Preparation and application of bacillus altitudinis bacterial agent
A highlander bacillus and microbial agent technology, applied in the direction of application, fungicide, bacteria, etc., to achieve high application value, stable control effect, and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
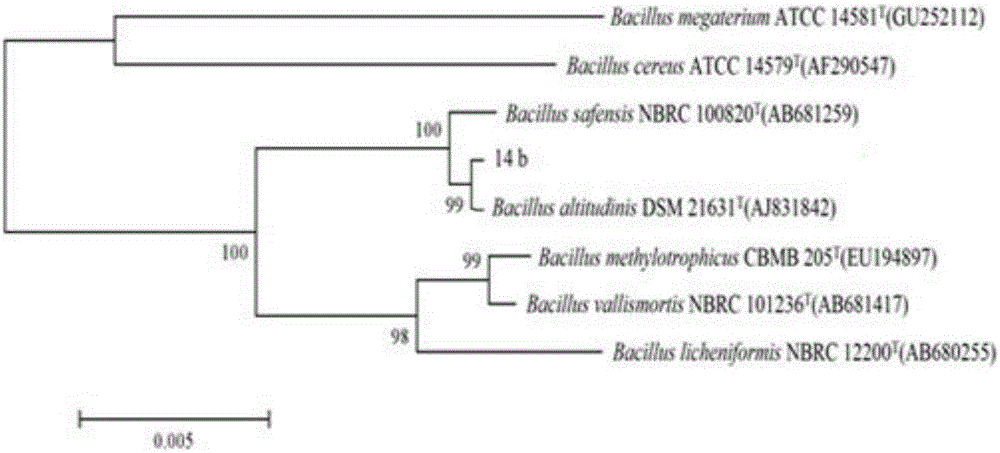
[0021] Example 1: Isolation and screening of Bacillus highlander 14b
[0022] In the peach orchard without chemical fertilizers and pesticides, the rhizosphere soil of peach trees was collected, and the dilution separation method was used to make 10 -1 、10 -2 、10 -3 and 10-4 soil dilution, use a pipette to draw 10 -2 、10 -3 and 10 -4 Add 0.1mL of the soil dilution solution to the NA medium plate, spread it evenly with a sterile applicator, and mark the serial number. After standing for one hour, reverse the culture plate and cultivate it at 37°C. From the second day of culture, single bacterial colonies were selected according to the characteristics of the colony shape, and transplanted to NA medium respectively, and were used for subsequent experiments after 48 hours of culture. The purified strains were stored on NA slant medium at 4°C.
[0023] Antagonist bacteria were screened by plate confrontation method. Inoculate the pathogenic bacteria cake (8mm puncher) in the...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: the preparation of microbial bacterial agent
[0025] The microbial bacterial agent used for preventing and treating postharvest fungal diseases of peaches includes fermentation broth and fermentation filtrate of Bacillus highlander 14b, and the preparation steps are as follows:
[0026] 1) Activated strain: transfer the preserved Bacillus uplander 14b to NA medium by streaking, and place in an incubator at 40°C for 24 hours of constant temperature and moisture cultivation;
[0027] 2) Preparation of seed solution: Pick a single colony of the antagonistic strain Bacillus upholsteria 14b that grew well on the NA medium and inoculate it into the NB liquid medium, culture it with shaking at 40°C for 48 hours, and the shaking frequency is 130-180r / min;
[0028] 3) Preparation of fermentation broth: inoculate the seed solution of strain 14b prepared in step 2) into NB liquid culture solution with an inoculum size of 3% by volume, and the charging amount is 50-1...
Embodiment 3
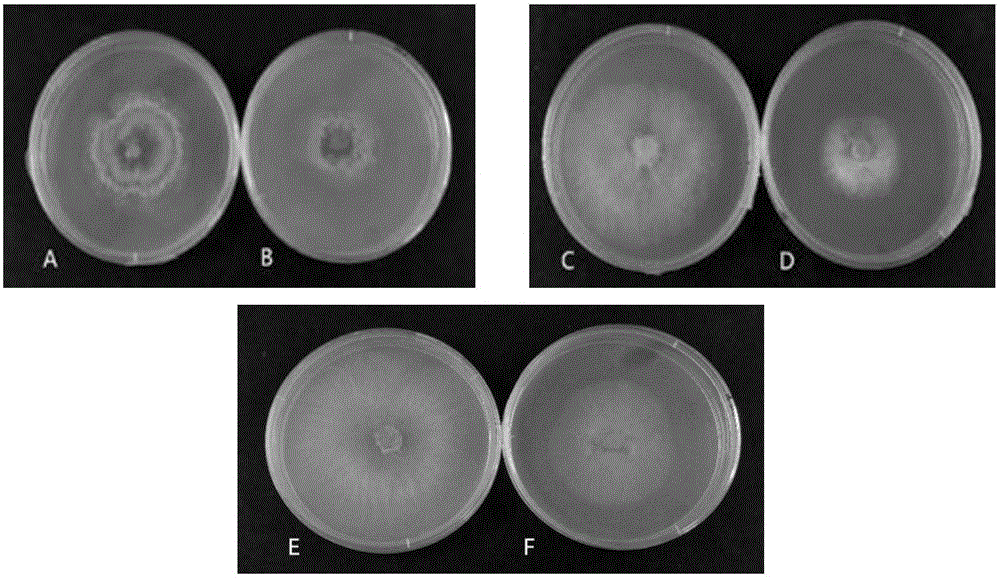
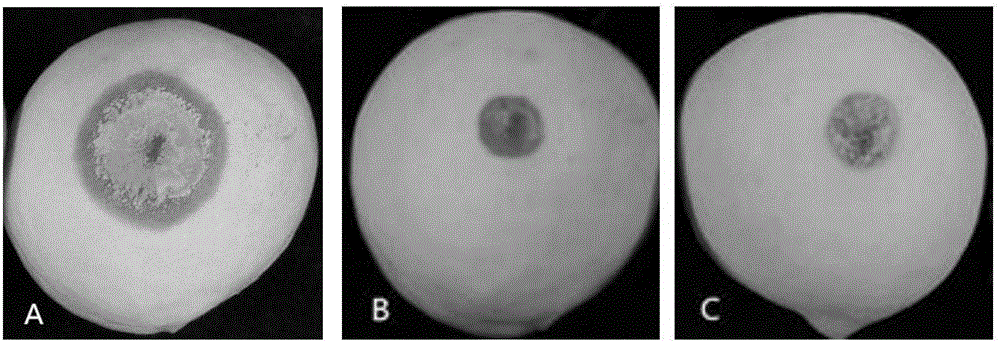
[0031] Embodiment 3: the influence of microbial bacterial agent on the growth of pathogenic bacteria mycelia
[0032] The microbial agent includes the fermentation liquid and the fermentation filtrate of Bacillus highlander 14b prepared in Example 2.
[0033] The filter paper method was used to measure the effect of strain 14b fermentation broth on mycelial growth. Inoculate the cakes of brown rot fungus, botrytis cinerea, soft rot fungus, and penicillium fungus in the center of the PDA plate respectively, dip a piece of sterile filter paper (Φ=8mm) into the fermentation broth of bio-control bacteria, and stick it symmetrically at a distance from the fungus cake of pathogenic bacteria Incubate at 26°C at 2.5 cm, observe and record the growth diameter of pathogenic bacteria after 3 days and calculate the inhibition rate, see Table 1 for details.
[0034] The plate method containing filtrate was used to measure the effect of fermentation broth on mycelia growth. After mixing t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com