Method for inducing embryonic stem cell to be differentiated into corneal endothelial cells and inducing culture medium
A technology for inducing culture medium and embryonic stem cells, applied in the fields of tissue engineering and ophthalmology, it can solve the problems of cumbersome and long feeder layer co-cultivation method, and achieve the effects of regular morphology, high biological safety and obvious characteristics.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0058] In the present invention, the preparation method of the pre-laid Matrigel preferably comprises the following steps:
[0059] Matrigel was diluted with DMEM / F12 medium and plated;
[0060] Place the plated Petri dish in a sterile environment with a temperature of 37°C and a CO2 volume concentration of 5% for 1-2 hours to gel;
[0061] The gelled DMEM / F12 medium was replaced with mTeSR1 medium to obtain a medium pre-coated with Matrigel. The source of the mTeSR1 medium is preferably purchased from Stem Cell Company.
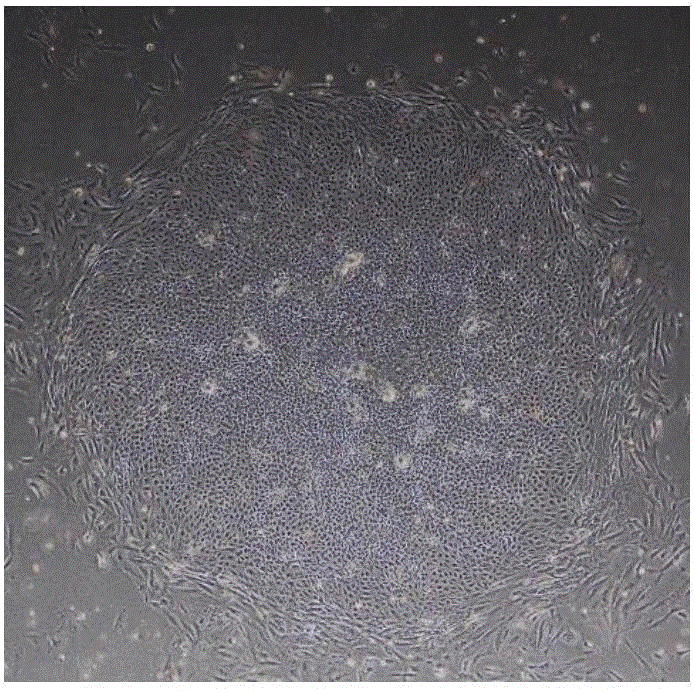
[0062] In the present invention, the time for the basal culture is 3-4 days. After basal culture, human embryonic stem cells reached about 20-100 cells / clones under an inverted phase-contrast microscope, and the clones were uniform in size. The purpose of the basal culture is to grow the stem cell clones to a size that meets the induction conditions.
[0063] To obtain the human embryonic stem cells of the basal culture, the present invention inoculates ...
Embodiment 1
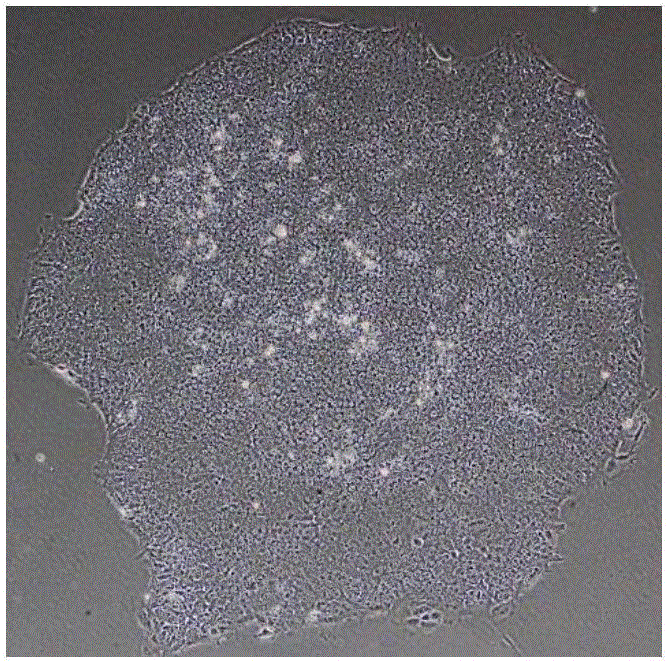
[0078] Culture of human embryonic stem cells: take an aliquoted Matrigel matrigel (purchased from BD Company, product number 354277), and melt on ice at 4°C. Pre-cool pipette tips, Petri dishes, and centrifuge tubes. Use 25ml of cold DMEM / F12 medium (purchased from Invitrogen, product number 11330) to dilute Matrigel to a concentration of 1-2%, and then add 1-2ml to each 60mm diameter petri dish for coating, until the Matrigel is completely After the culture surface was covered, the culture dish was moved into a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator, and replaced with fresh human embryonic stem cell medium mTeSR1 (purchased from Stem Cell Company, Cat. No. 05850) after 1 hour for future use. When human embryonic stem cells are cultured to a good morphological state (such as figure 1 Shown) Use 3ml of warm DMEM / F12 medium to wash twice, add about 1-1.5ml of the digestive solution Accutase (purchased from Sigma, Cat. 2 Digest in the incubator for 4-7 minutes, observe the edge of the clone un...
Embodiment 4
[0084] Immunofluorescence detection:
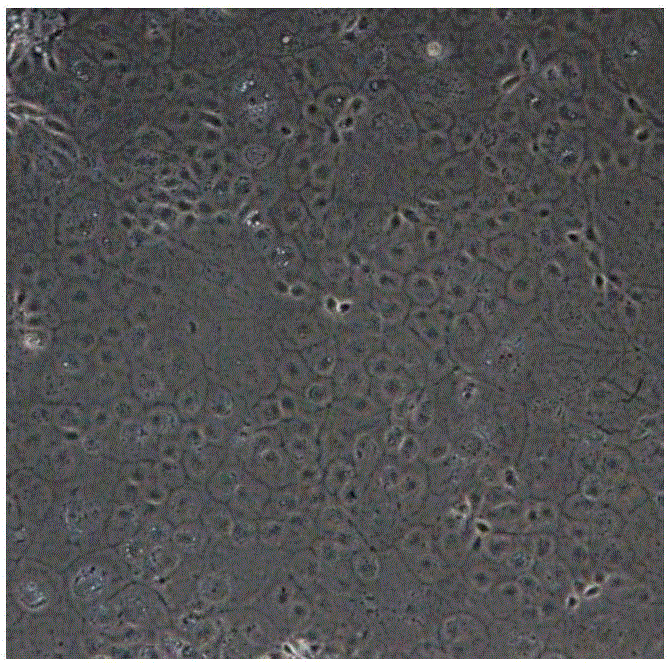
[0085] 1. 4% paraformaldehyde to fix the cells for 15 minutes; 2. Wash 3 times with PBS; 3. 0.1% TritonX-100 permeabilization for 15 minutes (this step can be omitted for membrane antigen); 4. Add 5% BSA to block at room temperature for 1 hour; 5. Add the corresponding primary antibody and incubate at room temperature for 2 hours or overnight at 4°C; 6. Add fluorescent secondary antibodies corresponding to the source of the primary antibody, and incubate at room temperature for 1 hour; 7. DAPI staining and take pictures under a fluorescent microscope. Fluorescent immunographs of cell markers such as Figure 5 and Figure 6 shown. Figure 5 Expression of corneal endothelial fluid pump function marker Na for differentiated cells + -K + - Immunofluorescence pictures of ATPase markers; Figure 6 It is a positive control picture, which is normal human corneal endothelial cells expressing the corneal endothelial cell fluid pump function ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com