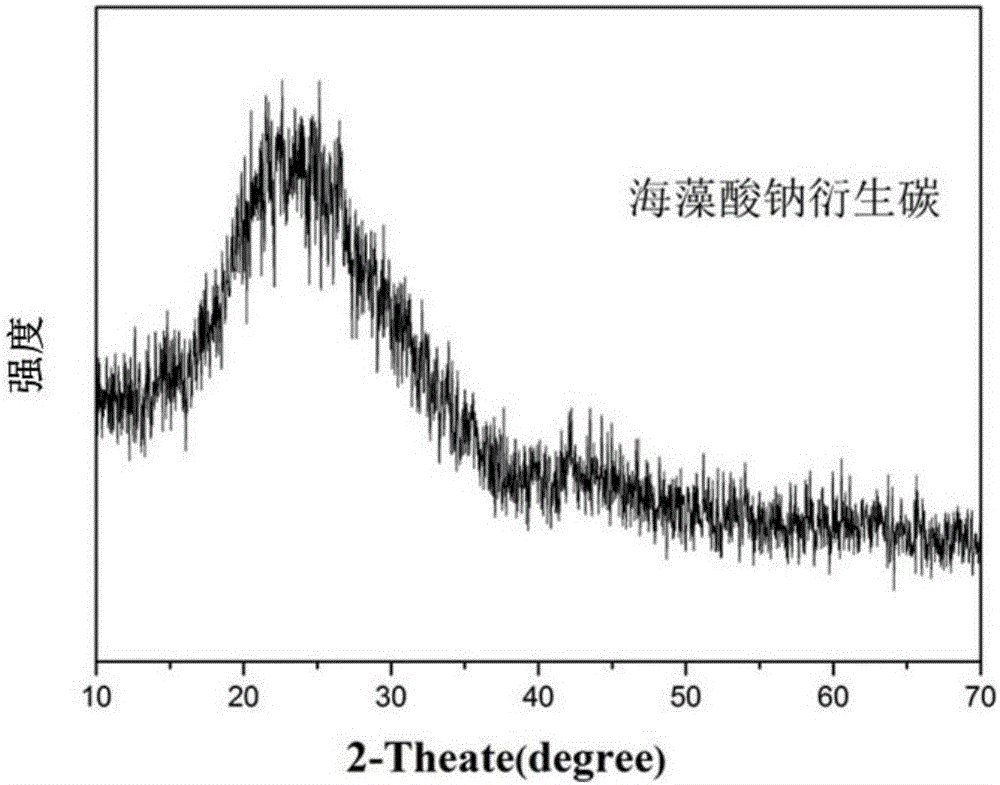
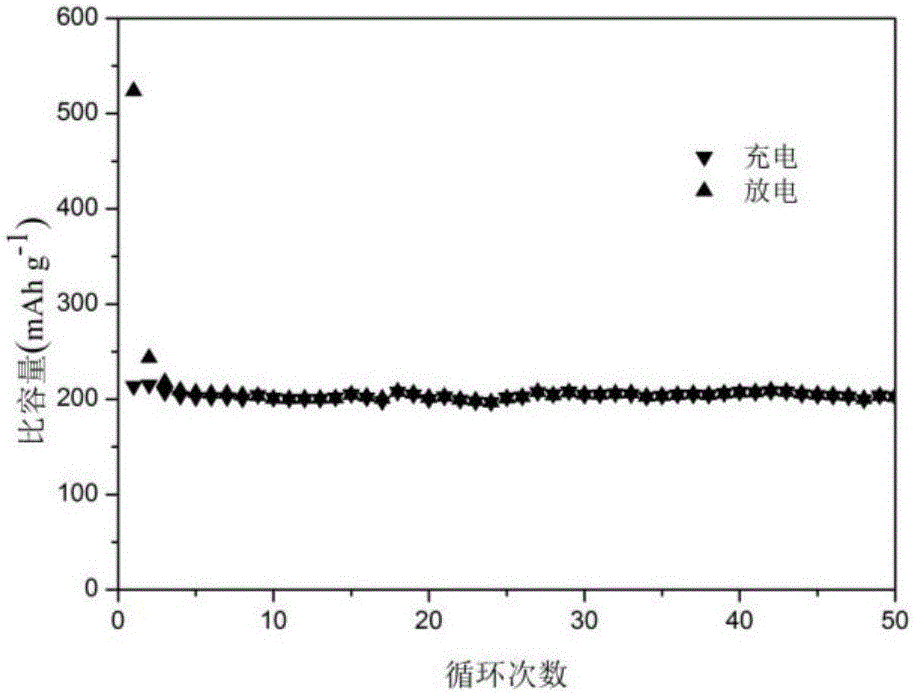
Method for preparing sodium-ion battery negative electrode material with sodium alga acid as carbon source
A sodium ion battery, sodium alginate technology, applied in battery electrodes, non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of low volume expansion of battery capacity, and achieve high repeatability, strong cycle stability, and simple operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
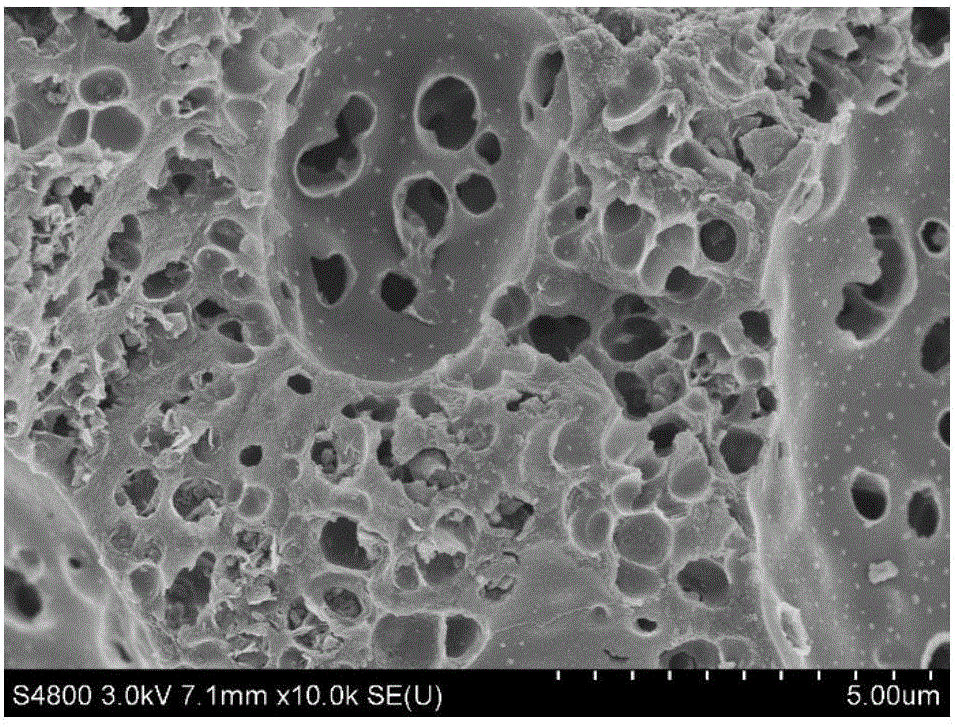
[0028] Weigh 2.0g of sodium alginate and add it to 50ml of deionized water, heat to 60°C and magnetically stir for 0.5h to obtain a uniform viscous liquid, freeze-dry the obtained uniform viscous liquid for 72 hours to obtain a spongy seaweed with a loose structure Sodium alginate; in an Ar atmosphere, the spongy sodium alginate was raised to 600°C at a rate of 2°C / min, calcined for 2 hours, and naturally cooled to room temperature after calcination, then soaked in 2mol / L hydrochloric acid until neutral , filtered by suction, washed with water and ethanol until neutral, and then vacuum-dried at 60° C. for 12 hours to obtain a negative electrode material for a sodium ion battery.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Weigh 10g of sodium alginate and add it to 250ml of deionized water, heat to 90°C and magnetically stir for 3 hours to obtain a uniform viscous liquid, freeze-dry the obtained uniform viscous liquid for 72 hours to obtain a spongy sodium alginate with a loose structure ;The spongy sodium alginate is raised to 1000°C at a heating rate of 2°C / min under an Ar atmosphere, and calcined for 12 hours. After the calcination is completed, it is naturally cooled to room temperature, soaked in 2mol / L nitric acid until neutral, and passed Suction filtration, washing with water and ethanol until neutral, and then vacuum drying at 100° C. for 12 hours to obtain a negative electrode material for a sodium ion battery.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Weigh 2.0g of sodium alginate and add it to 50ml of deionized water, heat to 80°C and magnetically stir for 3 hours to obtain a uniform viscous liquid, freeze-dry the obtained uniform viscous liquid for 12 hours to obtain a spongy alginic acid with a loose structure Sodium; the spongy sodium alginate in N 2 Under atmosphere, heat up to 600°C at a rate of 2°C / min, calcinate for 2 hours, cool to room temperature naturally after calcination, soak in 2mol / L nitric acid until neutral, then wash with water and ethanol until neutral through suction filtration , and then carry out vacuum drying at 100° C. for 12 hours to obtain a negative electrode material for a sodium ion battery.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com