A combined method for repairing heavy metal-contaminated soil
A technology of combined restoration of contaminated soil, applied in the restoration of contaminated soil, etc., can solve the problems of low phytoremediation efficiency, difficulty in mud-water separation, incomplete passivation, etc., and achieve the effects of preventing reactivation, reducing costs, and reducing content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
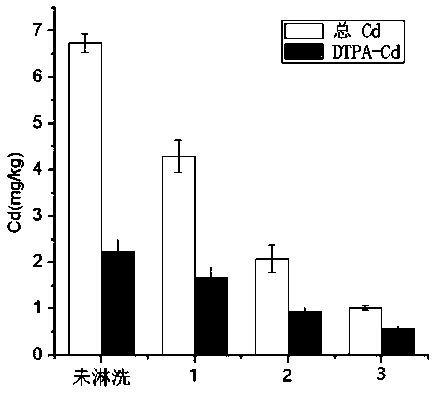
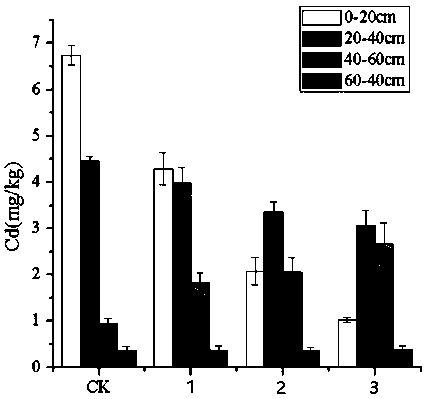
[0026] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific examples, but the present invention is not limited to the following examples. Example 1 In situ leaching of heavy metal contaminated soil - deep fixation
[0027] Table 1 Basic properties of soil
[0028]
[0029] The restoration project of this embodiment is located in a polluted farmland in Yixing, Jiangsu Province. The farmland soil belongs to yellow-brown soil and is acidic. The soil properties are shown in Table 1. The cadmium content is 6.32 mg / kg, which exceeds my country's "Soil Environmental Quality Standard" (GB15618-1995) More than ten times the secondary standard, which seriously threatens the local ecological environment and human health.
[0030] In this embodiment, the soil in-situ leaching-deep fixation steps are as follows:
[0031] 1. After leveling the polluted farmland, compact the field ridges around them, and the height of the field ridges is 15cm;
[0032] 2. D...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2 Soil Organic Fertilizer Improvement-Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil
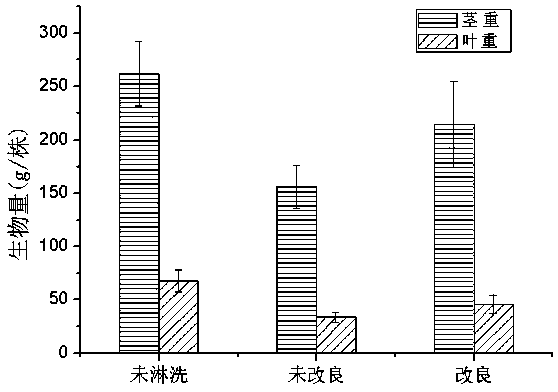
[0045] In Example 1, ferric chloride (group 3) was applied according to 2% of the dry weight of the plowed layer soil, and the removal rate of heavy metals in the soil was the best, but the soil acidification and nutrient loss were the most serious. This example will improve and phytoremediate the soil. The operation steps are as follows:
[0046] 1. After rinsing, apply commercially available organic fertilizers on the soil surface, and the application amount is 1% of the dry weight of the soil in the cultivated layer (the specific application ratio can also refer to the instructions of the organic fertilizers), and rotary tillage and mixing.
[0047] 2. Select 0.5-1.5cm thick weeping willow branches, remove the twigs, and cut them into cuttings about 15cm long. During the preparation of willow cuttings, minimize the wound area.
[0048] 3. Plant weeping willow in the...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3 Liu 785 remediation of heavy metal Cd polluted soil
[0056] This example is located in a park in Changshu City, Jiangsu Province. The soil is dredging sludge at the bottom of the lake. The Cd concentration in the soil is 0.93 mg / kg, which exceeds the maximum allowable content of pollutant cadmium in farmland soil in my country's second-level soil environmental quality standard. 0.6mg / kg, it will cause great harm to agricultural production and human health, so the soil in this area needs to be repaired urgently. The steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0057] 1. After leveling the soil, dig a 50-60cm deep trench with a width of 5-10cm and a distance of 0.5m-1m;
[0058] 2. Apply lime in the deep ditch, according to 2% of the dry soil weight of the cultivated layer (soil within 0-20cm from the surface soil), about 4.8kg / m 2 , and then backfill the contaminated soil;
[0059] 3. Evenly apply the eluting agent ferric chloride on the soil surface, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com