Tissue engineering cartilage composite stent and preparation method
A composite scaffold and tissue engineering technology, applied in tissue regeneration, additive processing, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient mechanical strength of hydrogel scaffolds, achieve good biodegradability, biocompatibility, and good mechanical strength Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
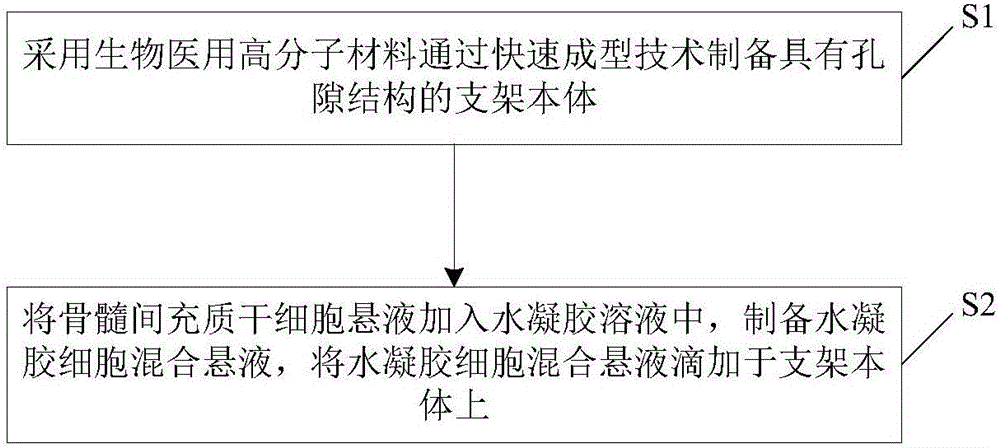
[0054] see figure 2 , is a flow chart of the preparation method of the tissue engineered cartilage composite scaffold according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. The tissue engineered cartilage composite scaffold as mentioned above can be prepared by this method. Such as figure 2 Shown, the preparation method of this tissue engineered cartilage composite scaffold comprises the following steps:
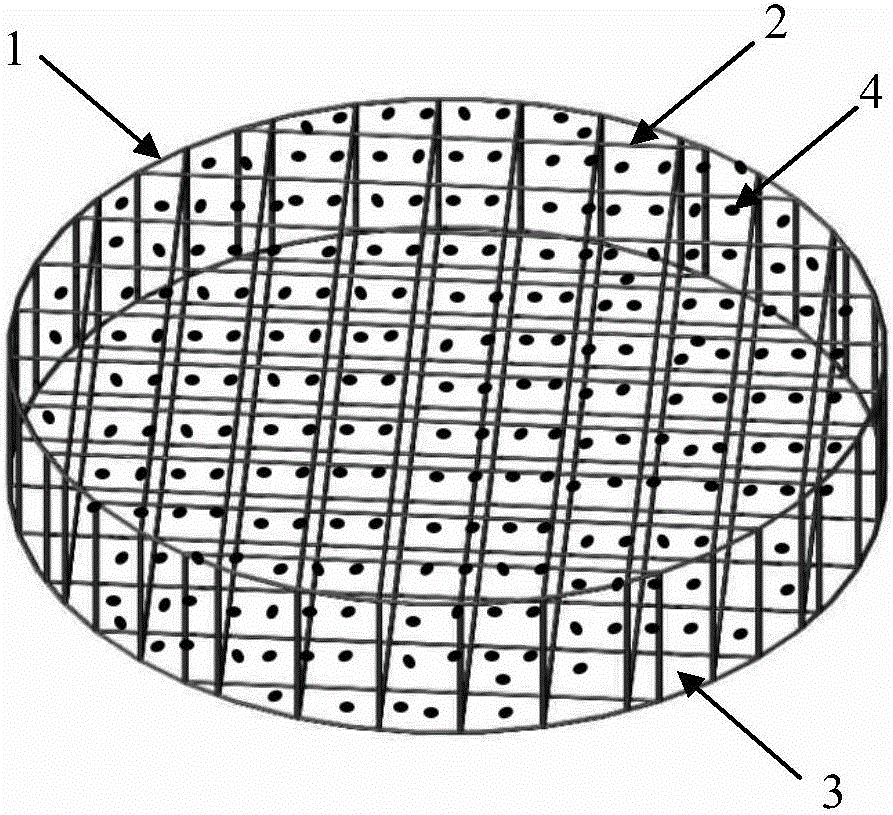
[0055] S1. A stent body 1 with a pore structure is prepared by using a medical polymer material through rapid prototyping technology. The medical polymer materials include but not limited to polycaprolactone (PCL), polylactic acid (PLA), polyglycolic acid (PGA), polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA), polyethylene glycol (PEG) and poly Ether ether ketone (PEEK) and other materials. The scaffold prepared by rapid prototyping technology, especially fused deposition modeling, has a porous structure connected in three dimensions. The porosity and pore structure of the i...
Embodiment 1
[0070] 1. Set the weight average molecular weight (Mw) to 60000gmol -1 The PCL is placed in the nozzle of the fused deposition modeling 3D printer and heated to 130°C, and is ready to print at an air pressure of 800kPa.
[0071] 2. Set the fiber diameter to 350 μm, the fiber spacing to 350 μm, and print out the cylindrical stent body at a speed of 0.88 mm / s. The cylinder has a diameter of 9 mm and a thickness of 2 mm.
[0072] 3. Dissolve PLGA-PEG-PLGA triblock copolymer and phosphate buffered saline solution at 4°C to form a triblock copolymer solution, wherein the mass fraction of PLGA-PEG-PLGA triblock copolymer is 14% . The PLGA-PEG-PLGA triblock copolymer in this experiment was synthesized and provided by Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
[0073] 4. Mix the triblock copolymer solution and the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell suspension at 20°C to form a mixed hydrogel cell suspension that wraps cells; wherein, the bone marrow mese...
Embodiment 2 to 14
[0076] Examples 2 to 14 were carried out in substantially the same manner as Example 1 except for the contents of Table 1 below.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cell concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com