Zero-discharge reusing treatment method for organic waste liquid
A technology of organic waste liquid and treatment method, applied in filtration treatment, precipitation treatment, multi-stage water treatment, etc., can solve the problems of clogging incinerators and evaporators, easy clogging of main reactors, and high equipment investment, so as to reduce investment and operation. Cost, significant economic benefits, high removal efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
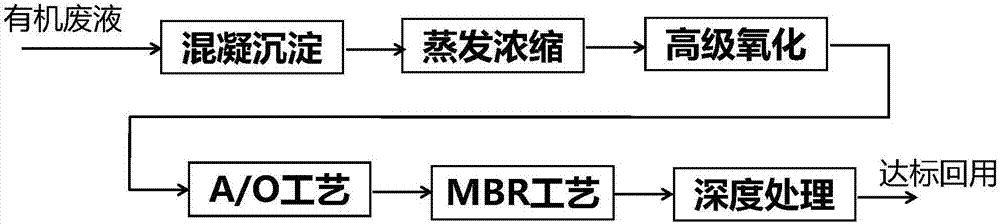
[0038] A high-concentration organic waste liquid in an electronics industry, COD is above 20,000mg / L, and the organic waste liquid contains high-concentration copper ions, fluoride ions and chloride ions. This zero-emission treatment method is adopted:
[0039] (1) Firstly, after primary and secondary coagulation and sedimentation pretreatment, the pH value is generally controlled at 8 to 10. The coagulants used include lime, PAC (polyaluminum chloride), PAM (polyacrylamide), and secondary The coagulant used in coagulation and sedimentation includes recapture agent, PAC, PAM; the lime is water lime, adjusted to about 5% with water; the dosage of lime is 200-500mg / L, and the dosage of PAC is 0.5-5.0mg / L , the dosage of PAM is 0.5~1.0mg / L;
[0040] (2) The effluent of coagulation and precipitation is evaporated and concentrated, and the device used is a thin film drying device, and the supporting devices include a spray tower and a condensed water tank;
[0041] (3) After evapo...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A high-concentration organic waste liquid in a pharmaceutical industry has a COD of 30,000-100,000 mg / L. The organic waste liquid contains high-concentration salt ions. This zero-emission treatment method is adopted:
[0046] (1) After coagulation and sedimentation pretreatment, the pH value is generally controlled at 8 to 10. The coagulants used include recapture agents, PAC, and PAM to remove some organic pollutants and salts; recapture agent dosage 200~500mg / L, PAC dosage 0.5~5.0mg / L, PAM dosage 0.5~1.0mg / L;
[0047] (2) The effluent of coagulation and precipitation is evaporated and concentrated, and the device used is a thin film drying device, and the supporting devices include a spray tower and a condensed water tank;
[0048] (3) After evaporation and concentration, advanced oxidation treatment is adopted, and the advanced oxidation method mainly adopts Fenton oxidation device; Fenton oxidation adopts sulfuric acid to adjust the pH value, and the pH is 4 to 6; t...
Embodiment 3
[0052] A petrochemical industry has high-concentration organic waste liquid, COD is above 20,000 mg / L, and the organic waste liquid contains high-concentration fluoride ions. This zero-emission treatment method is adopted:
[0053] (1) Firstly, after coagulation and sedimentation pretreatment, the pH value is generally controlled at 8 to 10, and the coagulants used include lime, PAC, and PAM; the lime is water lime, which is adjusted to about 5% with water; the dosage of lime is 200 ~500mg / L, PAC dosage 0.5~5.0mg / L, PAM dosage 0.5~1.0mg / L;
[0054] (2) The effluent of coagulation and precipitation is evaporated and concentrated, and the device used is a thin film drying device, and the supporting devices include a spray tower and a condensed water tank;
[0055] (3) After evaporation and concentration, advanced oxidation treatment is adopted, and the advanced oxidation method mainly adopts wet oxidation method; the reaction temperature is 180-280 degrees;
[0056] (4) Subsequen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| chemical oxygen demand (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| chemical oxygen demand (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com