A fluorescent silicon nano-dot and its preparation method and application
A silicon nanometer and fluorescence technology, applied in the fields of nanomaterials and biology, can solve the problems of poor stability, high cost, short imaging time, etc., and achieve the effects of good cleaning resistance, cheap raw materials, and simple preparation method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Taking AEEA as an example, the preparation of fluorescent silicon nanodots includes the following steps:
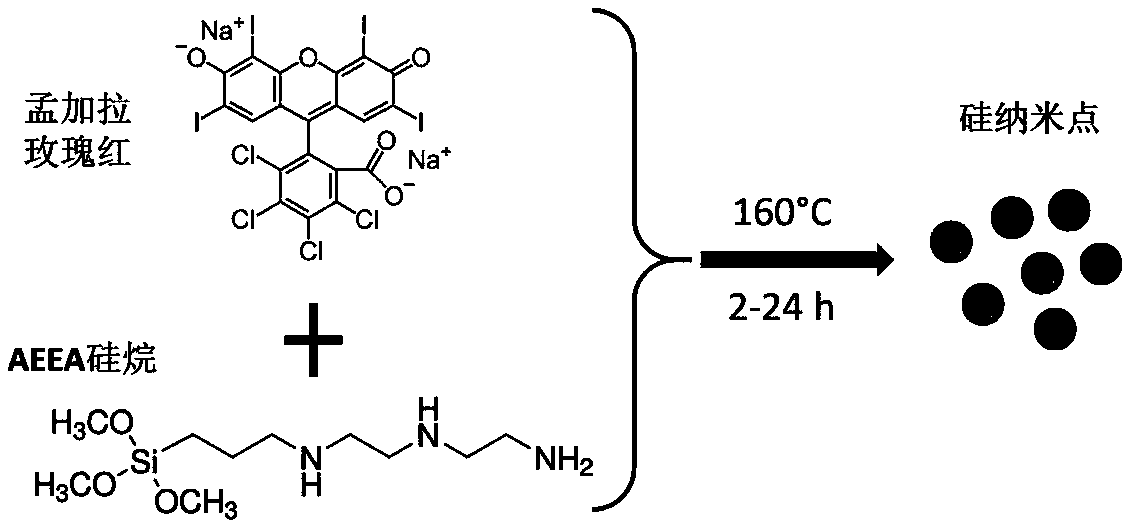
[0049] (1) Weigh Rose Bengal and fully dissolve it in ultrapure water, add an appropriate volume of AEEA so that the mass ratio of AEEA to Rose Bengal is 100:3. The two are fully mixed and transferred to a hydrothermal reaction kettle;
[0050] (2) Reaction: React at 160°C for 3 hours in a hydrothermal reactor to form a silicon nanodot solution;
[0051] (3) Purification: the target ultra-bright fluorescent silicon nano-dot solution is obtained by dialysis.
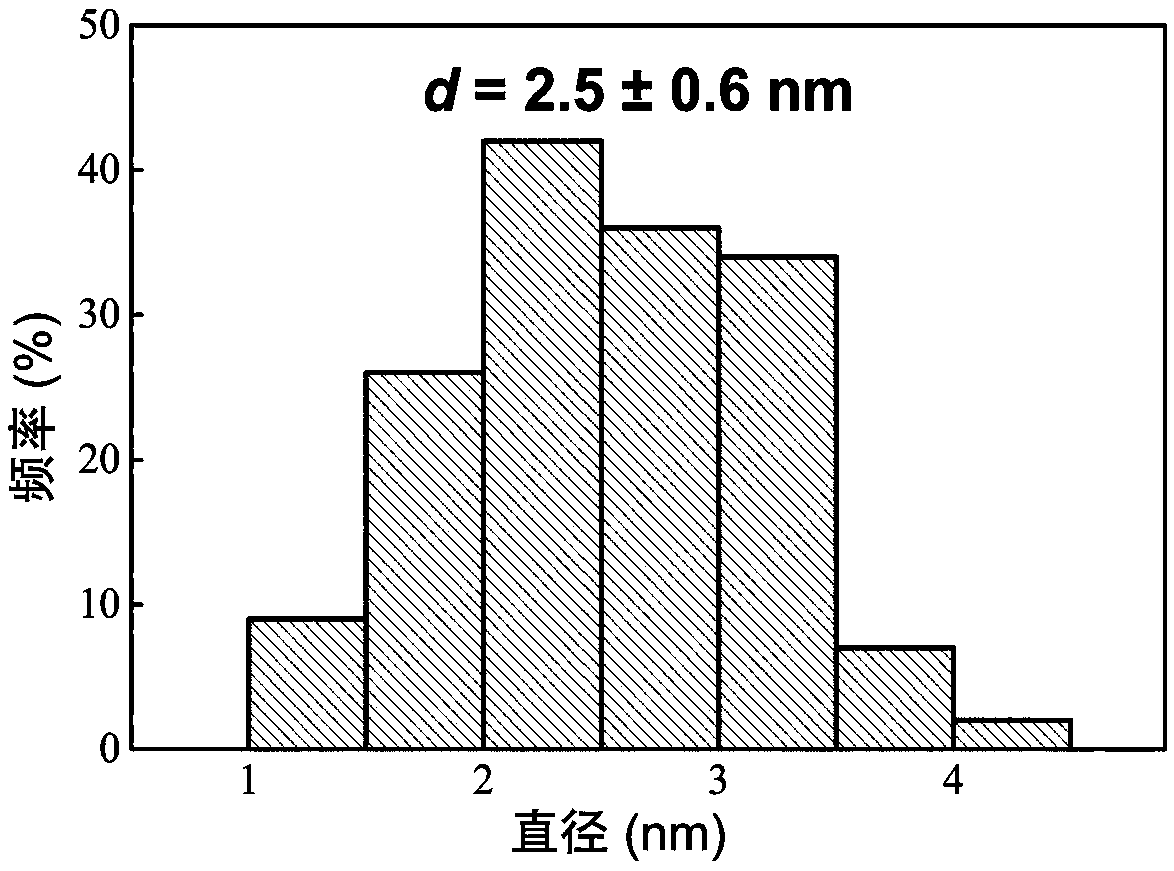
[0052] For a schematic diagram of the reaction, see figure 1 , the transmission electron microscopy results of the prepared SiNDs are shown in figure 2 , the statistical results of particle size distribution are shown in image 3 ,, its UV-Vis absorption spectrum see Figure 4 , and its fluorescence excitation emission spectrum is shown in Figure 5 , its extinction at 650nm in different pH environments...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The lysosome imaging effect of SiNDs prepared in Example 1 on A549 cells was tested as follows:
[0055] (1) Cell culture: A549 cells were cultured at 5×10 3 The density of cells / well will be seeded in a 96-well plate at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate in the environment for 24h;
[0056] (2) Cell staining: replace the culture medium in each well with fresh culture medium containing 20 g / mL SiNDs, and incubate at 37°C, 5% CO 2 After culturing in the environment for 2, 4, 18 and 24 hours respectively, they were washed twice with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Then, stain with commercial red lysosome fluorescent dye (LT-Red) and cell nucleus staining reagent (Hoechst 33342) for 30 and 10 minutes, respectively. Finally, wash the cells twice with PBS;
[0057] (3) Confocal fluorescence microscope imaging observation: using lasers with wavelengths of 405, 488 and 552nm as excitation light, Hoechst 33342 dye emits blue fluorescence under excitation of 405nm excitation light, wh...
Embodiment 3 and 4
[0060] The lysosome imaging effect of commercial lysosomal green fluorescent dye (LT-Green) and red fluorescent dye (LT-Red) on A549 cells was tested.
[0061] The operation process of Examples 3 and 4 is basically the same as that of Example 1, only need to replace SiNDs in step (2) with 1 LT-Green and LT-Red for 30 min, 4 h and 8 h respectively.
[0062] Lysosome imaging effect see Figure 8 and 9 . Observed Figure 8 and Figure 9 It can be seen that the change of dosing time has little effect on the green lysosomal fluorescent dye LT-Green, but it greatly changes the staining site of LT-Red. As the dosing time was extended to 4h, LT-Red was transferred to the cytoplasm and nuclear membrane other than the lysosome, and even at 8h, some dyes had entered the nucleus. It can be seen that, compared with LT-Red, the SiNDs synthesized in the present invention are more suitable for long-term tracking of lysosome imaging.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com