Fluorescent nanospheres with pH-responsiveness and aggregation-induced fluorescence enhancement properties and their applications
A technology of aggregation-induced fluorescence and fluorescent nanometers, applied in fluorescent nanospheres and their applications in targeted tumor imaging and disease detection, can solve problems such as reducing photobleaching efficiency, and achieve good monodispersity and good fluorescence stability. Sexual, low biotoxicity effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] (1) Measure 5 mL of styrene (analytical grade, the polymerization inhibitor was removed by distillation under reduced pressure) and disperse it in 100 mL of deionized water, add 0.167 g of N,N,N-trimethylvinylbenzyl ammonium chloride (VBTAC) and 0.113 mL of acrylic acid (AAc). Under the protection of nitrogen at room temperature, mechanically stir (400rpm) for 30min to remove the oxygen in the reaction system. Then the temperature was gradually raised to 70° C., and 10 mL of azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.037 mmol / mL was added to initiate polymerization. The reaction was completed under nitrogen protection for 8 hours to obtain polymer nanospheres. Precipitation was obtained by high-speed centrifugation (18900 rpm), and the precipitated nanospheres were redispersed in 50 mL of deionized water to obtain a pH-responsive polymer nanosphere emulsion.
[0034] (2) Measure 5 mL of the emulsion obtained in step (1), add 5 mL of ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Measure 5 mL of styrene (analytical grade, the polymerization inhibitor was removed by distillation under reduced pressure) and disperse it in 100 mL of deionized water, add 0.125 g of N,N,N-trimethylvinylbenzyl ammonium chloride (VBTAC) and 0.127 mL of acrylic acid (AAc). Under the protection of nitrogen at room temperature, mechanically stir (400rpm) for 30min to remove the oxygen in the reaction system. Then the temperature was gradually raised to 70° C., and 10 mL of azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.037 mmol / mL was added to initiate polymerization. The reaction was carried out under the protection of nitrogen for 8 hours to obtain polymer nanospheres. Precipitation was obtained by high-speed centrifugation (18000 rpm), and the precipitated nanospheres were redispersed in 50 mL of deionized water to obtain a pH-responsive polymer nanosphere emulsion.
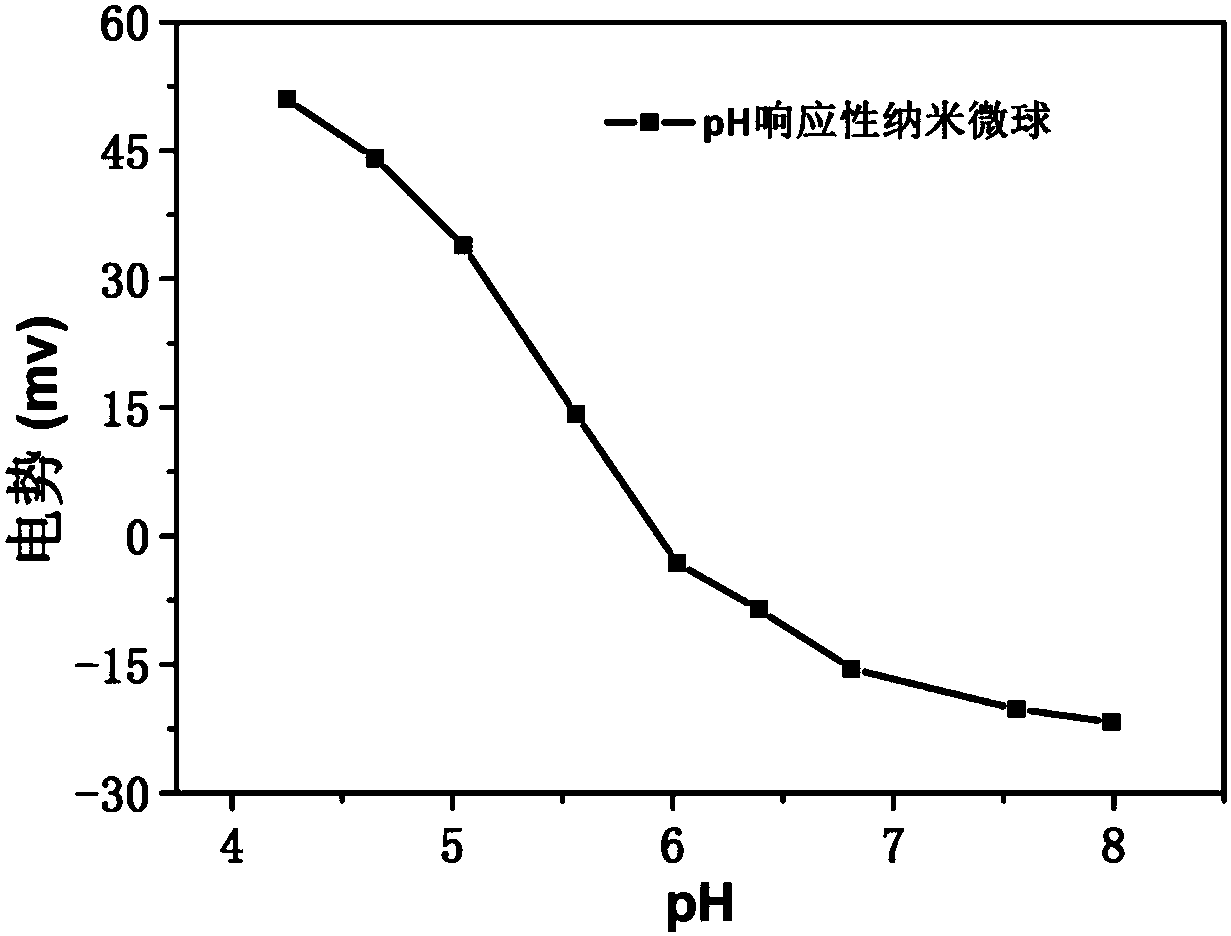
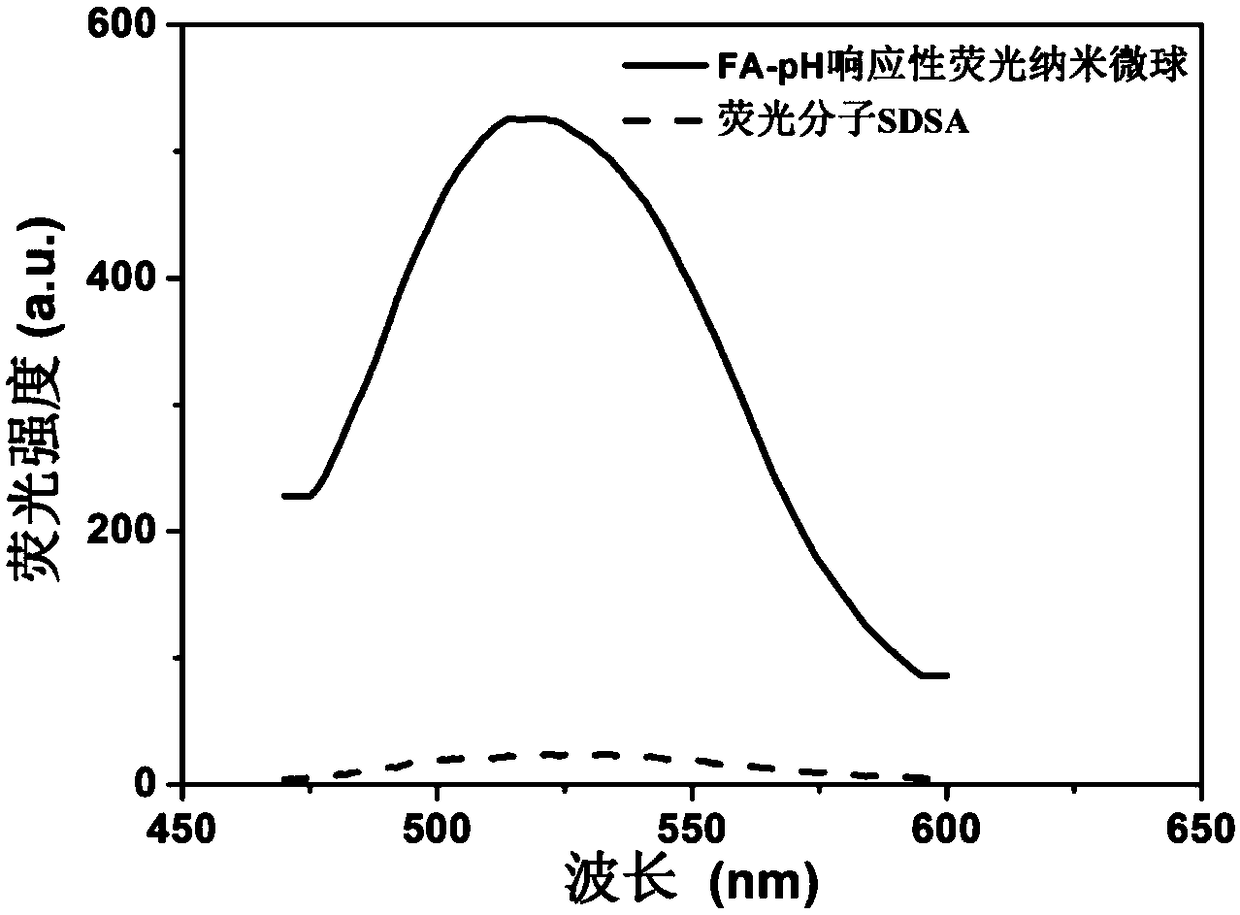
[0039] We found that the properties of the pH-responsive nanosph...
Embodiment 3
[0041] (1) Measure 5 mL of styrene (analytical grade, the polymerization inhibitor was removed by distillation under reduced pressure) and disperse it in 100 mL of deionized water, add 0.25 g of N,N,N-trimethylvinylbenzyl ammonium chloride (VBTAC) and 0.085 mL of acrylic acid (AAc). Under the protection of nitrogen at room temperature, mechanically stir (400rpm) for 30min to remove the oxygen in the reaction system. Then the temperature was gradually raised to 70° C., and 10 mL of azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.037 mmol / mL was added to initiate polymerization. The reaction was completed under nitrogen protection for 8 hours, and polymer nanospheres were prepared. Precipitation was obtained by high-speed centrifugation (18900 rpm), and the precipitated nanospheres were redispersed in 50 mL of deionized water to obtain a pH-responsive polymer nanosphere emulsion.
[0042] We found that the properties of the pH-responsive nanosphe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com