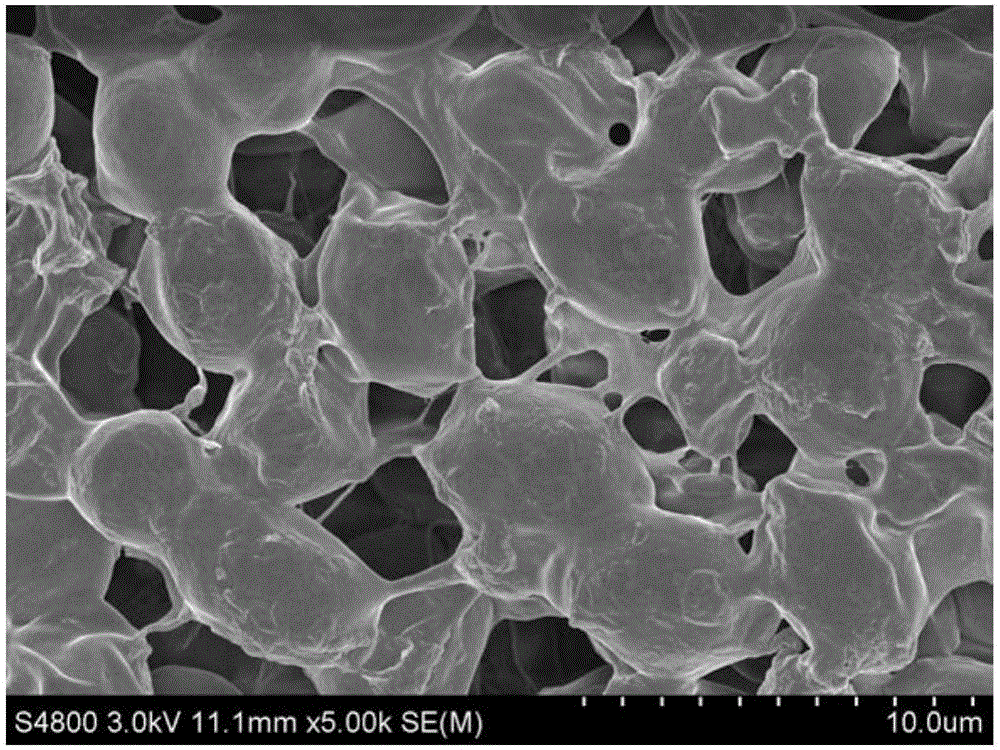
Porous composite capable of adsorbing heavy metals ions and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for porous composite materials and adsorption of heavy metals, applied in alkali metal compounds, chemical instruments and methods, adsorption of water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve secondary pollution, poor adsorption of porous materials, environmental pollution, etc., to achieve Facilitate degradation and promote the effect of heavy metal adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
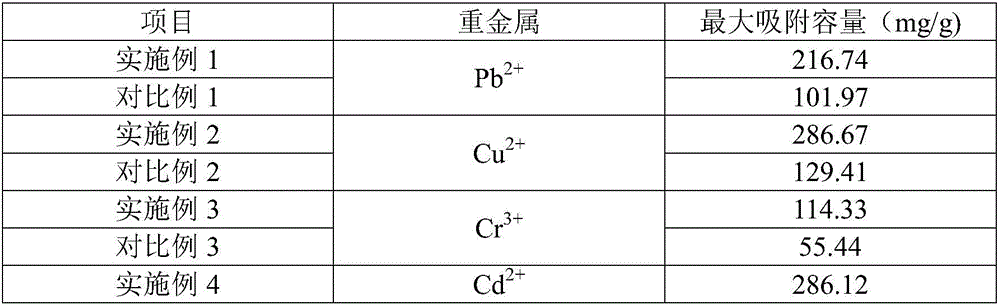
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A method for preparing a porous material, comprising the steps of:
[0038]1) Preparation of foam matrix: Add 0.1 parts of gum arabic, 10 parts of hydroxyethyl chitosan, and 20 parts of polymalic acid to 1000 parts of deionized water, and stir at 10°C for 1 Hours, to obtain foam matrix mixed solution.
[0039] 2) Microorganism culture and matrix foaming: 0.2 parts by mass of chlorella, 0.15 parts of sodium nitrate, 0.06 parts of ferric ammonium citrate, 0.06 parts of magnesium sulfate, 0.05 parts of pH potassium citrate-citric acid The buffer solution was added to 40 parts of the foamed matrix mixture obtained in step 1), the stirring speed was set to 500 r / min, stirred for 0.1 hour, and placed in a constant temperature incubator at 25° C. to obtain the foamed matrix.
[0040] 3) Foaming matrix gelation molding: put the foamed matrix in step 2) in an environment of -50°C to freeze, thaw in an environment of 20°C, and irradiate with ultraviolet light for 2 hours.
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A method for preparing a porous material, comprising the steps of:
[0050] 1) Preparation of foaming matrix: Add 10 parts by mass of starch, 0.5 part of cellulose, 0.1 part of polyvinyl alcohol, and 0.6 part of polyethylene glycol to 800 parts of deionized water, and heat at 100°C Under stirring for 2 hours, a foaming matrix mixed solution was obtained.
[0051] 2) Microbial culture and matrix foaming: the mass parts are 0.1 parts of Escherichia coli, 0.02 parts of glucose, 0.01 parts of magnesium sulfate, 0.02 parts of calcium carbonate, 10 parts of distilled water, 5 parts of tartaric acid-sodium malate The buffer solution was added to 10 parts of the foamed matrix mixture obtained in step 1), the stirring speed was set to 100 r / min, stirred for 0.1 hour, and placed in a constant temperature incubator at 37° C. to obtain the foamed matrix.
[0052] 3) Gelation molding of the foamed matrix: the foamed matrix in step 2) was frozen at -50°C, thawed at 50°C, and cycled ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] A method for preparing an adsorbable porous material, comprising the steps of:
[0062] 1) Preparation of foam matrix: add 6 parts by mass of sodium alginate, 0.2 part of hydroxyethyl cellulose, 0.2 part of gelatin, 20 parts of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer to 100 parts of deionized water, stirred at 120° C. for 12 hours to obtain a foaming matrix mixture.
[0063] 2) Microorganism culture and matrix foaming: 0.6 parts by mass of Gram-positive cocci, 1000 parts of wort, 0.06 parts of sodium nitrate, 0.15 parts of magnesium sulfate, 0.05 parts of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate-potassium dihydrogen phosphate The buffer solution was added to 100 parts of the foamed matrix mixture obtained in step 1), the stirring speed was set to 50 r / min, stirred for 5 hours, and placed in a constant temperature incubator at a temperature of 30° C. to obtain the foamed matrix.
[0064] 3) Gelation molding of the foamed matrix: heat the foamed matrix in step 2) to 50°C, keep at a const...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com