Maize zmstp1 protein and its coding gene and application
A gene and corn technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems such as different monosaccharide absorption capacity, and achieve the effect of improving plant nitrogen efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Embodiment 1, the cloning of corn sugar transporter gene ZmSTP1 gene
[0057] The amino acid sequences of monosaccharide transporters in Arabidopsis thaliana, rice, and wheat were obtained from NCBI, Maizesequence, and Uniprot databases, and compared using ClustalW1.8 (Thompson et al. 1994 Nucleic Acids Research 22, 4673-4680). Phylogenetic tree analysis showed that the genetic relationship with AtSTP1 was the closest, so the gene was named ZmSTP1 ( figure 1 ).
[0058] 1. Total RNA extraction
[0059] Take 200mg of fresh B73 corn roots and grind them in liquid nitrogen; add 1ml of Trizol extract provided in the kit, shake at room temperature for 5 minutes; then add 200μl of chloroform, shake for 30 seconds, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C; Add 0.5ml of isopropanol, let stand at room temperature for 1 hour, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm at 4°C for 15 minutes; take the precipitate, add 1ml of 70% ethanol, shake for 1 minute, and centrifuge at 10,000 rpm at 4°...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 2, Real-Time PCR analysis of the expression characteristics of various tissues of the maize ZmSPT1 gene.
[0081] The test materials were planted at the Shangzhuang Experimental Station of China Agricultural University. Corn samples of different tissues were harvested one week after silking, quickly placed in liquid nitrogen, and brought back to the laboratory and placed in a -80 degree refrigerator for later use.
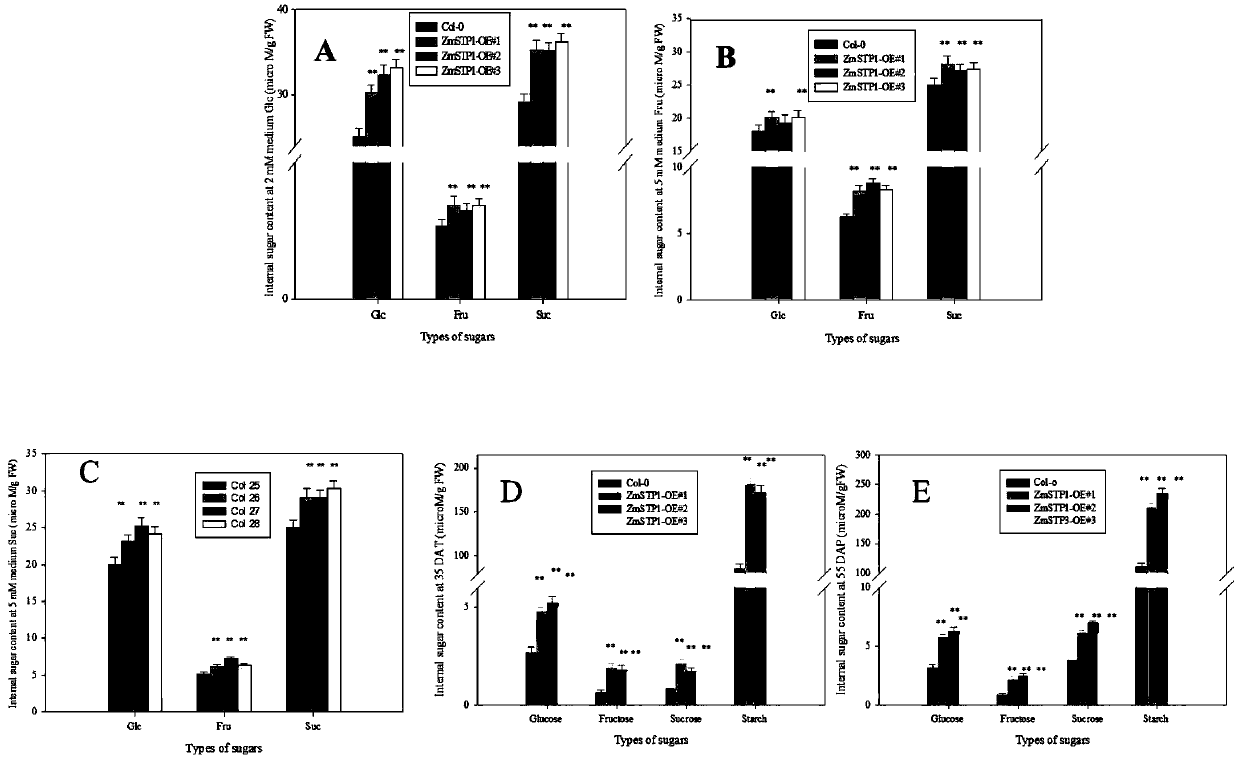
[0082] Quantitative results showed that ZmSTP1 had the highest expression level in roots ( figure 2 ).
[0083] Attached Real-Time PCR operation steps:
[0084] 1, extract the total RNA in different processing sample roots (method is with embodiment 1);
[0085] 2. Take 50 μg of total RNA, and use DNase I (TaKaRa Company, catalog number: D2215) to remove genomic DNA, as follows:
[0086] Reaction system (50μl):
[0087]
[0088] React at 37°C for 30 minutes;
[0089] Add 150 μl DEPC water, add 200 μl phenol / chloroform / isoamyl alcohol (25:24:...
Embodiment 3
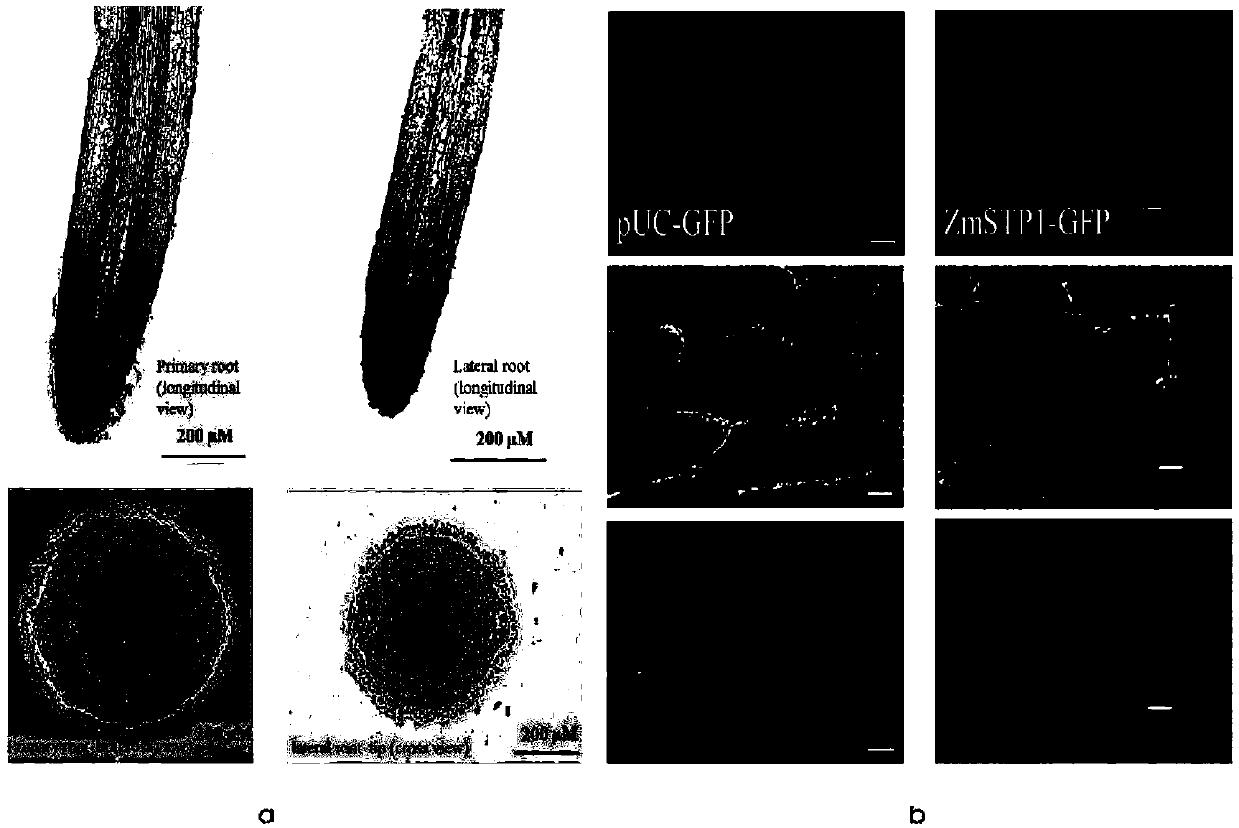
[0103] Example 3. ZmSPT1 expression localization analysis using in situ hybridization and green fluorescent protein technology.
[0104] 1. Preparation of Plant Material
[0105] Hoagland medium was used for plant culture, and root tip samples were taken from corn seedlings at the three-leaf stage. Cut root tip 0.5-1cm and put it into FAA fixative solution (composition per 100ml fixative solution contains: 50% ethanol 90ml, glacial acetic acid 5ml, formaldehyde 5ml);
[0106] The plant material is then dehydrated, cleared and dipped in wax as follows:
[0107] Discard the FAA fixative, wash with DEPC twice;
[0108] 50% ethanol, 50% ethanol+10% tert-butanol, 50% ethanol+20% tert-butanol, 50% ethanol+35% tert-butanol, 50% ethanol+50% tert-butanol, 25% ethanol+75% tert-butanol, 25% ethanol+75% tert-butanol+0.1% eosin (Y), and 100% tert-butanol were treated successively for 2 hours;
[0109] Transfer to 2 / 3 tert-butanol + 1 / 3 paraffin oil and place for 4 hours;
[0110] Pour...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com