Preparation method of amphoteric ion modified ultra-fine iron oxide particles
A technology of iron oxide particles and zwitterions, which can be used in preparations for in vivo tests, pharmaceutical formulations, nuclear magnetic resonance/magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents, etc. It can solve the problems of not finding MRI diagnostic applications and achieve the realization of magnetic resonance blood pools The effect of imaging, easy operation, and increased half-life of blood circulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
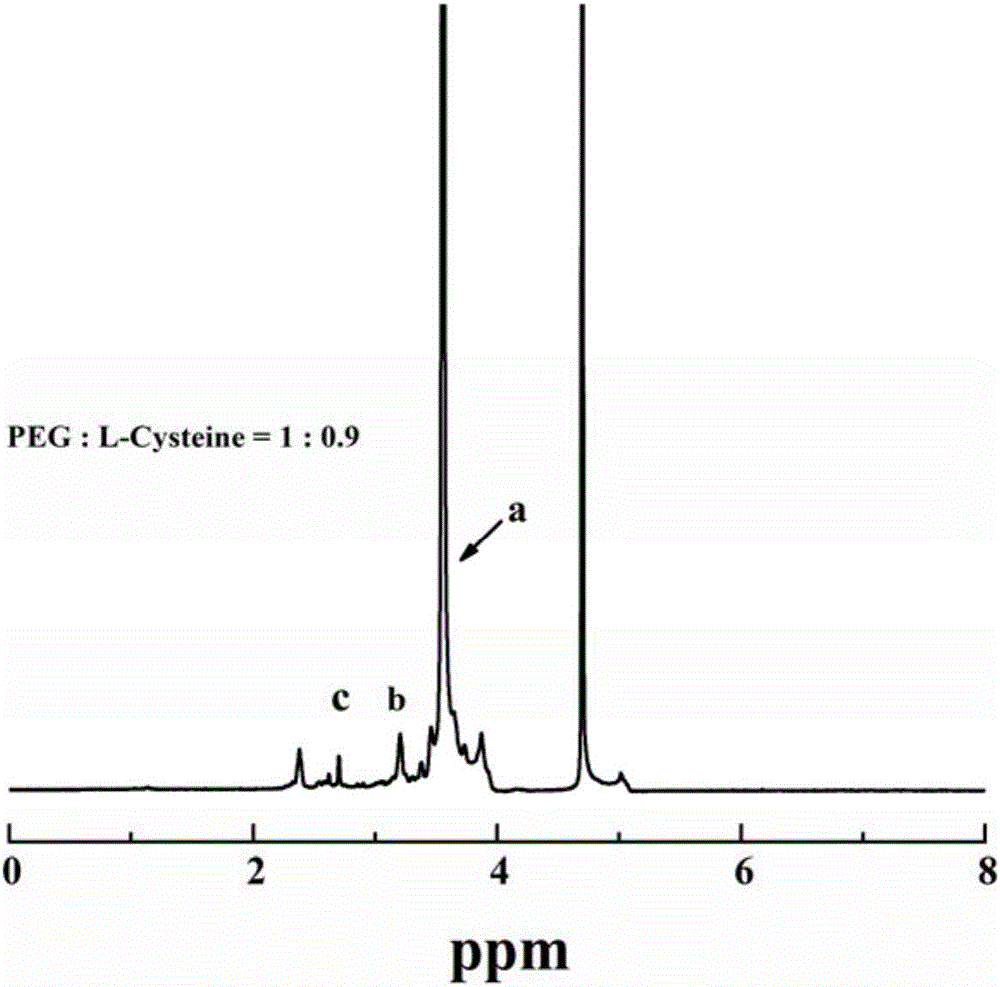
[0049] 1.09g of ferric chloride hexahydrate was dissolved in 40mL of diethylene glycol (also known as diethylene glycol, DEG), and then 0.47g of sodium citrate (Na 3 Cit) was dissolved in the above solution, and stirred at 80° C. for 1 hour under an air atmosphere. After the sodium citrate was completely dissolved, 1.312 g of anhydrous sodium acetate was added to the above solution, and the stirring was continued until the sodium acetate powder was completely dissolved, and then Transfer the solution to a 50mL autoclave, and react at 200°C for 4 hours; after the reaction, cool to room temperature naturally, transfer the product to a 50mL centrifuge tube and centrifuge at 8500rpm for 15 minutes, discard the supernatant, and return to the solution with absolute ethanol. Dissolve, centrifuge at 8500rpm for 15 minutes, repeat the operation 3 times, and then dry the precipitate at 60°C to obtain ultra-small ferric oxide nanoparticles, that is, ultra-small iron oxide nanoparticles st...
Embodiment 2
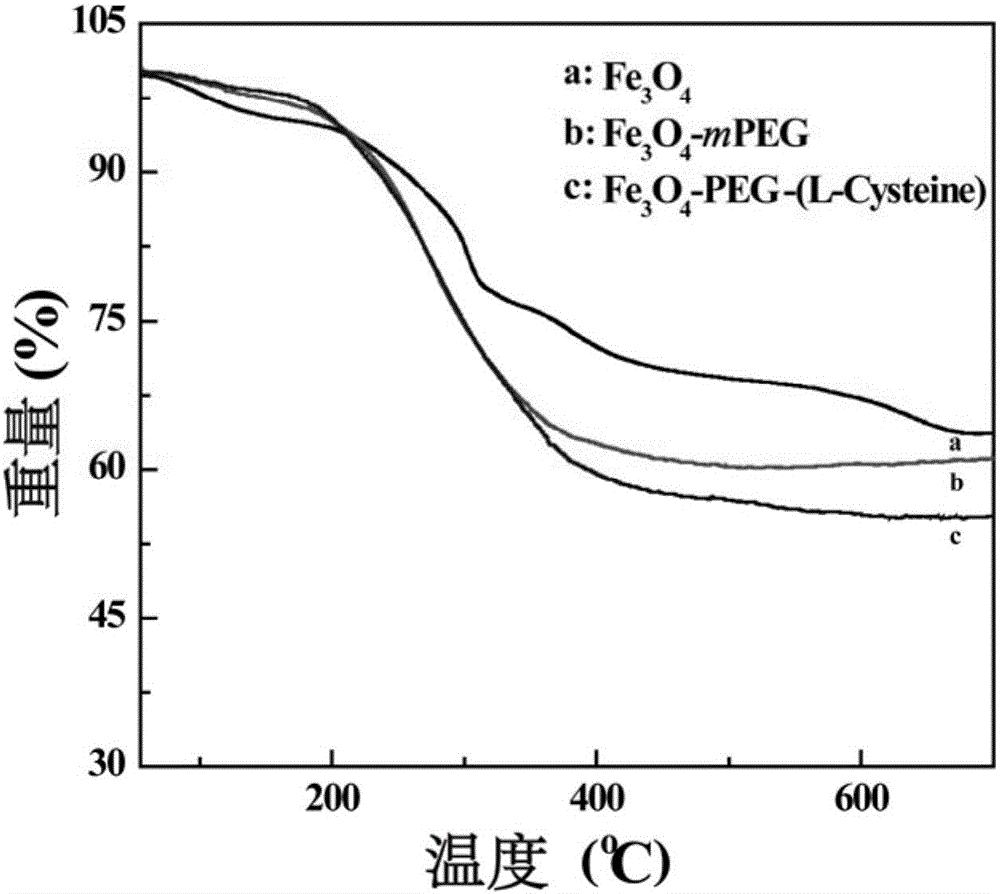
[0056] Get the Fe prepared by embodiment 1 respectively 3 o 4 , Fe 3 o 4 -PEG-(L-Cysteine) nanoparticles and the Fe prepared in Comparative Example 1 3 o 4 - Dissolve 2 mg of mPEG nanoparticles in ultrapure water to obtain a nanoparticle suspension, which is homogenized by ultrasound, and the surface potential and hydrated particle size are measured. Experimental result shows (table 1), the Fe that prepares 3 o 4 , Fe 3 o 4 -PEG-(L-Cysteine) and Fe 3 o 4 - The surface potentials of mPEG nanoparticles were -39.7, -15.7 and -16.4mV; the hydrated particle sizes were 30.9, 116.2 and 93.6nm, respectively. From the experimental results, the ultra-small iron oxide nanoparticles in the modification of NH 2 -PEG-(L-Cysteine) and mPEG-NH 2 After that, the surface potential increased and the hydrodynamic diameter increased, which was mainly caused by the surface modification of PEG or PEG / L-Cysteine. The changes of surface potential and hydrated particle size indicated that ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] In most cases, the route of administration of the contrast agent enters the body through intravenous injection. Therefore, the contrast agent will inevitably come into direct contact with the blood, and whether the intervention of the contrast agent will cause hemolysis or other adverse symptoms has become one of the important factors that researchers have to consider. In order to ensure that the nanoparticles prepared by the present invention can be safely used for in vivo bioimaging diagnosis, the prepared Fe 3 o 4 -PEG-(L-Cysteine) nanoparticles and control material Fe 3 o 4 - Hemocompatibility of mPEG. Calculate and weigh Fe according to the iron concentration calculation of two kinds of materials measured in embodiment 2 3 o 4 -PEG-(L-Cysteine) nanoparticles (embodiment 1) and contrast material Fe 3 o 4 -Two kinds of nanoparticles with 1 mg total iron content in mPEG (comparative example 1) were respectively dispersed in PBS to prepare a concentration of 1 m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hydrated particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com