Low-temperature melting permeation continuous separation method for aluminum industry carbon-based hazardous wastes, and product obtained through the method
A separation method and carbon-based technology, applied in separation methods, dispersed particle separation, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as difficult processes, channel blockage, and high energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
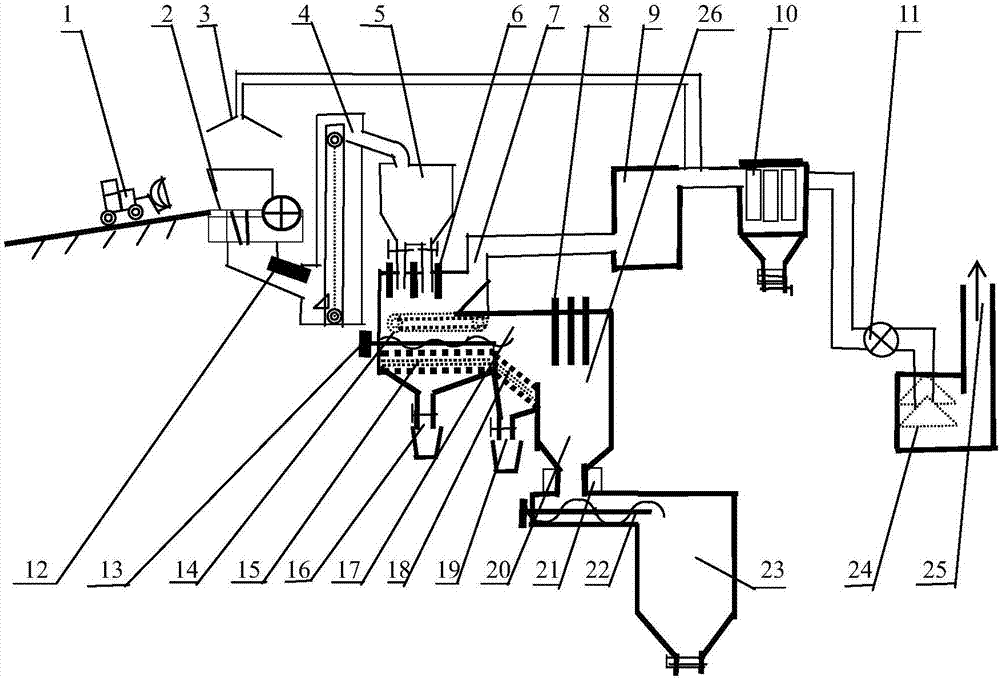
[0055] The process system structure that the present invention proposes sees figure 1 , a low-temperature melting and permeating continuous separation system for hazardous carbon waste in the aluminum industry, including: jaw crusher 2, iron remover 12, low-temperature electric calciner 6, low-temperature flue gas outlet 7, high-temperature electric calciner 8, high-temperature flue gas heat energy Using device 14, fluoride salt molten liquid permeation separator 15, liquid fluoride salt collection port 16, high temperature flue gas channel 17, impurity molten liquid permeation separator 18, liquid impurity collection port 19, natural gradient cooling zone 20, circulation cooling Device 21, frequency conversion carbon discharger 22, carbon collection bin 23, spray device 24, high temperature electric calcining area 26;
[0056] Hazardous carbon waste from the aluminum industry is transported by the loading forklift 1 to the jaw crusher 2 for crushing, and the jaw crusher is co...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Using the system of Example 1, the hazardous carbon waste of the aluminum industry to be treated is aluminum electrolysis anode carbon slag, and the mass content of fluoride salt is 69.8%; the specific process is as follows:
[0066] S1: Aluminum electrolysis anode carbon slag is crushed to a particle size of 0-30 mm (the inlet aperture of the discharger in this embodiment is 180 mm), iron is removed, and sent to a low-temperature electric calciner;
[0067]S2: Carry out low-temperature electric calcining at 1050-1200°C on the pretreated anode carbon slag, the fluoride in the anode carbon slag is melted, the melt is infiltrated and separated, and the fluoride salt molten liquid permeates through the separator 15 for salting. Ingot casting.
[0068] According to the melt penetration separation test of anode carbon slag at 1050-1200°C, it can be seen that most of the fluoride salt in the anode carbon slag (ie fluoride salt: carbon ≈ 69.8:30.2) is separated.
[0069] In t...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Adopt the system of embodiment 1, the carbonaceous hazardous waste of the aluminum industry that handles is aluminum electrolysis waste cathode, wherein fluoride salt content is 30.5% (mass percentage, i.e. fluoride salt: carbon ≈ 30.5:69.5), specific process is as follows:
[0077] S1: The waste cathodes are crushed to a particle size of 0-45 mm (the inlet aperture of the discharger in this embodiment is 180 mm), and then sent to the raw material bin after iron removal. In the sealed AC low-temperature electric calciner 6,
[0078] S2: The pretreated anode carbon slag is subjected to low-temperature electric calcining at 1050-1200°C, the fluoride salt in the spent cathode carbon block is melted, and the melt is infiltrated and separated through the fluoride salt molten liquid permeation separator 15 and is Cast into salt ingots.
[0079] According to the melt permeation separation test of spent cathode carbon blocks at 1050-1200°C, most of the fluoride salts in 30.5% ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com