Internally-plasticized antistatic polyformaldehyde material and preparation method thereof
A polyoxymethylene material and antistatic technology, applied in the field of polyoxymethylene materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of reduced thermal stability of the mechanical properties of polyoxymethylene materials, and achieve excellent chemical and thermal stability, smaller size, and simple industrial preparation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
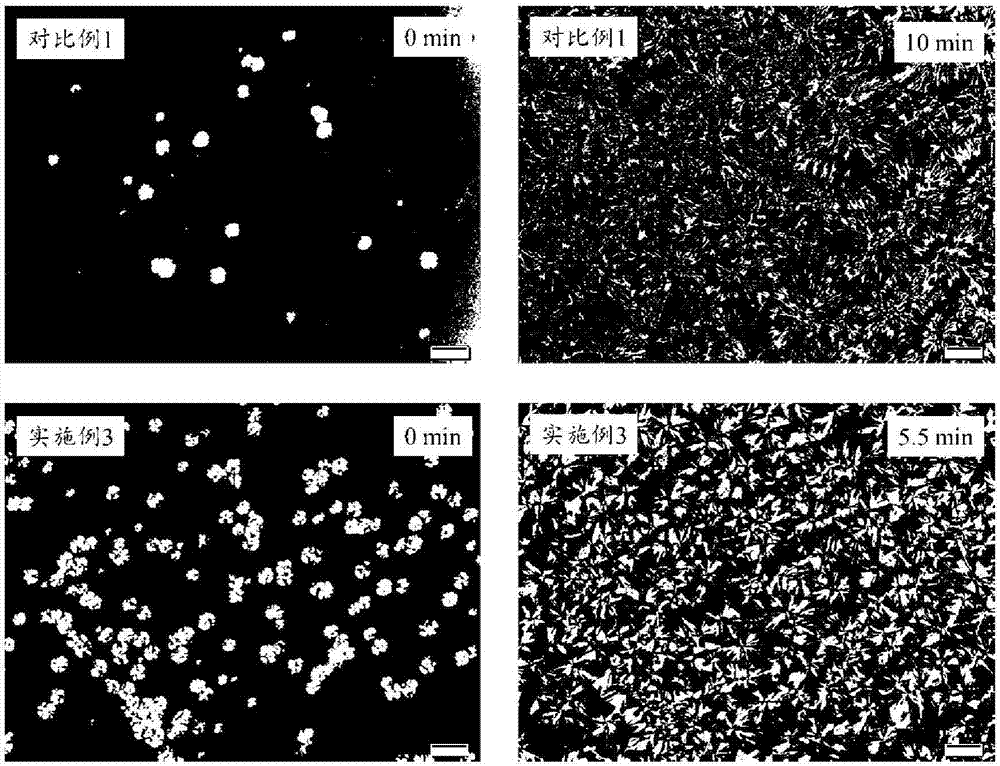
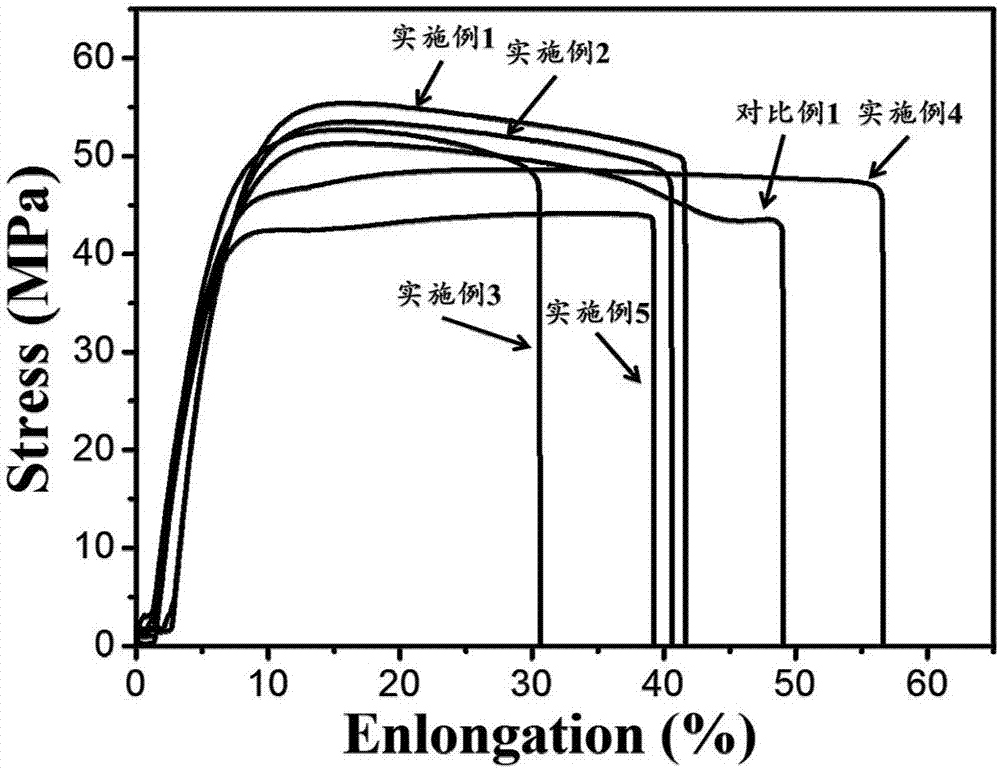
Embodiment 1
[0065] Step (1): POM and tri-n-butyloctylphosphine bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide salt were vacuum-dried at 80°C for 24 hours;
[0066] Step (2): Add 100g of dried polyoxymethylene and 0.25g of tri-n-butyloctylphosphine bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide salt to an internal mixer for melting and mixing at 190°C. The rotor speed is 20rpm, melt kneading for 2min, then increase the rotor speed to 50rpm, melt kneading for 5min, to obtain the mixture:
[0067] In step (3), the mixture is discharged from the melting and kneading equipment and cooled to room temperature to obtain a polyoxymethylene material.
[0068] The mass ratio of polyoxymethylene and tri-n-butyloctylphosphine bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide salt in the polyoxymethylene material prepared in Example 1 is 100:0.25
[0069] The test results of the samples are shown in Table 1
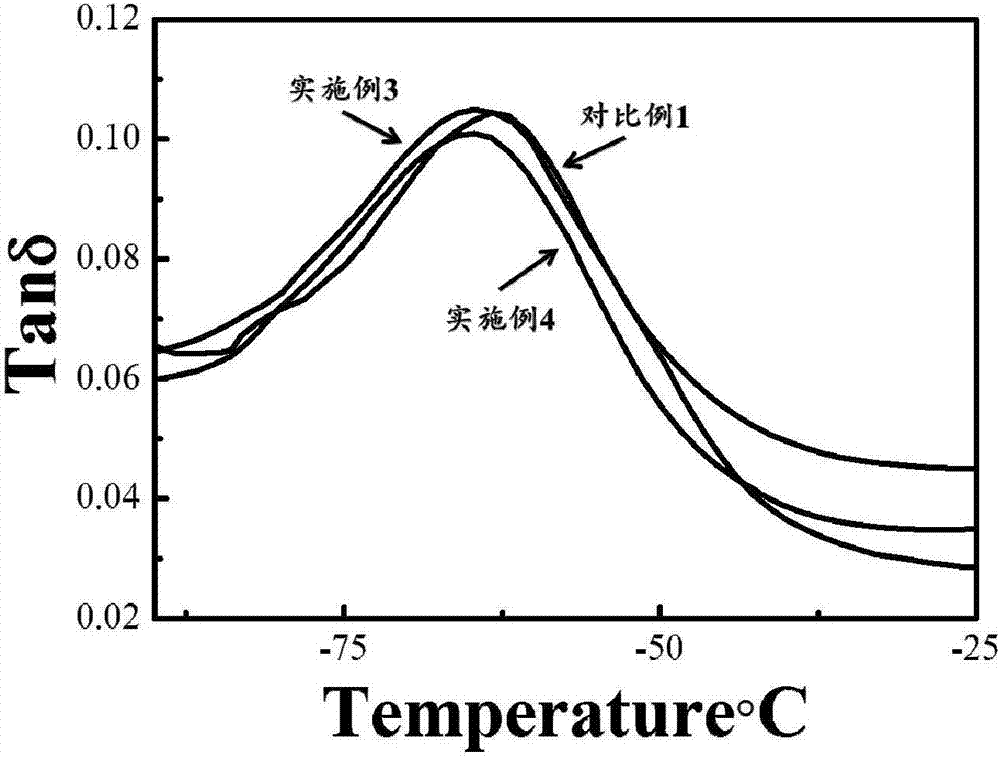
Embodiment 2
[0071] Step (1): POM and tri-n-butyloctylphosphine bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide salt were vacuum-dried at 80°C for 24 hours;
[0072] Step (2): Add 100g of dried polyoxymethylene and 0.5g of tri-n-butyloctylphosphine bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide salt to an internal mixer for melting and mixing at 190°C. The rotor speed is 20rpm, melt kneading for 2min, then increase the rotor speed to 50rpm, melt kneading for 5min, to obtain the mixture:
[0073] In step (3), the mixture is discharged from the melting and kneading equipment and cooled to room temperature to obtain a polyoxymethylene material.
[0074] The mass ratio of polyoxymethylene and tri-n-butyloctylphosphine bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide salt in the polyoxymethylene material prepared in Example 2 is 100:0.5
[0075] The test results of the samples are shown in Table 1
Embodiment 3
[0077] Step (1): POM and tri-n-butyloctylphosphine bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide salt were vacuum-dried at 80°C for 24 hours;
[0078] Step (2): Add 100g of dried polyoxymethylene and 1g of tri-n-butyloctylphosphine bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide salt into the internal mixer at 190°C for melting and mixing. The rotor speed is 20rpm, melt kneading for 2min, then increase the rotor speed to 50rpm, melt kneading for 5min, to obtain the mixture:
[0079] In step (3), the mixture is discharged from the melting and kneading equipment and cooled to room temperature to obtain a polyoxymethylene material.
[0080] The mass ratio of polyoxymethylene and tri-n-butyloctylphosphine bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide salt in the polyoxymethylene material prepared in Example 3 is 100:1
[0081] The test results of the samples are shown in Table 1
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com