic hydrolysis: add commercial cellu...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Step 1, acid hydrolysis: air-dry and crush the bran of various edible fungi such as Pingru, Coprinus comatus, and Golden Needle to about 10 mesh. ℃ treatment for 120min, after filtration, the filtrate and liquid residue were obtained;
[0029] The content of xylose in the measured filtrate is about 7g / L, and the conversion rate of hemicellulose can reach 89%. The filtrate is neutralized, concentrated, decolorized, ion-exchanged and crystallized to prepare food-grade xylose, and the yield of xylose can reach 97g / kg fungus chaff.
[0030] Step 2, alkali hydrolysis: add the filter residue to a sodium hydroxide solution with a mass concentration of 5% at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:20, treat at 60°C for 60 minutes, neutralize with acid to neutral, and measure the cellulose content;
[0031] Step 3, enzymatic hydrolysis: add commercial cellulase ( CTec2, produced by Danish Novozymes Enzyme Preparation Company), the dosage is 15FPU / g cellulose, under the conditions of 50°...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com